Ellen Grant
AGE2HIE: Transfer Learning from Brain Age to Predicting Neurocognitive Outcome for Infant Brain Injury
Nov 07, 2024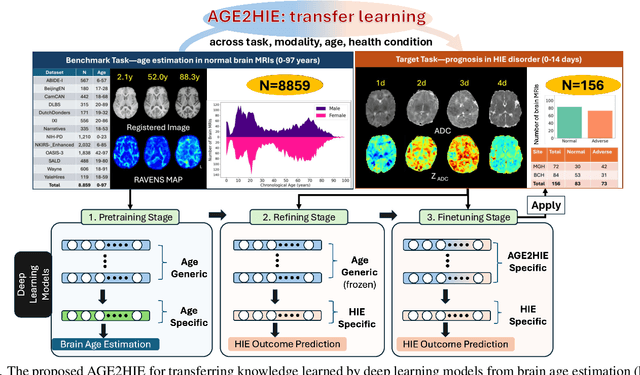
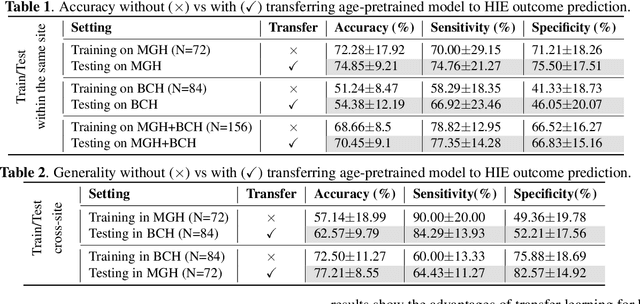
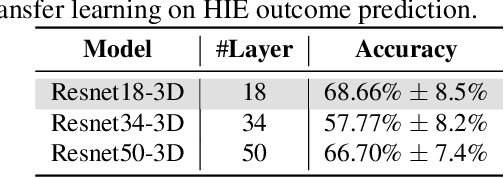
Abstract:Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) affects 1 to 5 out of every 1,000 newborns, with 30% to 50% of cases resulting in adverse neurocognitive outcomes. However, these outcomes can only be reliably assessed as early as age 2. Therefore, early and accurate prediction of HIE-related neurocognitive outcomes using deep learning models is critical for improving clinical decision-making, guiding treatment decisions and assessing novel therapies. However, a major challenge in developing deep learning models for this purpose is the scarcity of large, annotated HIE datasets. We have assembled the first and largest public dataset, however it contains only 156 cases with 2-year neurocognitive outcome labels. In contrast, we have collected 8,859 normal brain black Magnetic Resonance Imagings (MRIs) with 0-97 years of age that are available for brain age estimation using deep learning models. In this paper, we introduce AGE2HIE to transfer knowledge learned by deep learning models from healthy controls brain MRIs to a diseased cohort, from structural to diffusion MRIs, from regression of continuous age estimation to prediction of the binary neurocognitive outcomes, and from lifespan age (0-97 years) to infant (0-2 weeks). Compared to training from scratch, transfer learning from brain age estimation significantly improves not only the prediction accuracy (3% or 2% improvement in same or multi-site), but also the model generalization across different sites (5% improvement in cross-site validation).
Foundation AI Model for Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:Foundation models refer to artificial intelligence (AI) models that are trained on massive amounts of data and demonstrate broad generalizability across various tasks with high accuracy. These models offer versatile, one-for-many or one-for-all solutions, eliminating the need for developing task-specific AI models. Examples of such foundation models include the Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (ChatGPT) and the Segment Anything Model (SAM). These models have been trained on millions to billions of samples and have shown wide-ranging and accurate applications in numerous tasks such as text processing (using ChatGPT) and natural image segmentation (using SAM). In medical image segmentation - finding target regions in medical images - there is a growing need for these one-for-many or one-for-all foundation models. Such models could obviate the need to develop thousands of task-specific AI models, which is currently standard practice in the field. They can also be adapted to tasks with datasets too small for effective training. We discuss two paths to achieve foundation models for medical image segmentation and comment on progress, challenges, and opportunities. One path is to adapt or fine-tune existing models, originally developed for natural images, for use with medical images. The second path entails building models from scratch, exclusively training on medical images.
SE-Equivariant and Noise-Invariant 3D Motion Tracking in Medical Images
Dec 21, 2023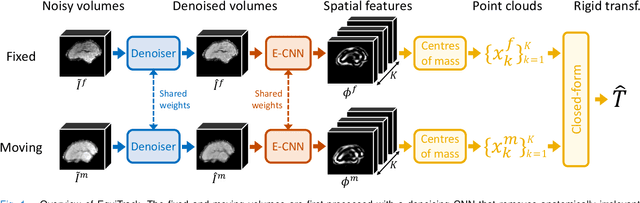
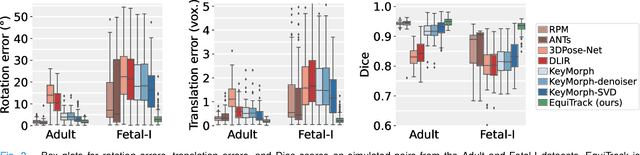
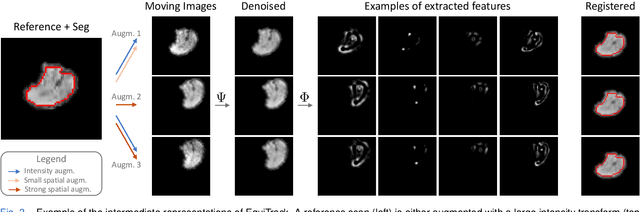
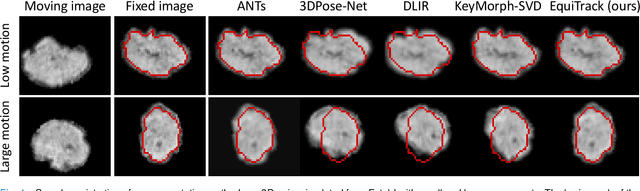
Abstract:Rigid motion tracking is paramount in many medical imaging applications where movements need to be detected, corrected, or accounted for. Modern strategies rely on convolutional neural networks (CNN) and pose this problem as rigid registration. Yet, CNNs do not exploit natural symmetries in this task, as they are equivariant to translations (their outputs shift with their inputs) but not to rotations. Here we propose EquiTrack, the first method that uses recent steerable SE(3)-equivariant CNNs (E-CNN) for motion tracking. While steerable E-CNNs can extract corresponding features across different poses, testing them on noisy medical images reveals that they do not have enough learning capacity to learn noise invariance. Thus, we introduce a hybrid architecture that pairs a denoiser with an E-CNN to decouple the processing of anatomically irrelevant intensity features from the extraction of equivariant spatial features. Rigid transforms are then estimated in closed-form. EquiTrack outperforms state-of-the-art learning and optimisation methods for motion tracking in adult brain MRI and fetal MRI time series. Our code is available at github.com/BBillot/equitrack.
Fetal Pose Estimation in Volumetric MRI using a 3D Convolution Neural Network
Jul 10, 2019



Abstract:The performance and diagnostic utility of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in pregnancy is fundamentally constrained by fetal motion. Motion of the fetus, which is unpredictable and rapid on the scale of conventional imaging times, limits the set of viable acquisition techniques to single-shot imaging with severe compromises in signal-to-noise ratio and diagnostic contrast, and frequently results in unacceptable image quality. Surprisingly little is known about the characteristics of fetal motion during MRI and here we propose and demonstrate methods that exploit a growing repository of MRI observations of the gravid abdomen that are acquired at low spatial resolution but relatively high temporal resolution and over long durations (10-30 minutes). We estimate fetal pose per frame in MRI volumes of the pregnant abdomen via deep learning algorithms that detect key fetal landmarks. Evaluation of the proposed method shows that our framework achieves quantitatively an average error of 4.47 mm and 96.4\% accuracy (with error less than 10 mm). Fetal pose estimation in MRI time series yields novel means of quantifying fetal movements in health and disease, and enables the learning of kinematic models that may enhance prospective mitigation of fetal motion artifacts during MRI acquisition.
Temporal Registration in In-Utero Volumetric MRI Time Series
Aug 12, 2016
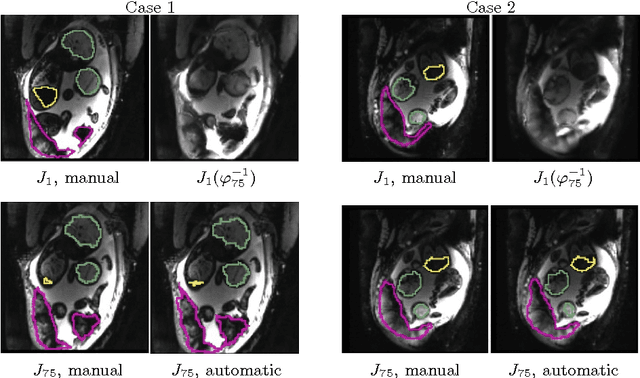
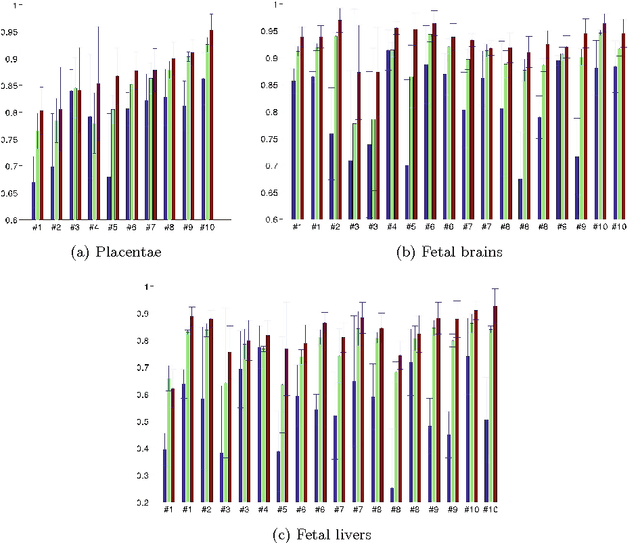
Abstract:We present a robust method to correct for motion and deformations for in-utero volumetric MRI time series. Spatio-temporal analysis of dynamic MRI requires robust alignment across time in the presence of substantial and unpredictable motion. We make a Markov assumption on the nature of deformations to take advantage of the temporal structure in the image data. Forward message passing in the corresponding hidden Markov model (HMM) yields an estimation algorithm that only has to account for relatively small motion between consecutive frames. We demonstrate the utility of the temporal model by showing that its use improves the accuracy of the segmentation propagation through temporal registration. Our results suggest that the proposed model captures accurately the temporal dynamics of deformations in in-utero MRI time series.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge