Kengo Uchida
Dyadic Mamba: Long-term Dyadic Human Motion Synthesis
May 14, 2025Abstract:Generating realistic dyadic human motion from text descriptions presents significant challenges, particularly for extended interactions that exceed typical training sequence lengths. While recent transformer-based approaches have shown promising results for short-term dyadic motion synthesis, they struggle with longer sequences due to inherent limitations in positional encoding schemes. In this paper, we introduce Dyadic Mamba, a novel approach that leverages State-Space Models (SSMs) to generate high-quality dyadic human motion of arbitrary length. Our method employs a simple yet effective architecture that facilitates information flow between individual motion sequences through concatenation, eliminating the need for complex cross-attention mechanisms. We demonstrate that Dyadic Mamba achieves competitive performance on standard short-term benchmarks while significantly outperforming transformer-based approaches on longer sequences. Additionally, we propose a new benchmark for evaluating long-term motion synthesis quality, providing a standardized framework for future research. Our results demonstrate that SSM-based architectures offer a promising direction for addressing the challenging task of long-term dyadic human motion synthesis from text descriptions.
MoLA: Motion Generation and Editing with Latent Diffusion Enhanced by Adversarial Training
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:In motion generation, controllability as well as generation quality and speed is becoming more and more important. There are various motion editing tasks, such as in-betweening, upper body editing, and path-following, but existing methods perform motion editing with a data-space diffusion model, which is slow in inference compared to a latent diffusion model. In this paper, we propose MoLA, which provides fast and high-quality motion generation and also can deal with multiple editing tasks in a single framework. For high-quality and fast generation, we employ a variational autoencoder and latent diffusion model, and improve the performance with adversarial training. In addition, we apply a training-free guided generation framework to achieve various editing tasks with motion control inputs. We quantitatively show the effectiveness of adversarial learning in text-to-motion generation, and demonstrate the applicability of our editing framework to multiple editing tasks in the motion domain.
HQ-VAE: Hierarchical Discrete Representation Learning with Variational Bayes
Dec 31, 2023



Abstract:Vector quantization (VQ) is a technique to deterministically learn features with discrete codebook representations. It is commonly performed with a variational autoencoding model, VQ-VAE, which can be further extended to hierarchical structures for making high-fidelity reconstructions. However, such hierarchical extensions of VQ-VAE often suffer from the codebook/layer collapse issue, where the codebook is not efficiently used to express the data, and hence degrades reconstruction accuracy. To mitigate this problem, we propose a novel unified framework to stochastically learn hierarchical discrete representation on the basis of the variational Bayes framework, called hierarchically quantized variational autoencoder (HQ-VAE). HQ-VAE naturally generalizes the hierarchical variants of VQ-VAE, such as VQ-VAE-2 and residual-quantized VAE (RQ-VAE), and provides them with a Bayesian training scheme. Our comprehensive experiments on image datasets show that HQ-VAE enhances codebook usage and improves reconstruction performance. We also validated HQ-VAE in terms of its applicability to a different modality with an audio dataset.
Zero- and Few-shot Sound Event Localization and Detection
Sep 17, 2023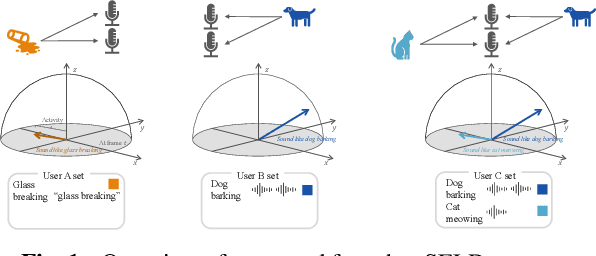



Abstract:Sound event localization and detection (SELD) systems estimate direction-of-arrival (DOA) and temporal activation for sets of target classes. Neural network (NN)-based SELD systems have performed well in various sets of target classes, but they only output the DOA and temporal activation of preset classes that are trained before inference. To customize target classes after training, we tackle zero- and few-shot SELD tasks, in which we set new classes with a text sample or a few audio samples. While zero-shot sound classification tasks are achievable by embedding from contrastive language-audio pretraining (CLAP), zero-shot SELD tasks require assigning an activity and a DOA to each embedding, especially in overlapping cases. To tackle the assignment problem in overlapping cases, we propose an embed-ACCDOA model, which is trained to output track-wise CLAP embedding and corresponding activity-coupled Cartesian direction-of-arrival (ACCDOA). In our experimental evaluations on zero- and few-shot SELD tasks, the embed-ACCDOA model showed a better location-dependent scores than a straightforward combination of the CLAP audio encoder and a DOA estimation model. Moreover, the proposed combination of the embed-ACCDOA model and CLAP audio encoder with zero- or few-shot samples performed comparably to an official baseline system trained with complete train data in an evaluation dataset.
STARSS23: An Audio-Visual Dataset of Spatial Recordings of Real Scenes with Spatiotemporal Annotations of Sound Events
Jun 15, 2023



Abstract:While direction of arrival (DOA) of sound events is generally estimated from multichannel audio data recorded in a microphone array, sound events usually derive from visually perceptible source objects, e.g., sounds of footsteps come from the feet of a walker. This paper proposes an audio-visual sound event localization and detection (SELD) task, which uses multichannel audio and video information to estimate the temporal activation and DOA of target sound events. Audio-visual SELD systems can detect and localize sound events using signals from a microphone array and audio-visual correspondence. We also introduce an audio-visual dataset, Sony-TAu Realistic Spatial Soundscapes 2023 (STARSS23), which consists of multichannel audio data recorded with a microphone array, video data, and spatiotemporal annotation of sound events. Sound scenes in STARSS23 are recorded with instructions, which guide recording participants to ensure adequate activity and occurrences of sound events. STARSS23 also serves human-annotated temporal activation labels and human-confirmed DOA labels, which are based on tracking results of a motion capture system. Our benchmark results show that the audio-visual SELD system achieves lower localization error than the audio-only system. The data is available at https://zenodo.org/record/7880637.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge