Hua Lan
Joint State Estimation and Noise Identification Based on Variational Optimization
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:In this article, the state estimation problems with unknown process noise and measurement noise covariances for both linear and nonlinear systems are considered. By formulating the joint estimation of system state and noise parameters into an optimization problem, a novel adaptive Kalman filter method based on conjugate-computation variational inference, referred to as CVIAKF, is proposed to approximate the joint posterior probability density function of the latent variables. Unlike the existing adaptive Kalman filter methods utilizing variational inference in natural-parameter space, CVIAKF performs optimization in expectation-parameter space, resulting in a faster and simpler solution. Meanwhile, CVIAKF divides optimization objectives into conjugate and non-conjugate parts of nonlinear dynamical models, whereas conjugate computations and stochastic mirror-descent are applied, respectively. Remarkably, the reparameterization trick is used to reduce the variance of stochastic gradients of the non-conjugate parts. The effectiveness of CVIAKF is validated through synthetic and real-world datasets of maneuvering target tracking.
Classification-Aided Robust Multiple Target Tracking Using Neural Enhanced Message Passing
Oct 19, 2023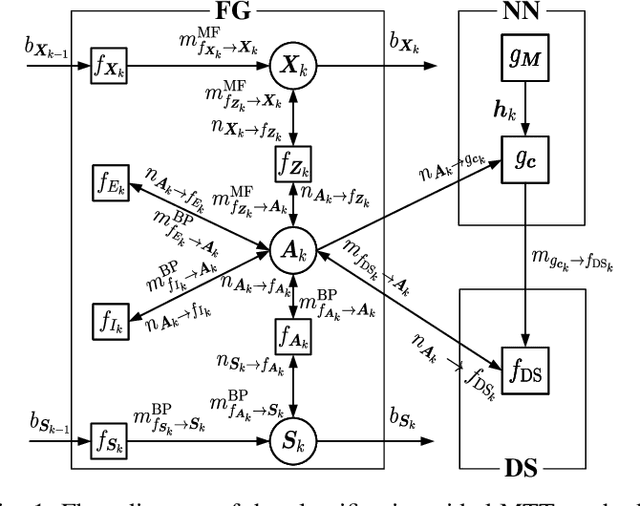
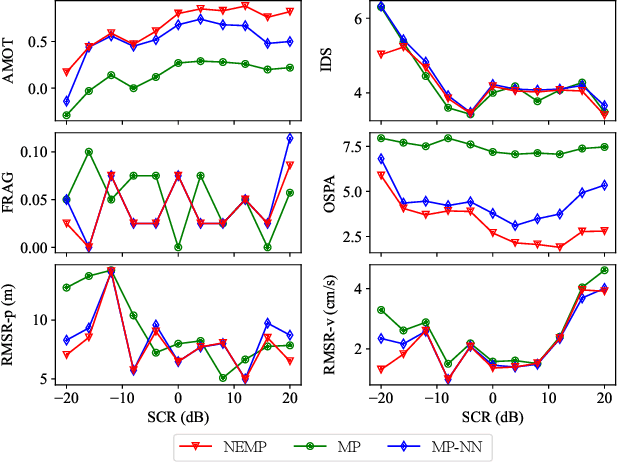
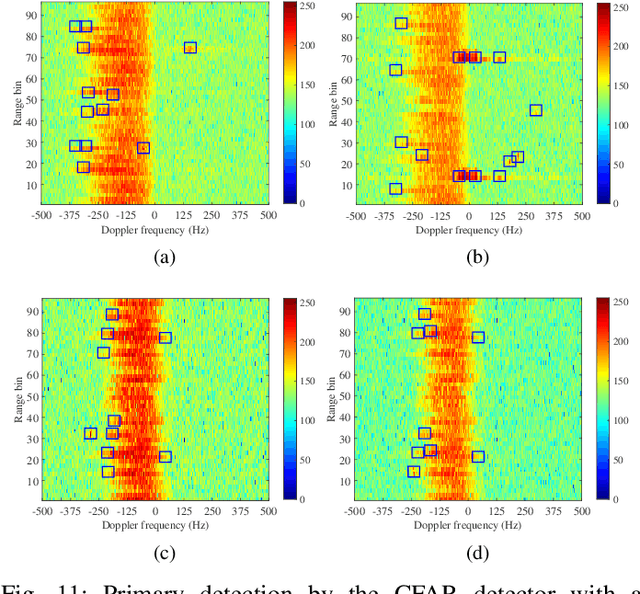
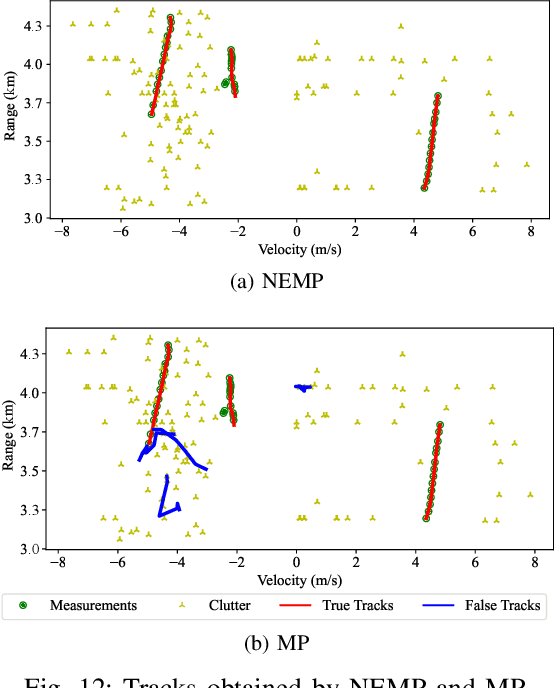
Abstract:We address the challenge of tracking an unknown number of targets in strong clutter environments using measurements from a radar sensor. Leveraging the range-Doppler spectra information, we identify the measurement classes, which serve as additional information to enhance clutter rejection and data association, thus bolstering the robustness of target tracking. We first introduce a novel neural enhanced message passing approach, where the beliefs obtained by the unified message passing are fed into the neural network as additional information. The output beliefs are then utilized to refine the original beliefs. Then, we propose a classification-aided robust multiple target tracking algorithm, employing the neural enhanced message passing technique. This algorithm is comprised of three modules: a message-passing module, a neural network module, and a Dempster-Shafer module. The message-passing module is used to represent the statistical model by the factor graph and infers target kinematic states, visibility states, and data associations based on the spatial measurement information. The neural network module is employed to extract features from range-Doppler spectra and derive beliefs on whether a measurement is target-generated or clutter-generated. The Dempster-Shafer module is used to fuse the beliefs obtained from both the factor graph and the neural network. As a result, our proposed algorithm adopts a model-and-data-driven framework, effectively enhancing clutter suppression and data association, leading to significant improvements in multiple target tracking performance. We validate the effectiveness of our approach using both simulated and real data scenarios, demonstrating its capability to handle challenging tracking scenarios in practical radar applications.
Variational Nonlinear Kalman Filtering with Unknown Process Noise Covariance
May 06, 2023



Abstract:Motivated by the maneuvering target tracking with sensors such as radar and sonar, this paper considers the joint and recursive estimation of the dynamic state and the time-varying process noise covariance in nonlinear state space models. Due to the nonlinearity of the models and the non-conjugate prior, the state estimation problem is generally intractable as it involves integrals of general nonlinear functions and unknown process noise covariance, resulting in the posterior probability distribution functions lacking closed-form solutions. This paper presents a recursive solution for joint nonlinear state estimation and model parameters identification based on the approximate Bayesian inference principle. The stochastic search variational inference is adopted to offer a flexible, accurate, and effective approximation of the posterior distributions. We make two contributions compared to existing variational inference-based noise adaptive filtering methods. First, we introduce an auxiliary latent variable to decouple the latent variables of dynamic state and process noise covariance, thereby improving the flexibility of the posterior inference. Second, we split the variational lower bound optimization into conjugate and non-conjugate parts, whereas the conjugate terms are directly optimized that admit a closed-form solution and the non-conjugate terms are optimized by natural gradients, achieving the trade-off between inference speed and accuracy. The performance of the proposed method is verified on radar target tracking applications by both simulated and real-world data.
Joint Detection and Tracking for Multipath Targets: A Variational Bayesian Approach
Oct 27, 2016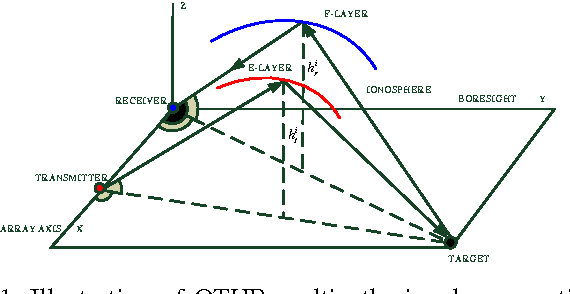
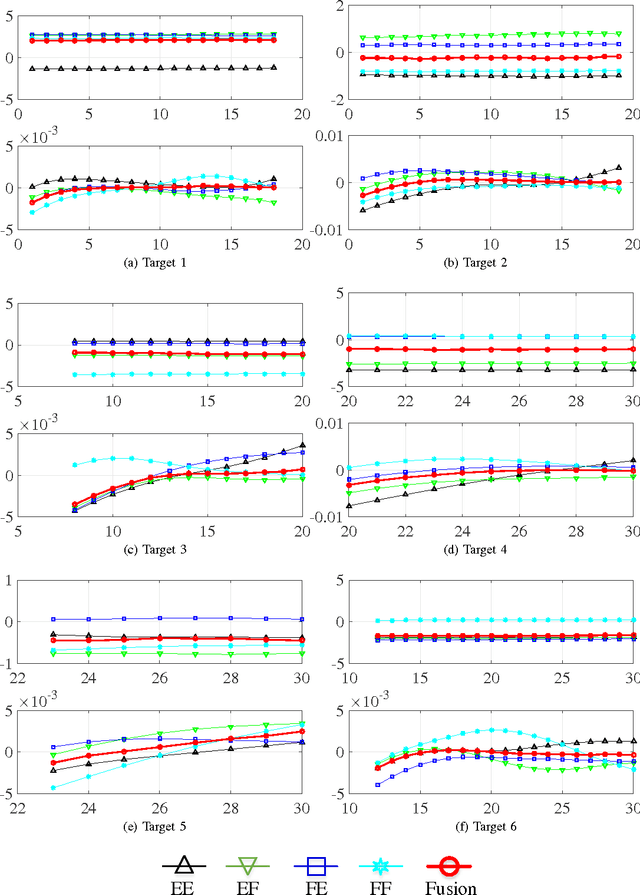
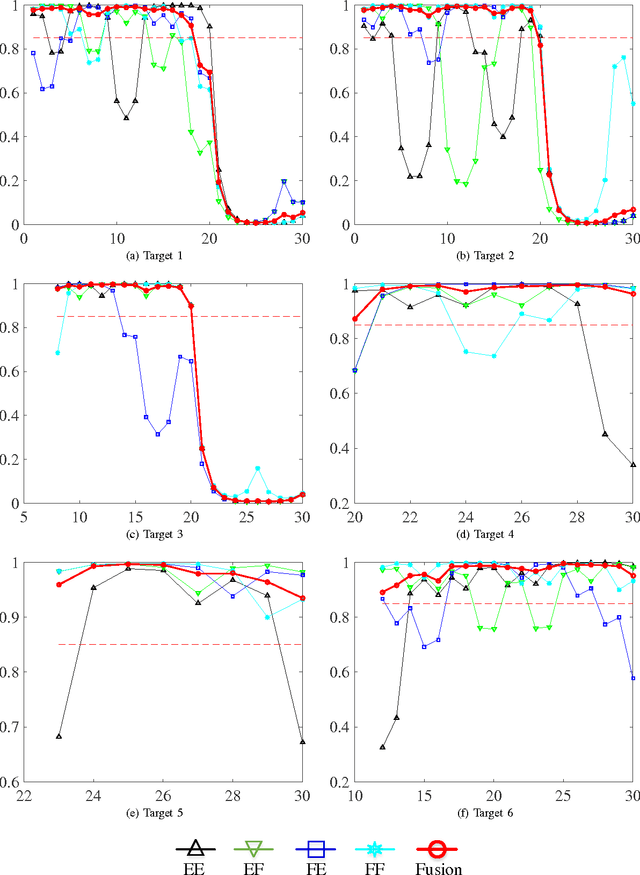

Abstract:Different from traditional point target tracking systems assuming that a target generates at most one single measurement per scan, there exists a class of multipath target tracking systems where each measurement may originate from the interested target via one of multiple propagation paths or from clutter, while the correspondence among targets, measurements, and propagation paths is unknown. The performance of multipath target tracking systems can be improved if multiple measurements from the same target are effectively utilized, but suffers from two major challenges. The first is multipath detection that detects appearing and disappearing targets automatically, while one target may produce $s$ tracks for $s$ propagation paths. The second is multipath tracking that calculates the target-to-measurement-to-path assignment matrices to estimate target states, which is computationally intractable due to the combinatorial explosion. Based on variational Bayesian framework, this paper introduces a novel probabilistic joint detection and tracking algorithm (JDT-VB) that incorporates data association, path association, state estimation and automatic track management. The posterior probabilities of these latent variables are derived in a closed-form iterative manner, which is effective for dealing with the coupling issue of multipath data association identification risk and state estimation error. Loopy belief propagation (LBP) is exploited to approximate the multipath data association, which significantly reduces the computational cost. The proposed JDT-VB algorithm can simultaneously deal with the track initiation, maintenance, and termination for multiple multipath target tracking with time-varying number of targets, and its performance is verified by a numerical simulation of over-the-horizon radar.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge