Hongbei Meng
Wearable intelligent throat enables natural speech in stroke patients with dysarthria
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:Wearable silent speech systems hold significant potential for restoring communication in patients with speech impairments. However, seamless, coherent speech remains elusive, and clinical efficacy is still unproven. Here, we present an AI-driven intelligent throat (IT) system that integrates throat muscle vibrations and carotid pulse signal sensors with large language model (LLM) processing to enable fluent, emotionally expressive communication. The system utilizes ultrasensitive textile strain sensors to capture high-quality signals from the neck area and supports token-level processing for real-time, continuous speech decoding, enabling seamless, delay-free communication. In tests with five stroke patients with dysarthria, IT's LLM agents intelligently corrected token errors and enriched sentence-level emotional and logical coherence, achieving low error rates (4.2% word error rate, 2.9% sentence error rate) and a 55% increase in user satisfaction. This work establishes a portable, intuitive communication platform for patients with dysarthria with the potential to be applied broadly across different neurological conditions and in multi-language support systems.
Deep Learning-Based Longitudinal Prediction of Childhood Myopia Progression Using Fundus Image Sequences and Baseline Refraction Data
Jul 31, 2024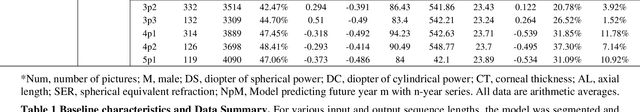

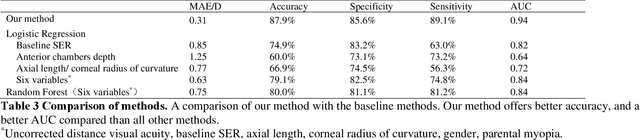
Abstract:Childhood myopia constitutes a significant global health concern. It exhibits an escalating prevalence and has the potential to evolve into severe, irreversible conditions that detrimentally impact familial well-being and create substantial economic costs. Contemporary research underscores the importance of precisely predicting myopia progression to enable timely and effective interventions, thereby averting severe visual impairment in children. Such predictions predominantly rely on subjective clinical assessments, which are inherently biased and resource-intensive, thus hindering their widespread application. In this study, we introduce a novel, high-accuracy method for quantitatively predicting the myopic trajectory and myopia risk in children using only fundus images and baseline refraction data. This approach was validated through a six-year longitudinal study of 3,408 children in Henan, utilizing 16,211 fundus images and corresponding refractive data. Our method based on deep learning demonstrated predictive accuracy with an error margin of 0.311D per year and AUC scores of 0.944 and 0.995 for forecasting the risks of developing myopia and high myopia, respectively. These findings confirm the utility of our model in supporting early intervention strategies and in significantly reducing healthcare costs, particularly by obviating the need for additional metadata and repeated consultations. Furthermore, our method was designed to rely only on fundus images and refractive error data, without the need for meta data or multiple inquiries from doctors, strongly reducing the associated medical costs and facilitating large-scale screening. Our model can even provide good predictions based on only a single time measurement. Consequently, the proposed method is an important means to reduce medical inequities caused by economic disparities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge