Xuemeng Li
Generalised Label-free Artefact Cleaning for Real-time Medical Pulsatile Time Series
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Artefacts compromise clinical decision-making in the use of medical time series. Pulsatile waveforms offer probabilities for accurate artefact detection, yet most approaches rely on supervised manners and overlook patient-level distribution shifts. To address these issues, we introduce a generalised label-free framework, GenClean, for real-time artefact cleaning and leverage an in-house dataset of 180,000 ten-second arterial blood pressure (ABP) samples for training. We first investigate patient-level generalisation, demonstrating robust performances under both intra- and inter-patient distribution shifts. We further validate its effectiveness through challenging cross-disease cohort experiments on the MIMIC-III database. Additionally, we extend our method to photoplethysmography (PPG), highlighting its applicability to diverse medical pulsatile signals. Finally, its integration into ICM+, a clinical research monitoring software, confirms the real-time feasibility of our framework, emphasising its practical utility in continuous physiological monitoring. This work provides a foundational step toward precision medicine in improving the reliability of high-resolution medical time series analysis
High-Order Associative Learning Based on Memristive Circuits for Efficient Learning
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Memristive associative learning has gained significant attention for its ability to mimic fundamental biological learning mechanisms while maintaining system simplicity. In this work, we introduce a high-order memristive associative learning framework with a biologically realistic structure. By utilizing memristors as synaptic modules and their state information to bridge different orders of associative learning, our design effectively establishes associations between multiple stimuli and replicates the transient nature of high-order associative learning. In Pavlov's classical conditioning experiments, our design achieves a 230% improvement in learning efficiency compared to previous works, with memristor power consumption in the synaptic modules remaining below 11 {\mu}W. In large-scale image recognition tasks, we utilize a 20*20 memristor array to represent images, enabling the system to recognize and label test images with semantic information at 100% accuracy. This scalability across different tasks highlights the framework's potential for a wide range of applications, offering enhanced learning efficiency for current memristor-based neuromorphic systems.
Deep Learning-Based Longitudinal Prediction of Childhood Myopia Progression Using Fundus Image Sequences and Baseline Refraction Data
Jul 31, 2024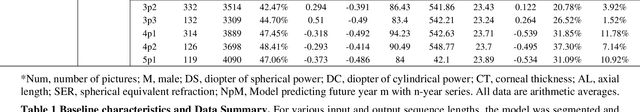

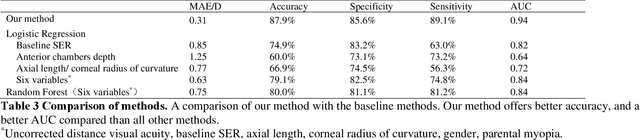
Abstract:Childhood myopia constitutes a significant global health concern. It exhibits an escalating prevalence and has the potential to evolve into severe, irreversible conditions that detrimentally impact familial well-being and create substantial economic costs. Contemporary research underscores the importance of precisely predicting myopia progression to enable timely and effective interventions, thereby averting severe visual impairment in children. Such predictions predominantly rely on subjective clinical assessments, which are inherently biased and resource-intensive, thus hindering their widespread application. In this study, we introduce a novel, high-accuracy method for quantitatively predicting the myopic trajectory and myopia risk in children using only fundus images and baseline refraction data. This approach was validated through a six-year longitudinal study of 3,408 children in Henan, utilizing 16,211 fundus images and corresponding refractive data. Our method based on deep learning demonstrated predictive accuracy with an error margin of 0.311D per year and AUC scores of 0.944 and 0.995 for forecasting the risks of developing myopia and high myopia, respectively. These findings confirm the utility of our model in supporting early intervention strategies and in significantly reducing healthcare costs, particularly by obviating the need for additional metadata and repeated consultations. Furthermore, our method was designed to rely only on fundus images and refractive error data, without the need for meta data or multiple inquiries from doctors, strongly reducing the associated medical costs and facilitating large-scale screening. Our model can even provide good predictions based on only a single time measurement. Consequently, the proposed method is an important means to reduce medical inequities caused by economic disparities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge