Jing Fu
Constructing a Question-Answering Simulator through the Distillation of LLMs
Sep 11, 2025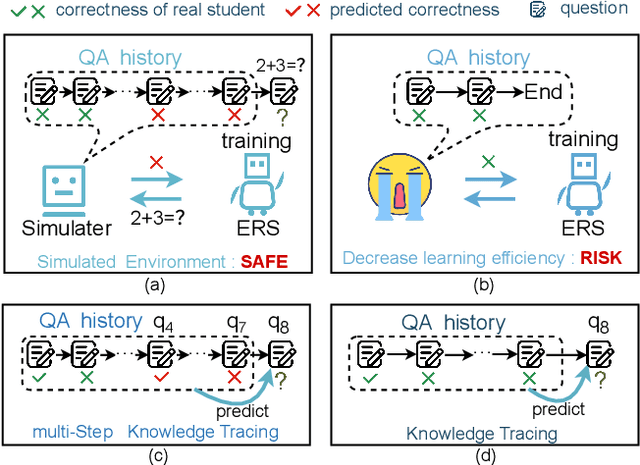
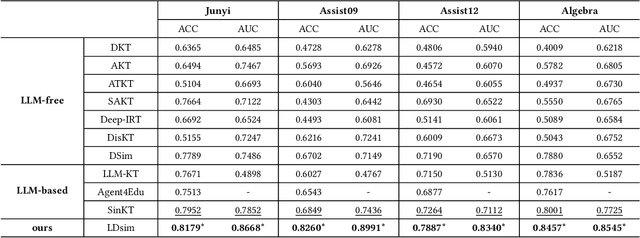
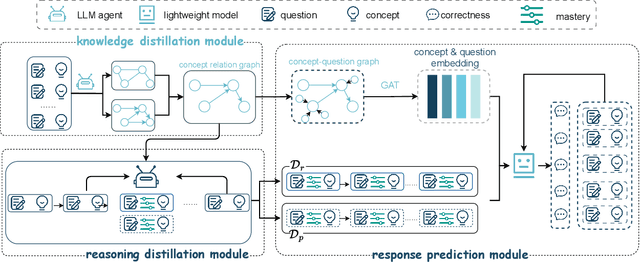
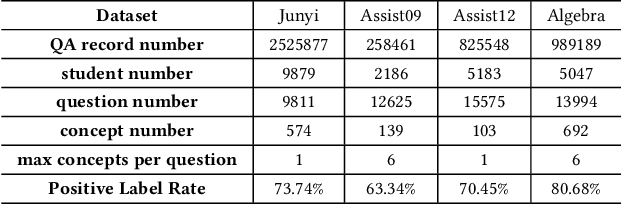
Abstract:The question-answering (QA) simulator is a model that mimics real student learning behaviors and predicts their correctness of their responses to questions. QA simulators enable educational recommender systems (ERS) to collect large amounts of training data without interacting with real students, thereby preventing harmful recommendations made by an undertrained ERS from undermining actual student learning. Given the QA history, there are two categories of solutions to predict the correctness, conducting the simulation: (1) LLM-free methods, which apply a traditional sequential model to transfer the QA history into a vector representation first, and make predictions based on the representation; (2) LLM-based methods, which leverage the domain knowledge and reasoning capability of LLM to enhence the prediction. LLM-free methods offer fast inference but generally yield suboptimal performance. In contrast, most LLM-based methods achieve better results, but at the cost of slower inference speed and higher GPU memory consumption. In this paper, we propose a method named LLM Distillation based Simulator (LDSim), which distills domain knowledge and reasoning capability from an LLM to better assist prediction, thereby improving simulation performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LDSim achieves strong results on both the simulation task and the knowledge tracing (KT) task. Our code is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LDSim-05A9.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
Uniform Planar Array Based Weighted Cooperative Spectrum Sensing for Cognitive Radio Networks
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Cooperative spectrum sensing (CSS) is essential for improving the spectrum efficiency and reliability of cognitive radio applications. Next-generation wireless communication networks increasingly employ uniform planar arrays (UPA) due to their ability to steer beamformers towards desired directions, mitigating interference and eavesdropping. However, the application of UPA-based CSS in cognitive radio remains largely unexplored. This paper proposes a multi-beam UPA-based weighted CSS (WCSS) framework to enhance detection reliability, applicable to various cognitive radio networks, including cellular, vehicular, and satellite communications. We first propose a weighting factor for commonly used energy detection (ED) and eigenvalue detection (EVD) techniques, based on the spatial variation of signal strengths resulting from UPA antenna beamforming. We then analytically characterize the performance of both weighted ED and weighted EVD by deriving closed-form expressions for false alarm and detection probabilities. Our numerical results, considering both static and dynamic user behaviors, demonstrate the superiority of WCSS in enhancing sensing performance compared to uniformly weighted detectors.
Multi-Action Restless Bandits with Weakly Coupled Constraints: Simultaneous Learning and Control
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:We study a system with finitely many groups of multi-action bandit processes, each of which is a Markov decision process (MDP) with finite state and action spaces and potentially different transition matrices when taking different actions. The bandit processes of the same group share the same state and action spaces and, given the same action that is taken, the same transition matrix. All the bandit processes across various groups are subject to multiple weakly coupled constraints over their state and action variables. Unlike the past studies that focused on the offline case, we consider the online case without assuming full knowledge of transition matrices and reward functions a priori and propose an effective scheme that enables simultaneous learning and control. We prove the convergence of the relevant processes in both the timeline and the number of the bandit processes, referred to as the convergence in the time and the magnitude dimensions. Moreover, we prove that the relevant processes converge exponentially fast in the magnitude dimension, leading to exponentially diminishing performance deviation between the proposed online algorithms and offline optimality.
Deep Learning-Based Longitudinal Prediction of Childhood Myopia Progression Using Fundus Image Sequences and Baseline Refraction Data
Jul 31, 2024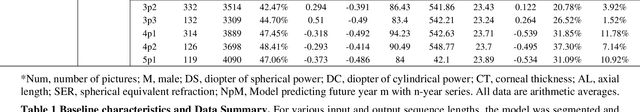

Abstract:Childhood myopia constitutes a significant global health concern. It exhibits an escalating prevalence and has the potential to evolve into severe, irreversible conditions that detrimentally impact familial well-being and create substantial economic costs. Contemporary research underscores the importance of precisely predicting myopia progression to enable timely and effective interventions, thereby averting severe visual impairment in children. Such predictions predominantly rely on subjective clinical assessments, which are inherently biased and resource-intensive, thus hindering their widespread application. In this study, we introduce a novel, high-accuracy method for quantitatively predicting the myopic trajectory and myopia risk in children using only fundus images and baseline refraction data. This approach was validated through a six-year longitudinal study of 3,408 children in Henan, utilizing 16,211 fundus images and corresponding refractive data. Our method based on deep learning demonstrated predictive accuracy with an error margin of 0.311D per year and AUC scores of 0.944 and 0.995 for forecasting the risks of developing myopia and high myopia, respectively. These findings confirm the utility of our model in supporting early intervention strategies and in significantly reducing healthcare costs, particularly by obviating the need for additional metadata and repeated consultations. Furthermore, our method was designed to rely only on fundus images and refractive error data, without the need for meta data or multiple inquiries from doctors, strongly reducing the associated medical costs and facilitating large-scale screening. Our model can even provide good predictions based on only a single time measurement. Consequently, the proposed method is an important means to reduce medical inequities caused by economic disparities.
Interference Mitigation in LEO Constellations with Limited Radio Environment Information
Feb 19, 2024Abstract:This research paper delves into interference mitigation within Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, particularly when operating under constraints of limited radio environment information. Leveraging cognitive capabilities facilitated by the Radio Environment Map (REM), we explore strategies to mitigate the impact of both intentional and unintentional interference using planar antenna array (PAA) beamforming techniques. We address the complexities encountered in the design of beamforming weights, a challenge exacerbated by the array size and the increasing number of directions of interest and avoidance. Furthermore, we conduct an extensive analysis of beamforming performance from various perspectives associated with limited REM information: static versus dynamic, partial versus full, and perfect versus imperfect. To substantiate our findings, we provide simulation results and offer conclusions based on the outcomes of our investigation.
An Index Policy Based on Sarsa and Q-learning for Heterogeneous Smart Target Tracking
Feb 19, 2024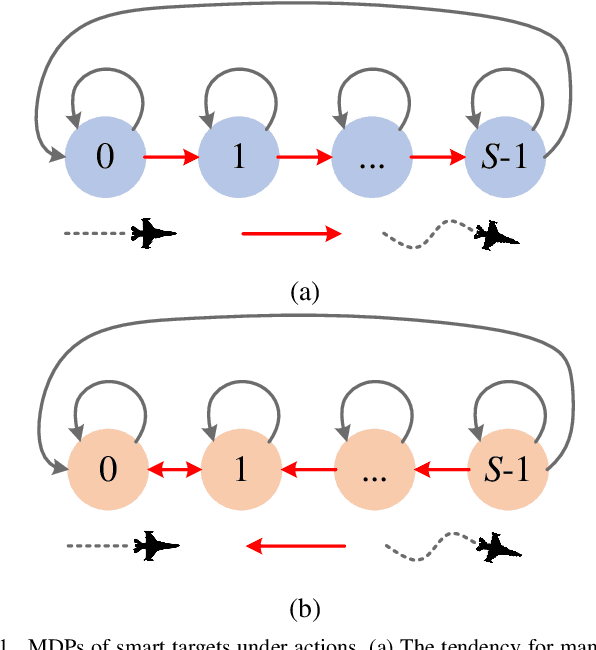
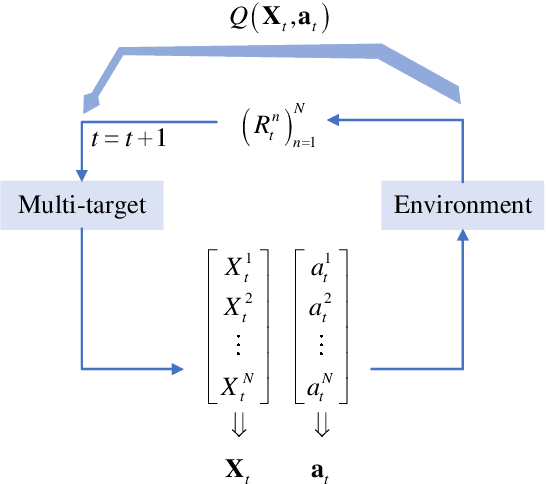
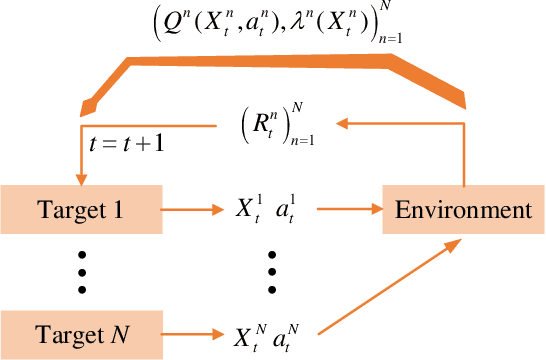
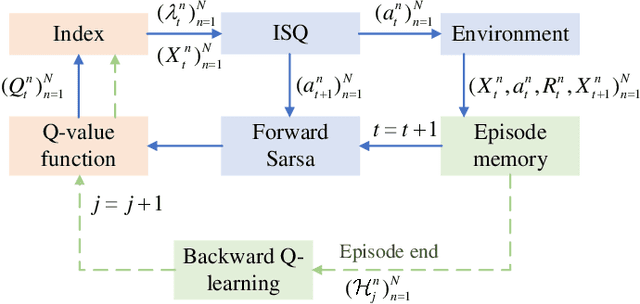
Abstract:In solving the non-myopic radar scheduling for multiple smart target tracking within an active and passive radar network, we need to consider both short-term enhanced tracking performance and a higher probability of target maneuvering in the future with active tracking. Acquiring the long-term tracking performance while scheduling the beam resources of active and passive radars poses a challenge. To address this challenge, we model this problem as a Markov decision process consisting of parallel restless bandit processes. Each bandit process is associated with a smart target, of which the estimation state evolves according to different discrete dynamic models for different actions - whether or not the target is being tracked. The discrete state is defined by the dynamic mode. The problem exhibits the curse of dimensionality, where optimal solutions are in general intractable. We resort to heuristics through the famous restless multi-armed bandit techniques. It follows with efficient scheduling policies based on the indices that are real numbers representing the marginal rewards of taking different actions. For the inevitable practical case with unknown transition matrices, we propose a new method that utilizes the forward Sarsa and backward Q-learning to approximate the indices through adapting the state-action value functions, or equivalently the Q-functions, and propose a new policy, namely ISQ, aiming to maximize the long-term tracking rewards. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed ISQ policy outperforms conventional Q-learning-based methods and rapidly converges to the well-known Whittle index policy with revealed state transition models, which is considered the benchmark.
Joint State Estimation and Noise Identification Based on Variational Optimization
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:In this article, the state estimation problems with unknown process noise and measurement noise covariances for both linear and nonlinear systems are considered. By formulating the joint estimation of system state and noise parameters into an optimization problem, a novel adaptive Kalman filter method based on conjugate-computation variational inference, referred to as CVIAKF, is proposed to approximate the joint posterior probability density function of the latent variables. Unlike the existing adaptive Kalman filter methods utilizing variational inference in natural-parameter space, CVIAKF performs optimization in expectation-parameter space, resulting in a faster and simpler solution. Meanwhile, CVIAKF divides optimization objectives into conjugate and non-conjugate parts of nonlinear dynamical models, whereas conjugate computations and stochastic mirror-descent are applied, respectively. Remarkably, the reparameterization trick is used to reduce the variance of stochastic gradients of the non-conjugate parts. The effectiveness of CVIAKF is validated through synthetic and real-world datasets of maneuvering target tracking.
Experts' cognition-driven ensemble deep learning for external validation of predicting pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy from histological images in breast cancer
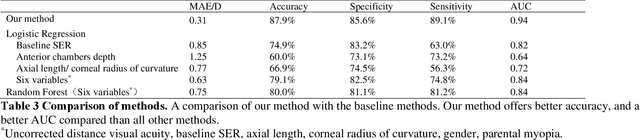
Jun 19, 2023Abstract:In breast cancer imaging, there has been a trend to directly predict pathological complete response (pCR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) from histological images based on deep learning (DL). However, it has been a commonly known problem that the constructed DL-based models numerically have better performances in internal validation than in external validation. The primary reason for this situation lies in that the distribution of the external data for validation is different from the distribution of the training data for the construction of the predictive model. In this paper, we aim to alleviate this situation with a more intrinsic approach. We propose an experts' cognition-driven ensemble deep learning (ECDEDL) approach for external validation of predicting pCR to NAC from histological images in breast cancer. The proposed ECDEDL, which takes the cognition of both pathology and artificial intelligence experts into consideration to improve the generalization of the predictive model to the external validation, more intrinsically approximates the working paradigm of a human being which will refer to his various working experiences to make decisions. The proposed ECDEDL approach was validated with 695 WSIs collected from the same center as the primary dataset to develop the predictive model and perform the internal validation, and 340 WSIs collected from other three centers as the external dataset to perform the external validation. In external validation, the proposed ECDEDL approach improves the AUCs of pCR prediction from 61.52(59.80-63.26) to 67.75(66.74-68.80) and the Accuracies of pCR prediction from 56.09(49.39-62.79) to 71.01(69.44-72.58). The proposed ECDEDL was quite effective for external validation, numerically more approximating the internal validation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge