Zengfu Wang
Unleashing Foundation Vision Models: Adaptive Transfer for Diverse Data-Limited Scientific Domains
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:In the big data era, the computer vision field benefits from large-scale datasets such as LAION-2B, LAION-400M, and ImageNet-21K, Kinetics, on which popular models like the ViT and ConvNeXt series have been pre-trained, acquiring substantial knowledge. However, numerous downstream tasks in specialized and data-limited scientific domains continue to pose significant challenges. In this paper, we propose a novel Cluster Attention Adapter (CLAdapter), which refines and adapts the rich representations learned from large-scale data to various data-limited downstream tasks. Specifically, CLAdapter introduces attention mechanisms and cluster centers to personalize the enhancement of transformed features through distribution correlation and transformation matrices. This enables models fine-tuned with CLAdapter to learn distinct representations tailored to different feature sets, facilitating the models' adaptation from rich pre-trained features to various downstream scenarios effectively. In addition, CLAdapter's unified interface design allows for seamless integration with multiple model architectures, including CNNs and Transformers, in both 2D and 3D contexts. Through extensive experiments on 10 datasets spanning domains such as generic, multimedia, biological, medical, industrial, agricultural, environmental, geographical, materials science, out-of-distribution (OOD), and 3D analysis, CLAdapter achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse data-limited scientific domains, demonstrating its effectiveness in unleashing the potential of foundation vision models via adaptive transfer. Code is available at https://github.com/qklee-lz/CLAdapter.
An Index Policy Based on Sarsa and Q-learning for Heterogeneous Smart Target Tracking
Feb 19, 2024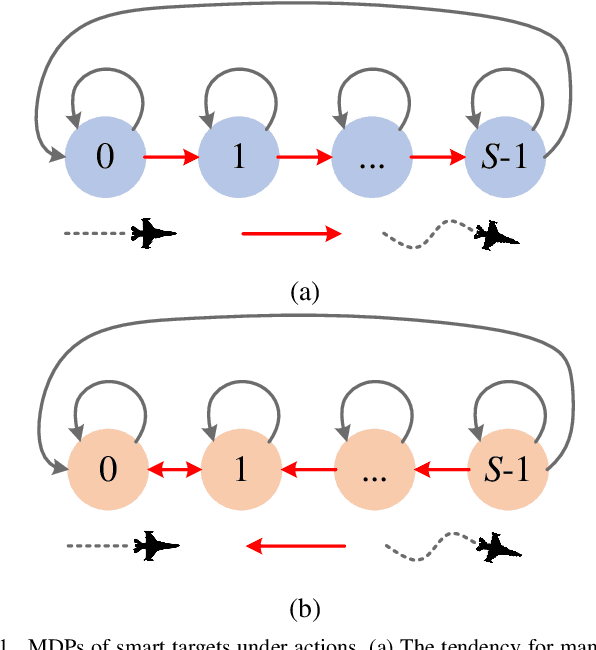
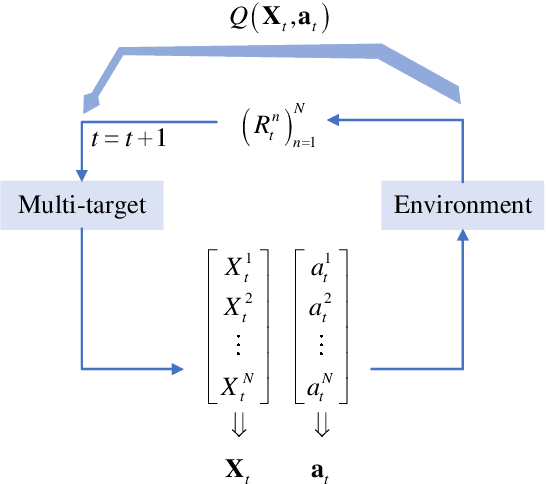
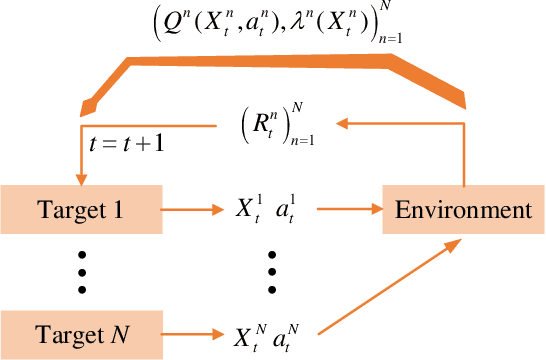
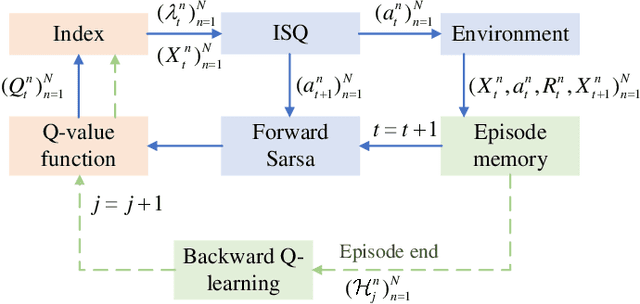
Abstract:In solving the non-myopic radar scheduling for multiple smart target tracking within an active and passive radar network, we need to consider both short-term enhanced tracking performance and a higher probability of target maneuvering in the future with active tracking. Acquiring the long-term tracking performance while scheduling the beam resources of active and passive radars poses a challenge. To address this challenge, we model this problem as a Markov decision process consisting of parallel restless bandit processes. Each bandit process is associated with a smart target, of which the estimation state evolves according to different discrete dynamic models for different actions - whether or not the target is being tracked. The discrete state is defined by the dynamic mode. The problem exhibits the curse of dimensionality, where optimal solutions are in general intractable. We resort to heuristics through the famous restless multi-armed bandit techniques. It follows with efficient scheduling policies based on the indices that are real numbers representing the marginal rewards of taking different actions. For the inevitable practical case with unknown transition matrices, we propose a new method that utilizes the forward Sarsa and backward Q-learning to approximate the indices through adapting the state-action value functions, or equivalently the Q-functions, and propose a new policy, namely ISQ, aiming to maximize the long-term tracking rewards. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed ISQ policy outperforms conventional Q-learning-based methods and rapidly converges to the well-known Whittle index policy with revealed state transition models, which is considered the benchmark.
Joint State Estimation and Noise Identification Based on Variational Optimization
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:In this article, the state estimation problems with unknown process noise and measurement noise covariances for both linear and nonlinear systems are considered. By formulating the joint estimation of system state and noise parameters into an optimization problem, a novel adaptive Kalman filter method based on conjugate-computation variational inference, referred to as CVIAKF, is proposed to approximate the joint posterior probability density function of the latent variables. Unlike the existing adaptive Kalman filter methods utilizing variational inference in natural-parameter space, CVIAKF performs optimization in expectation-parameter space, resulting in a faster and simpler solution. Meanwhile, CVIAKF divides optimization objectives into conjugate and non-conjugate parts of nonlinear dynamical models, whereas conjugate computations and stochastic mirror-descent are applied, respectively. Remarkably, the reparameterization trick is used to reduce the variance of stochastic gradients of the non-conjugate parts. The effectiveness of CVIAKF is validated through synthetic and real-world datasets of maneuvering target tracking.
Classification-Aided Robust Multiple Target Tracking Using Neural Enhanced Message Passing
Oct 19, 2023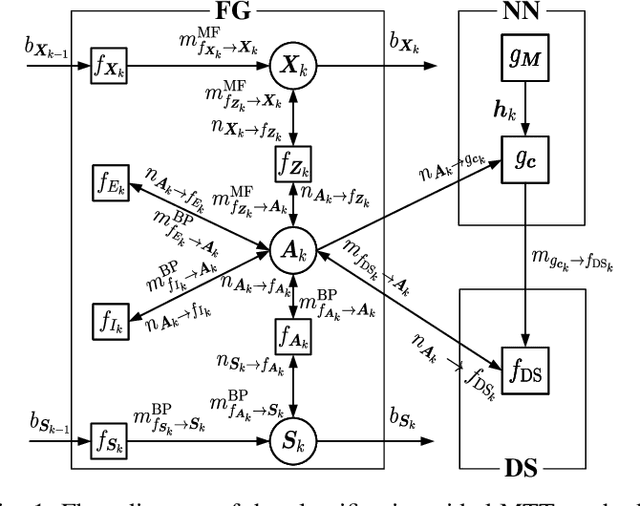
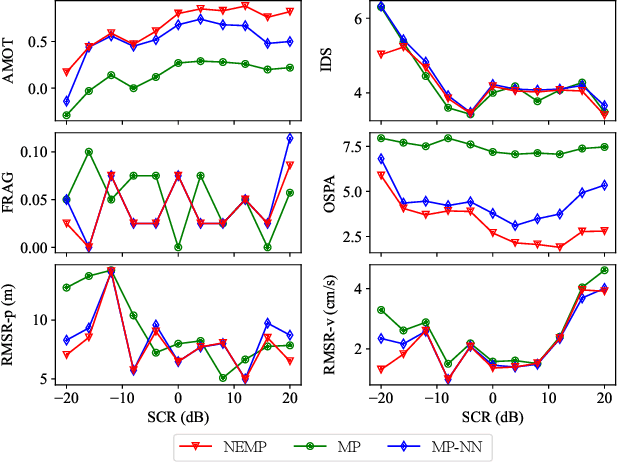
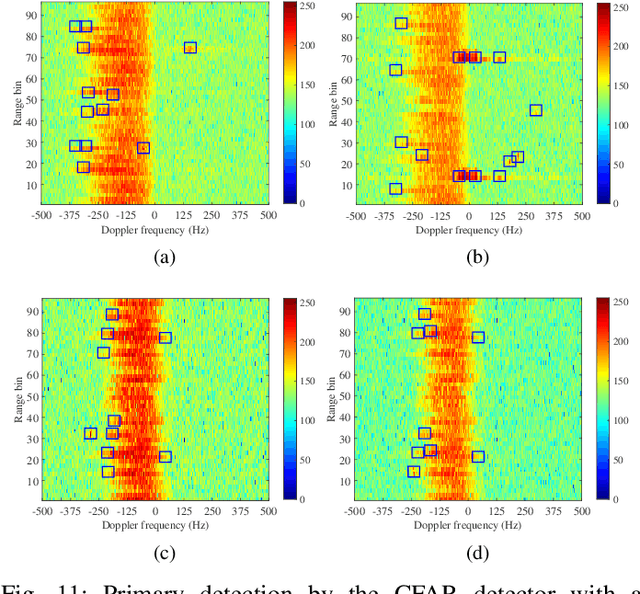
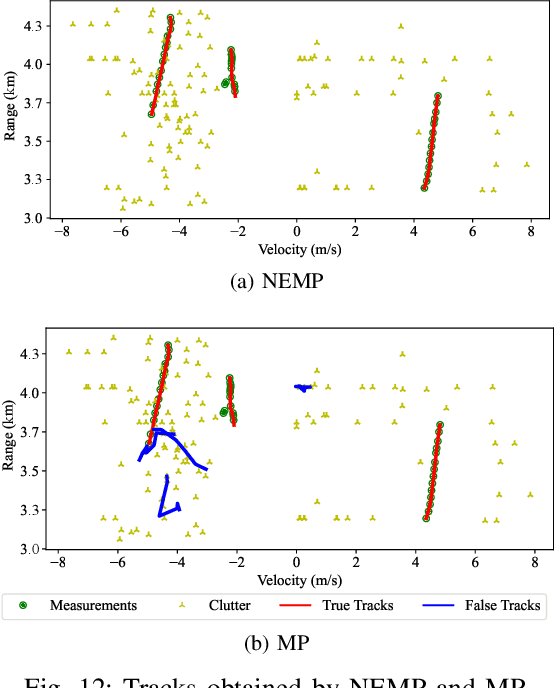
Abstract:We address the challenge of tracking an unknown number of targets in strong clutter environments using measurements from a radar sensor. Leveraging the range-Doppler spectra information, we identify the measurement classes, which serve as additional information to enhance clutter rejection and data association, thus bolstering the robustness of target tracking. We first introduce a novel neural enhanced message passing approach, where the beliefs obtained by the unified message passing are fed into the neural network as additional information. The output beliefs are then utilized to refine the original beliefs. Then, we propose a classification-aided robust multiple target tracking algorithm, employing the neural enhanced message passing technique. This algorithm is comprised of three modules: a message-passing module, a neural network module, and a Dempster-Shafer module. The message-passing module is used to represent the statistical model by the factor graph and infers target kinematic states, visibility states, and data associations based on the spatial measurement information. The neural network module is employed to extract features from range-Doppler spectra and derive beliefs on whether a measurement is target-generated or clutter-generated. The Dempster-Shafer module is used to fuse the beliefs obtained from both the factor graph and the neural network. As a result, our proposed algorithm adopts a model-and-data-driven framework, effectively enhancing clutter suppression and data association, leading to significant improvements in multiple target tracking performance. We validate the effectiveness of our approach using both simulated and real data scenarios, demonstrating its capability to handle challenging tracking scenarios in practical radar applications.
Exploring Part-Informed Visual-Language Learning for Person Re-Identification
Aug 04, 2023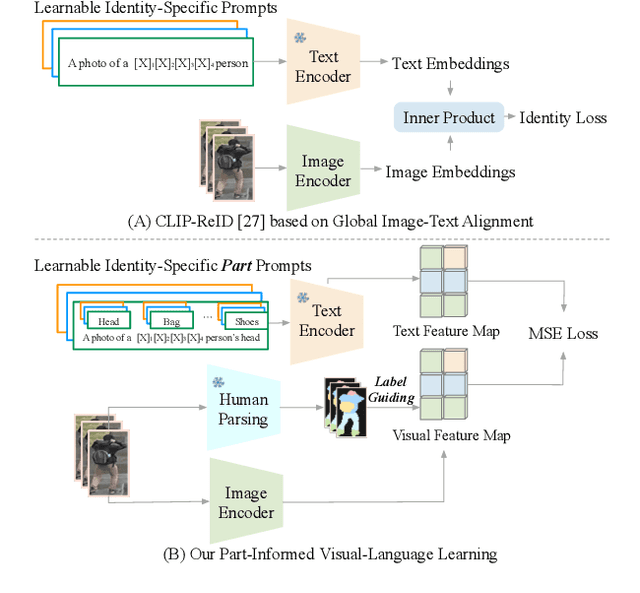
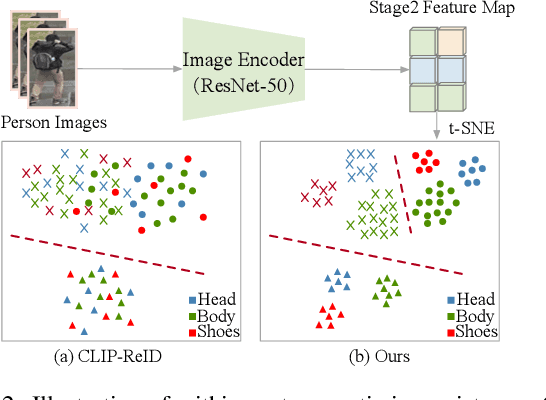
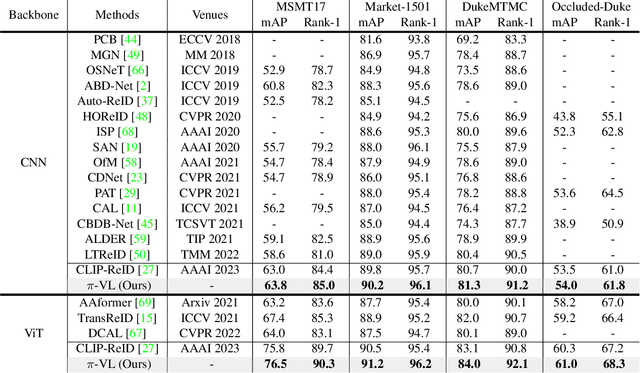
Abstract:Recently, visual-language learning has shown great potential in enhancing visual-based person re-identification (ReID). Existing visual-language learning-based ReID methods often focus on whole-body scale image-text feature alignment, while neglecting supervisions on fine-grained part features. This choice simplifies the learning process but cannot guarantee within-part feature semantic consistency thus hindering the final performance. Therefore, we propose to enhance fine-grained visual features with part-informed language supervision for ReID tasks. The proposed method, named Part-Informed Visual-language Learning ($\pi$-VL), suggests that (i) a human parsing-guided prompt tuning strategy and (ii) a hierarchical fusion-based visual-language alignment paradigm play essential roles in ensuring within-part feature semantic consistency. Specifically, we combine both identity labels and parsing maps to constitute pixel-level text prompts and fuse multi-stage visual features with a light-weight auxiliary head to perform fine-grained image-text alignment. As a plug-and-play and inference-free solution, our $\pi$-VL achieves substantial improvements over previous state-of-the-arts on four common-used ReID benchmarks, especially reporting 90.3% Rank-1 and 76.5% mAP for the most challenging MSMT17 database without bells and whistles.
Variational Nonlinear Kalman Filtering with Unknown Process Noise Covariance
May 06, 2023



Abstract:Motivated by the maneuvering target tracking with sensors such as radar and sonar, this paper considers the joint and recursive estimation of the dynamic state and the time-varying process noise covariance in nonlinear state space models. Due to the nonlinearity of the models and the non-conjugate prior, the state estimation problem is generally intractable as it involves integrals of general nonlinear functions and unknown process noise covariance, resulting in the posterior probability distribution functions lacking closed-form solutions. This paper presents a recursive solution for joint nonlinear state estimation and model parameters identification based on the approximate Bayesian inference principle. The stochastic search variational inference is adopted to offer a flexible, accurate, and effective approximation of the posterior distributions. We make two contributions compared to existing variational inference-based noise adaptive filtering methods. First, we introduce an auxiliary latent variable to decouple the latent variables of dynamic state and process noise covariance, thereby improving the flexibility of the posterior inference. Second, we split the variational lower bound optimization into conjugate and non-conjugate parts, whereas the conjugate terms are directly optimized that admit a closed-form solution and the non-conjugate terms are optimized by natural gradients, achieving the trade-off between inference speed and accuracy. The performance of the proposed method is verified on radar target tracking applications by both simulated and real-world data.
A Sea-Land Clutter Classification Framework for Over-the-Horizon-Radar Based on Weighted Loss Semi-supervised GAN
May 06, 2023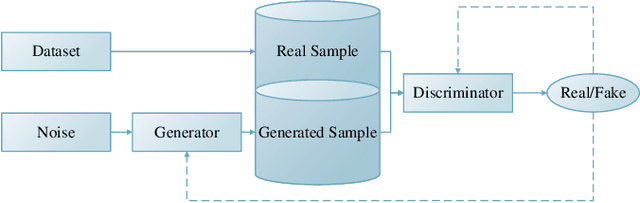
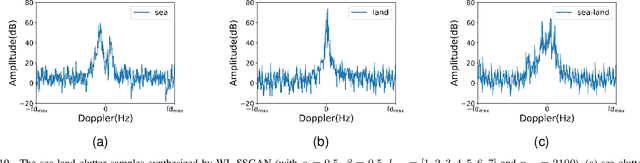
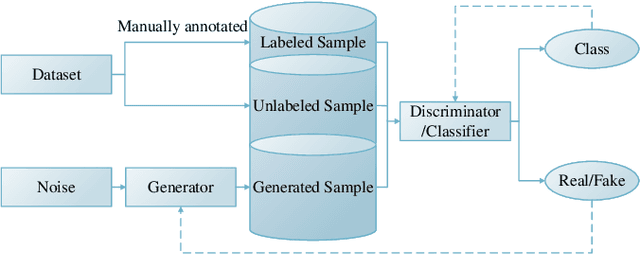
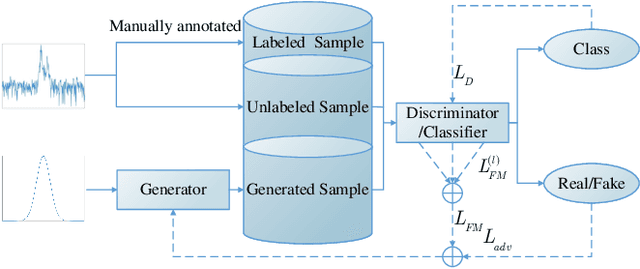
Abstract:Deep convolutional neural network has made great achievements in sea-land clutter classification for over-the-horizon-radar (OTHR). The premise is that a large number of labeled training samples must be provided for a sea-land clutter classifier. In practical engineering applications, it is relatively easy to obtain label-free sea-land clutter samples. However, the labeling process is extremely cumbersome and requires expertise in the field of OTHR. To solve this problem, we propose an improved generative adversarial network, namely weighted loss semi-supervised generative adversarial network (WL-SSGAN). Specifically, we propose a joint feature matching loss by weighting the middle layer features of the discriminator of semi-supervised generative adversarial network. Furthermore, we propose the weighted loss of WL-SSGAN by linearly weighting standard adversarial loss and joint feature matching loss. The semi-supervised classification performance of WL-SSGAN is evaluated on a sea-land clutter dataset. The experimental results show that WL-SSGAN can improve the performance of the fully supervised classifier with only a small number of labeled samples by utilizing a large number of unlabeled sea-land clutter samples. Further, the proposed weighted loss is superior to both the adversarial loss and the feature matching loss. Additionally, we compare WL-SSGAN with conventional semi-supervised classification methods and demonstrate that WL-SSGAN achieves the highest classification accuracy.
SSR-HEF: Crowd Counting with Multi-Scale Semantic Refining and Hard Example Focusing
Apr 15, 2022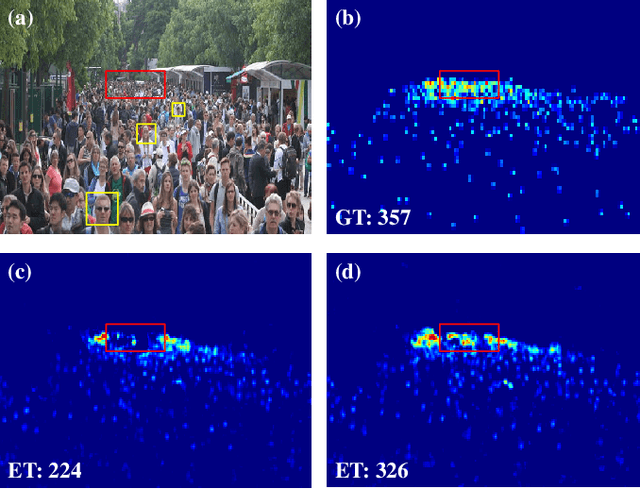
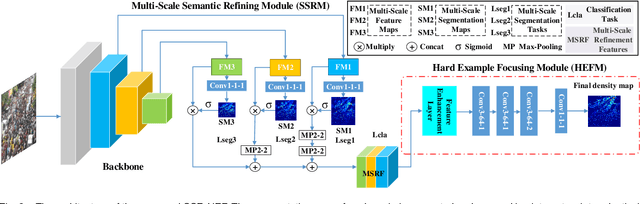
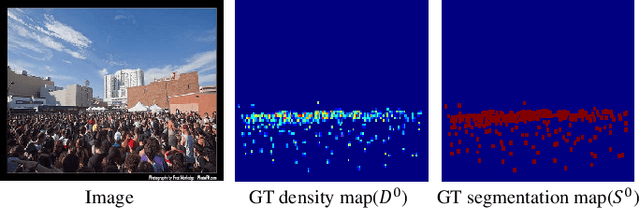
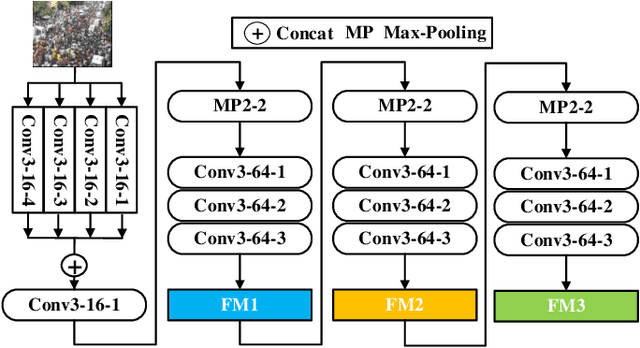
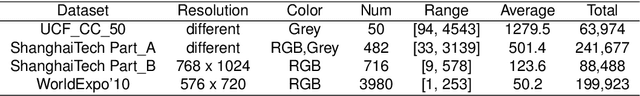
Abstract:Crowd counting based on density maps is generally regarded as a regression task.Deep learning is used to learn the mapping between image content and crowd density distribution. Although great success has been achieved, some pedestrians far away from the camera are difficult to be detected. And the number of hard examples is often larger. Existing methods with simple Euclidean distance algorithm indiscriminately optimize the hard and easy examples so that the densities of hard examples are usually incorrectly predicted to be lower or even zero, which results in large counting errors. To address this problem, we are the first to propose the Hard Example Focusing(HEF) algorithm for the regression task of crowd counting. The HEF algorithm makes our model rapidly focus on hard examples by attenuating the contribution of easy examples.Then higher importance will be given to the hard examples with wrong estimations. Moreover, the scale variations in crowd scenes are large, and the scale annotations are labor-intensive and expensive. By proposing a multi-Scale Semantic Refining (SSR) strategy, lower layers of our model can break through the limitation of deep learning to capture semantic features of different scales to sufficiently deal with the scale variation. We perform extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets to verify the proposed method. Results indicate the superiority of our proposed method over the state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, our designed model is smaller and faster.
* Accepted by IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL INFORMATICS
Crowd counting with segmentation attention convolutional neural network
Apr 15, 2022

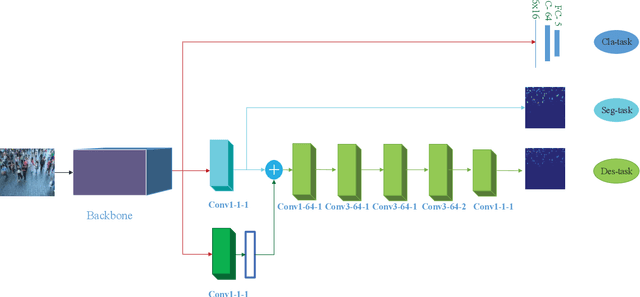

Abstract:Deep learning occupies an undisputed dominance in crowd counting. In this paper, we propose a novel convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture called SegCrowdNet. Despite the complex background in crowd scenes, the proposeSegCrowdNet still adaptively highlights the human head region and suppresses the non-head region by segmentation. With the guidance of an attention mechanism, the proposed SegCrowdNet pays more attention to the human head region and automatically encodes the highly refined density map. The crowd count can be obtained by integrating the density map. To adapt the variation of crowd counts, SegCrowdNet intelligently classifies the crowd count of each image into several groups. In addition, the multi-scale features are learned and extracted in the proposed SegCrowdNet to overcome the scale variations of the crowd. To verify the effectiveness of our proposed method, extensive experiments are conducted on four challenging datasets. The results demonstrate that our proposed SegCrowdNet achieves excellent performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
* Accepted by IET Image Processing
Crowd counting with crowd attention convolutional neural network
Apr 15, 2022


Abstract:Crowd counting is a challenging problem due to the scene complexity and scale variation. Although deep learning has achieved great improvement in crowd counting, scene complexity affects the judgement of these methods and they usually regard some objects as people mistakenly; causing potentially enormous errors in the crowd counting result. To address the problem, we propose a novel end-to-end model called Crowd Attention Convolutional Neural Network (CAT-CNN). Our CAT-CNN can adaptively assess the importance of a human head at each pixel location by automatically encoding a confidence map. With the guidance of the confidence map, the position of human head in estimated density map gets more attention to encode the final density map, which can avoid enormous misjudgements effectively. The crowd count can be obtained by integrating the final density map. To encode a highly refined density map, the total crowd count of each image is classified in a designed classification task and we first explicitly map the prior of the population-level category to feature maps. To verify the efficiency of our proposed method, extensive experiments are conducted on three highly challenging datasets. Results establish the superiority of our method over many state-of-the-art methods.
* Accepted by Neurocomputing
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge