Junsu Kim
Revisiting Reliability in the Reasoning-based Pose Estimation Benchmark
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:The reasoning-based pose estimation (RPE) benchmark has emerged as a widely adopted evaluation standard for pose-aware multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Despite its significance, we identified critical reproducibility and benchmark-quality issues that hinder fair and consistent quantitative evaluations. Most notably, the benchmark utilizes different image indices from those of the original 3DPW dataset, forcing researchers into tedious and error-prone manual matching processes to obtain accurate ground-truth (GT) annotations for quantitative metrics (\eg, MPJPE, PA-MPJPE). Furthermore, our analysis reveals several inherent benchmark-quality limitations, including significant image redundancy, scenario imbalance, overly simplistic poses, and ambiguous textual descriptions, collectively undermining reliable evaluations across diverse scenarios. To alleviate manual effort and enhance reproducibility, we carefully refined the GT annotations through meticulous visual matching and publicly release these refined annotations as an open-source resource, thereby promoting consistent quantitative evaluations and facilitating future advancements in human pose-aware multimodal reasoning.
Test-Time Adaptation with Binary Feedback
May 24, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models perform poorly when domain shifts exist between training and test data. Test-time adaptation (TTA) is a paradigm to mitigate this issue by adapting pre-trained models using only unlabeled test samples. However, existing TTA methods can fail under severe domain shifts, while recent active TTA approaches requiring full-class labels are impractical due to high labeling costs. To address this issue, we introduce a new setting of TTA with binary feedback. This setting uses a few binary feedback inputs from annotators to indicate whether model predictions are correct, thereby significantly reducing the labeling burden of annotators. Under the setting, we propose BiTTA, a novel dual-path optimization framework that leverages reinforcement learning to balance binary feedback-guided adaptation on uncertain samples with agreement-based self-adaptation on confident predictions. Experiments show BiTTA achieves 13.3%p accuracy improvements over state-of-the-art baselines, demonstrating its effectiveness in handling severe distribution shifts with minimal labeling effort. The source code is available at https://github.com/taeckyung/BiTTA.
Diffusion Meets Few-shot Class Incremental Learning
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) is challenging due to extremely limited training data; while aiming to reduce catastrophic forgetting and learn new information. We propose Diffusion-FSCIL, a novel approach that employs a text-to-image diffusion model as a frozen backbone. Our conjecture is that FSCIL can be tackled using a large generative model's capabilities benefiting from 1) generation ability via large-scale pre-training; 2) multi-scale representation; 3) representational flexibility through the text encoder. To maximize the representation capability, we propose to extract multiple complementary diffusion features to play roles as latent replay with slight support from feature distillation for preventing generative biases. Our framework realizes efficiency through 1) using a frozen backbone; 2) minimal trainable components; 3) batch processing of multiple feature extractions. Extensive experiments on CUB-200, miniImageNet, and CIFAR-100 show that Diffusion-FSCIL surpasses state-of-the-art methods, preserving performance on previously learned classes and adapting effectively to new ones.
LoRA Training Provably Converges to a Low-Rank Global Minimum or It Fails Loudly (But it Probably Won't Fail)
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) has become a standard approach for fine-tuning large foundation models. However, our theoretical understanding of LoRA remains limited as prior analyses of LoRA's training dynamics either rely on linearization arguments or consider highly simplified setups. In this work, we analyze the LoRA loss landscape without such restrictive assumptions. We define two regimes: a ``special regime'', which includes idealized setups where linearization arguments hold, and a ``generic regime'' representing more realistic setups where linearization arguments do not hold. In the generic regime, we show that LoRA training converges to a global minimizer with low rank and small magnitude, or a qualitatively distinct solution with high rank and large magnitude. Finally, we argue that the zero-initialization and weight decay in LoRA training induce an implicit bias toward the low-rank, small-magnitude region of the parameter space -- where global minima lie -- thus shedding light on why LoRA training usually succeeds in finding global minima.
B-RIGHT: Benchmark Re-evaluation for Integrity in Generalized Human-Object Interaction Testing
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Human-object interaction (HOI) is an essential problem in artificial intelligence (AI) which aims to understand the visual world that involves complex relationships between humans and objects. However, current benchmarks such as HICO-DET face the following limitations: (1) severe class imbalance and (2) varying number of train and test sets for certain classes. These issues can potentially lead to either inflation or deflation of model performance during evaluation, ultimately undermining the reliability of evaluation scores. In this paper, we propose a systematic approach to develop a new class-balanced dataset, Benchmark Re-evaluation for Integrity in Generalized Human-object Interaction Testing (B-RIGHT), that addresses these imbalanced problems. B-RIGHT achieves class balance by leveraging balancing algorithm and automated generation-and-filtering processes, ensuring an equal number of instances for each HOI class. Furthermore, we design a balanced zero-shot test set to systematically evaluate models on unseen scenario. Re-evaluating existing models using B-RIGHT reveals substantial the reduction of score variance and changes in performance rankings compared to conventional HICO-DET. Our experiments demonstrate that evaluation under balanced conditions ensure more reliable and fair model comparisons.
Unsupervised-to-Online Reinforcement Learning
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Offline-to-online reinforcement learning (RL), a framework that trains a policy with offline RL and then further fine-tunes it with online RL, has been considered a promising recipe for data-driven decision-making. While sensible, this framework has drawbacks: it requires domain-specific offline RL pre-training for each task, and is often brittle in practice. In this work, we propose unsupervised-to-online RL (U2O RL), which replaces domain-specific supervised offline RL with unsupervised offline RL, as a better alternative to offline-to-online RL. U2O RL not only enables reusing a single pre-trained model for multiple downstream tasks, but also learns better representations, which often result in even better performance and stability than supervised offline-to-online RL. To instantiate U2O RL in practice, we propose a general recipe for U2O RL to bridge task-agnostic unsupervised offline skill-based policy pre-training and supervised online fine-tuning. Throughout our experiments in nine state-based and pixel-based environments, we empirically demonstrate that U2O RL achieves strong performance that matches or even outperforms previous offline-to-online RL approaches, while being able to reuse a single pre-trained model for a number of different downstream tasks.
VPOcc: Exploiting Vanishing Point for Monocular 3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:Monocular 3D semantic occupancy prediction is becoming important in robot vision due to the compactness of using a single RGB camera. However, existing methods often do not adequately account for camera perspective geometry, resulting in information imbalance along the depth range of the image. To address this issue, we propose a vanishing point (VP) guided monocular 3D semantic occupancy prediction framework named VPOcc. Our framework consists of three novel modules utilizing VP. First, in the VPZoomer module, we initially utilize VP in feature extraction to achieve information balanced feature extraction across the scene by generating a zoom-in image based on VP. Second, we perform perspective geometry-aware feature aggregation by sampling points towards VP using a VP-guided cross-attention (VPCA) module. Finally, we create an information-balanced feature volume by effectively fusing original and zoom-in voxel feature volumes with a balanced feature volume fusion (BVFV) module. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance for both IoU and mIoU on SemanticKITTI and SSCBench-KITTI360. These results are obtained by effectively addressing the information imbalance in images through the utilization of VP. Our code will be available at www.github.com/anonymous.
VLM-PL: Advanced Pseudo Labeling approach Class Incremental Object Detection with Vision-Language Model
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:In the field of Class Incremental Object Detection (CIOD), creating models that can continuously learn like humans is a major challenge. Pseudo-labeling methods, although initially powerful, struggle with multi-scenario incremental learning due to their tendency to forget past knowledge. To overcome this, we introduce a new approach called Vision-Language Model assisted Pseudo-Labeling (VLM-PL). This technique uses Vision-Language Model (VLM) to verify the correctness of pseudo ground-truths (GTs) without requiring additional model training. VLM-PL starts by deriving pseudo GTs from a pre-trained detector. Then, we generate custom queries for each pseudo GT using carefully designed prompt templates that combine image and text features. This allows the VLM to classify the correctness through its responses. Furthermore, VLM-PL integrates refined pseudo and real GTs from upcoming training, effectively combining new and old knowledge. Extensive experiments conducted on the Pascal VOC and MS COCO datasets not only highlight VLM-PL's exceptional performance in multi-scenario but also illuminate its effectiveness in dual-scenario by achieving state-of-the-art results in both.
SDDGR: Stable Diffusion-based Deep Generative Replay for Class Incremental Object Detection
Feb 27, 2024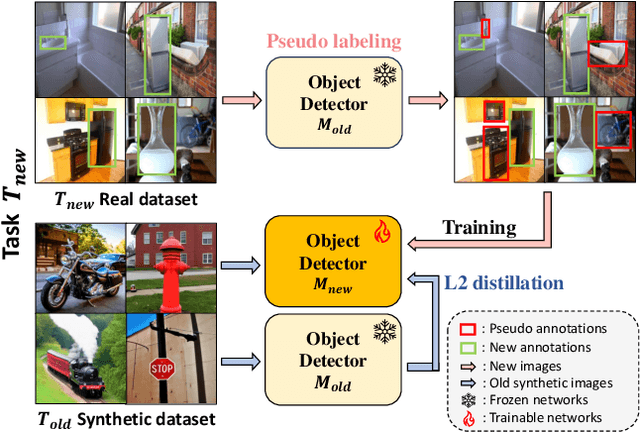
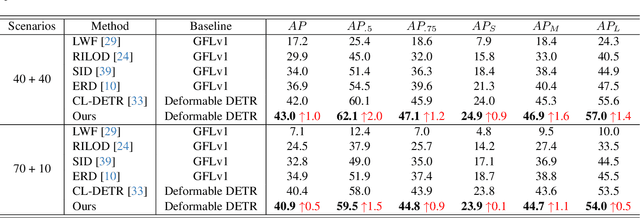
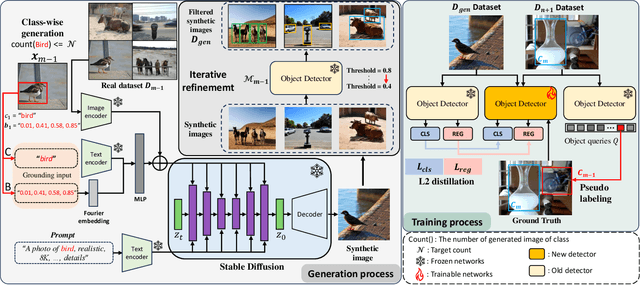
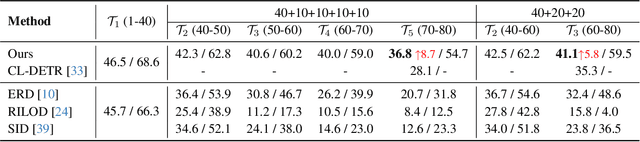
Abstract:In the field of class incremental learning (CIL), genera- tive replay has become increasingly prominent as a method to mitigate the catastrophic forgetting, alongside the con- tinuous improvements in generative models. However, its application in class incremental object detection (CIOD) has been significantly limited, primarily due to the com- plexities of scenes involving multiple labels. In this paper, we propose a novel approach called stable diffusion deep generative replay (SDDGR) for CIOD. Our method utilizes a diffusion-based generative model with pre-trained text- to-diffusion networks to generate realistic and diverse syn- thetic images. SDDGR incorporates an iterative refinement strategy to produce high-quality images encompassing old classes. Additionally, we adopt an L2 knowledge distilla- tion technique to improve the retention of prior knowledge in synthetic images. Furthermore, our approach includes pseudo-labeling for old objects within new task images, pre- venting misclassification as background elements. Exten- sive experiments on the COCO 2017 dataset demonstrate that SDDGR significantly outperforms existing algorithms, achieving a new state-of-the-art in various CIOD scenarios. The source code will be made available to the public.
Class-Wise Buffer Management for Incremental Object Detection: An Effective Buffer Training Strategy
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:Class incremental learning aims to solve a problem that arises when continuously adding unseen class instances to an existing model This approach has been extensively studied in the context of image classification; however its applicability to object detection is not well established yet. Existing frameworks using replay methods mainly collect replay data without considering the model being trained and tend to rely on randomness or the number of labels of each sample. Also, despite the effectiveness of the replay, it was not yet optimized for the object detection task. In this paper, we introduce an effective buffer training strategy (eBTS) that creates the optimized replay buffer on object detection. Our approach incorporates guarantee minimum and hierarchical sampling to establish the buffer customized to the trained model. %These methods can facilitate effective retrieval of prior knowledge. Furthermore, we use the circular experience replay training to optimally utilize the accumulated buffer data. Experiments on the MS COCO dataset demonstrate that our eBTS achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to the existing replay schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge