Jingpeng Li
EVADE: Multimodal Benchmark for Evasive Content Detection in E-Commerce Applications
May 23, 2025Abstract:E-commerce platforms increasingly rely on Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to detect illicit or misleading product content. However, these models remain vulnerable to evasive content: inputs (text or images) that superficially comply with platform policies while covertly conveying prohibited claims. Unlike traditional adversarial attacks that induce overt failures, evasive content exploits ambiguity and context, making it far harder to detect. Existing robustness benchmarks provide little guidance for this demanding, real-world challenge. We introduce EVADE, the first expert-curated, Chinese, multimodal benchmark specifically designed to evaluate foundation models on evasive content detection in e-commerce. The dataset contains 2,833 annotated text samples and 13,961 images spanning six demanding product categories, including body shaping, height growth, and health supplements. Two complementary tasks assess distinct capabilities: Single-Violation, which probes fine-grained reasoning under short prompts, and All-in-One, which tests long-context reasoning by merging overlapping policy rules into unified instructions. Notably, the All-in-One setting significantly narrows the performance gap between partial and full-match accuracy, suggesting that clearer rule definitions improve alignment between human and model judgment. We benchmark 26 mainstream LLMs and VLMs and observe substantial performance gaps: even state-of-the-art models frequently misclassify evasive samples. By releasing EVADE and strong baselines, we provide the first rigorous standard for evaluating evasive-content detection, expose fundamental limitations in current multimodal reasoning, and lay the groundwork for safer and more transparent content moderation systems in e-commerce. The dataset is publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/koenshen/EVADE-Bench.
Foundation AI Model for Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:Foundation models refer to artificial intelligence (AI) models that are trained on massive amounts of data and demonstrate broad generalizability across various tasks with high accuracy. These models offer versatile, one-for-many or one-for-all solutions, eliminating the need for developing task-specific AI models. Examples of such foundation models include the Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (ChatGPT) and the Segment Anything Model (SAM). These models have been trained on millions to billions of samples and have shown wide-ranging and accurate applications in numerous tasks such as text processing (using ChatGPT) and natural image segmentation (using SAM). In medical image segmentation - finding target regions in medical images - there is a growing need for these one-for-many or one-for-all foundation models. Such models could obviate the need to develop thousands of task-specific AI models, which is currently standard practice in the field. They can also be adapted to tasks with datasets too small for effective training. We discuss two paths to achieve foundation models for medical image segmentation and comment on progress, challenges, and opportunities. One path is to adapt or fine-tune existing models, originally developed for natural images, for use with medical images. The second path entails building models from scratch, exclusively training on medical images.
Accuracy of Segment-Anything Model in medical image segmentation tasks
Apr 27, 2023Abstract:The segment-anything model (SAM), was introduced as a fundamental model for segmenting images. It was trained using over 1 billion masks from 11 million natural images. The model can perform zero-shot segmentation of images by using various prompts such as masks, boxes, and points. In this report, we explored (1) the accuracy of SAM on 12 public medical image segmentation datasets which cover various organs (brain, breast, chest, lung, skin, liver, bowel, pancreas, and prostate), image modalities (2D X-ray, histology, endoscropy, and 3D MRI and CT), and health conditions (normal, lesioned). (2) if the computer vision foundational segmentation model SAM can provide promising research directions for medical image segmentation. We found that SAM without re-training on medical images does not perform as accurately as U-Net or other deep learning models trained on medical images.
Anchor-Free Person Search
Mar 22, 2021



Abstract:Person search aims to simultaneously localize and identify a query person from realistic, uncropped images, which can be regarded as the unified task of pedestrian detection and person re-identification (re-id). Most existing works employ two-stage detectors like Faster-RCNN, yielding encouraging accuracy but with high computational overhead. In this work, we present the Feature-Aligned Person Search Network (AlignPS), the first anchor-free framework to efficiently tackle this challenging task. AlignPS explicitly addresses the major challenges, which we summarize as the misalignment issues in different levels (i.e., scale, region, and task), when accommodating an anchor-free detector for this task. More specifically, we propose an aligned feature aggregation module to generate more discriminative and robust feature embeddings by following a "re-id first" principle. Such a simple design directly improves the baseline anchor-free model on CUHK-SYSU by more than 20% in mAP. Moreover, AlignPS outperforms state-of-the-art two-stage methods, with a higher speed. Code is available at https://github.com/daodaofr/AlignPS
A Hybrid Persian Sentiment Analysis Framework: Integrating Dependency Grammar Based Rules and Deep Neural Networks
Sep 30, 2019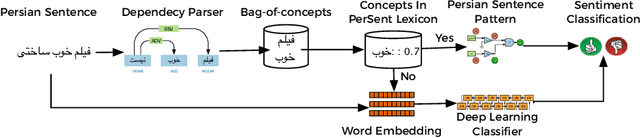
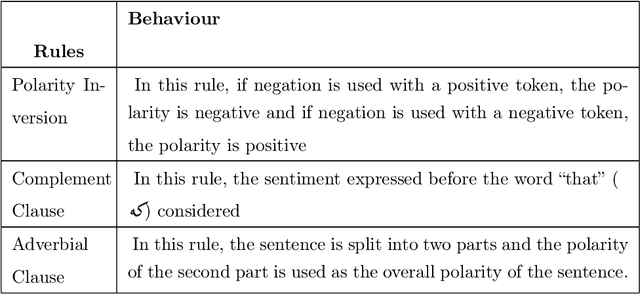
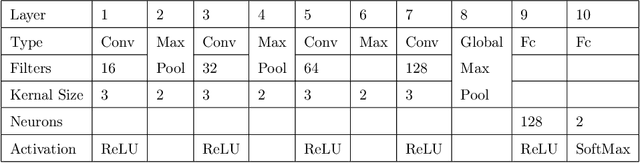
Abstract:Social media hold valuable, vast and unstructured information on public opinion that can be utilized to improve products and services. The automatic analysis of such data, however, requires a deep understanding of natural language. Current sentiment analysis approaches are mainly based on word co-occurrence frequencies, which are inadequate in most practical cases. In this work, we propose a novel hybrid framework for concept-level sentiment analysis in Persian language, that integrates linguistic rules and deep learning to optimize polarity detection. When a pattern is triggered, the framework allows sentiments to flow from words to concepts based on symbolic dependency relations. When no pattern is triggered, the framework switches to its subsymbolic counterpart and leverages deep neural networks (DNN) to perform the classification. The proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art approaches (including support vector machine, and logistic regression) and DNN classifiers (long short-term memory, and Convolutional Neural Networks) with a margin of 10-15% and 3-4% respectively, using benchmark Persian product and hotel reviews corpora.
An Evolutionary Squeaky Wheel Optimisation Approach to Personnel Scheduling
Oct 16, 2009



Abstract:The quest for robust heuristics that are able to solve more than one problem is ongoing. In this paper, we present, discuss and analyse a technique called Evolutionary Squeaky Wheel Optimisation and apply it to two different personnel scheduling problems. Evolutionary Squeaky Wheel Optimisation improves the original Squeaky Wheel Optimisation's effectiveness and execution speed by incorporating two extra steps (Selection and Mutation) for added evolution. In the Evolutionary Squeaky Wheel Optimisation, a cycle of Analysis-Selection-Mutation-Prioritization-Construction continues until stopping conditions are reached. The aim of the Analysis step is to identify below average solution components by calculating a fitness value for all components. The Selection step then chooses amongst these underperformers and discards some probabilistically based on fitness. The Mutation step further discards a few components at random. Solutions can become incomplete and thus repairs may be required. The repairs are carried out by using the Prioritization to first produce priorities that determine an order by which the following Construction step then schedules the remaining components. Therefore, improvement in the Evolutionary Squeaky Wheel Optimisation is achieved by selective solution disruption mixed with interative improvement and constructive repair. Strong experimental results are reported on two different domains of personnel scheduling: bus and rail driver scheduling and hospital nurse scheduling.
* 21 pages, 5 tables, 1 figure, IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation
A Component Based Heuristic Search Method with Evolutionary Eliminations
Oct 14, 2009



Abstract:Nurse rostering is a complex scheduling problem that affects hospital personnel on a daily basis all over the world. This paper presents a new component-based approach with evolutionary eliminations, for a nurse scheduling problem arising at a major UK hospital. The main idea behind this technique is to decompose a schedule into its components (i.e. the allocated shift pattern of each nurse), and then to implement two evolutionary elimination strategies mimicking natural selection and natural mutation process on these components respectively to iteratively deliver better schedules. The worthiness of all components in the schedule has to be continuously demonstrated in order for them to remain there. This demonstration employs an evaluation function which evaluates how well each component contributes towards the final objective. Two elimination steps are then applied: the first elimination eliminates a number of components that are deemed not worthy to stay in the current schedule; the second elimination may also throw out, with a low level of probability, some worthy components. The eliminated components are replenished with new ones using a set of constructive heuristics using local optimality criteria. Computational results using 52 data instances demonstrate the applicability of the proposed approach in solving real-world problems.
* 27 pages, 4 figures
An Estimation of Distribution Algorithm for Nurse Scheduling
May 16, 2008



Abstract:Schedules can be built in a similar way to a human scheduler by using a set of rules that involve domain knowledge. This paper presents an Estimation of Distribution Algorithm (eda) for the nurse scheduling problem, which involves choosing a suitable scheduling rule from a set for the assignment of each nurse. Unlike previous work that used Genetic Algorithms (ga) to implement implicit learning, the learning in the proposed algorithm is explicit, i.e. we identify and mix building blocks directly. The eda is applied to implement such explicit learning by building a Bayesian network of the joint distribution of solutions. The conditional probability of each variable in the network is computed according to an initial set of promising solutions. Subsequently, each new instance for each variable is generated by using the corresponding conditional probabilities, until all variables have been generated, i.e. in our case, a new rule string has been obtained. Another set of rule strings will be generated in this way, some of which will replace previous strings based on fitness selection. If stopping conditions are not met, the conditional probabilities for all nodes in the Bayesian network are updated again using the current set of promising rule strings. Computational results from 52 real data instances demonstrate the success of this approach. It is also suggested that the learning mechanism in the proposed approach might be suitable for other scheduling problems.
A Bayesian Optimisation Algorithm for the Nurse Scheduling Problem
May 16, 2008



Abstract:A Bayesian optimization algorithm for the nurse scheduling problem is presented, which involves choosing a suitable scheduling rule from a set for each nurses assignment. Unlike our previous work that used Gas to implement implicit learning, the learning in the proposed algorithm is explicit, ie. Eventually, we will be able to identify and mix building blocks directly. The Bayesian optimization algorithm is applied to implement such explicit learning by building a Bayesian network of the joint distribution of solutions. The conditional probability of each variable in the network is computed according to an initial set of promising solutions. Subsequently, each new instance for each variable is generated, ie in our case, a new rule string has been obtained. Another set of rule strings will be generated in this way, some of which will replace previous strings based on fitness selection. If stopping conditions are not met, the conditional probabilities for all nodes in the Bayesian network are updated again using the current set of promising rule strings. Computational results from 52 real data instances demonstrate the success of this approach. It is also suggested that the learning mechanism in the proposed approach might be suitable for other scheduling problems.
Explicit Learning: an Effort towards Human Scheduling Algorithms
Apr 03, 2008Abstract:Scheduling problems are generally NP-hard combinatorial problems, and a lot of research has been done to solve these problems heuristically. However, most of the previous approaches are problem-specific and research into the development of a general scheduling algorithm is still in its infancy. Mimicking the natural evolutionary process of the survival of the fittest, Genetic Algorithms (GAs) have attracted much attention in solving difficult scheduling problems in recent years. Some obstacles exist when using GAs: there is no canonical mechanism to deal with constraints, which are commonly met in most real-world scheduling problems, and small changes to a solution are difficult. To overcome both difficulties, indirect approaches have been presented (in [1] and [2]) for nurse scheduling and driver scheduling, where GAs are used by mapping the solution space, and separate decoding routines then build solutions to the original problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge