Jie Gu
Rhombot: Rhombus-shaped Modular Robots for Stable, Medium-Independent Reconfiguration Motion
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we present Rhombot, a novel deformable planar lattice modular self-reconfigurable robot (MSRR) with a rhombus shaped module. Each module consists of a parallelogram skeleton with a single centrally mounted actuator that enables folding and unfolding along its diagonal. The core design philosophy is to achieve essential MSRR functionalities such as morphing, docking, and locomotion with minimal control complexity. This enables a continuous and stable reconfiguration process that is independent of the surrounding medium, allowing the system to reliably form various configurations in diverse environments. To leverage the unique kinematics of Rhombot, we introduce morphpivoting, a novel motion primitive for reconfiguration that differs from advanced MSRR systems, and propose a strategy for its continuous execution. Finally, a series of physical experiments validate the module's stable reconfiguration ability, as well as its positional and docking accuracy.
Self-Reconfiguration Planning for Deformable Quadrilateral Modular Robots
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:For lattice modular self-reconfigurable robots (MSRRs), maintaining stable connections during reconfiguration is crucial for physical feasibility and deployability. This letter presents a novel self-reconfiguration planning algorithm for deformable quadrilateral MSRRs that guarantees stable connection. The method first constructs feasible connect/disconnect actions using a virtual graph representation, and then organizes these actions into a valid execution sequence through a Dependence-based Reverse Tree (DRTree) that resolves interdependencies. We also prove that reconfiguration sequences satisfying motion characteristics exist for any pair of configurations with seven or more modules (excluding linear topologies). Finally, comparisons with a modified BiRRT algorithm highlight the superior efficiency and stability of our approach, while deployment on a physical robotic platform confirms its practical feasibility.
LLA: Enhancing Security and Privacy for Generative Models with Logic-Locked Accelerators
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce LLA, an effective intellectual property (IP) protection scheme for generative AI models. LLA leverages the synergy between hardware and software to defend against various supply chain threats, including model theft, model corruption, and information leakage. On the software side, it embeds key bits into neurons that can trigger outliers to degrade performance and applies invariance transformations to obscure the key values. On the hardware side, it integrates a lightweight locking module into the AI accelerator while maintaining compatibility with various dataflow patterns and toolchains. An accelerator with a pre-stored secret key acts as a license to access the model services provided by the IP owner. The evaluation results show that LLA can withstand a broad range of oracle-guided key optimization attacks, while incurring a minimal computational overhead of less than 0.1% for 7,168 key bits.
Egocentric Instruction-oriented Affordance Prediction via Large Multimodal Model
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Affordance is crucial for intelligent robots in the context of object manipulation. In this paper, we argue that affordance should be task-/instruction-dependent, which is overlooked by many previous works. That is, different instructions can lead to different manipulation regions and directions even for the same object. According to this observation, we present a new dataset comprising fifteen thousand object-instruction-affordance triplets. All scenes in the dataset are from an egocentric viewpoint, designed to approximate the perspective of a human-like robot. Furthermore, we investigate how to enable large multimodal models (LMMs) to serve as affordance predictors by implementing a ``search against verifiers'' pipeline. An LMM is asked to progressively predict affordances, with the output at each step being verified by itself during the iterative process, imitating a reasoning process. Experiments show that our method not only unlocks new instruction-oriented affordance prediction capabilities, but also achieves outstanding performance broadly.
Stimulating Imagination: Towards General-purpose Object Rearrangement
Aug 03, 2024



Abstract:General-purpose object placement is a fundamental capability of an intelligent generalist robot, i.e., being capable of rearranging objects following human instructions even in novel environments. To achieve this, we break the rearrangement down into three parts, including object localization, goal imagination and robot control, and propose a framework named SPORT. SPORT leverages pre-trained large vision models for broad semantic reasoning about objects, and learns a diffusion-based 3D pose estimator to ensure physically-realistic results. Only object types (to be moved or reference) are communicated between these two parts, which brings two benefits. One is that we can fully leverage the powerful ability of open-set object localization and recognition since no specific fine-tuning is needed for robotic scenarios. Furthermore, the diffusion-based estimator only need to "imagine" the poses of the moving and reference objects after the placement, while no necessity for their semantic information. Thus the training burden is greatly reduced and no massive training is required. The training data for goal pose estimation is collected in simulation and annotated with GPT-4. A set of simulation and real-world experiments demonstrate the potential of our approach to accomplish general-purpose object rearrangement, placing various objects following precise instructions.
Tackling Missing Values in Probabilistic Wind Power Forecasting: A Generative Approach
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Machine learning techniques have been successfully used in probabilistic wind power forecasting. However, the issue of missing values within datasets due to sensor failure, for instance, has been overlooked for a long time. Although it is natural to consider addressing this issue by imputing missing values before model estimation and forecasting, we suggest treating missing values and forecasting targets indifferently and predicting all unknown values simultaneously based on observations. In this paper, we offer an efficient probabilistic forecasting approach by estimating the joint distribution of features and targets based on a generative model. It is free of preprocessing, and thus avoids introducing potential errors. Compared with the traditional "impute, then predict" pipeline, the proposed approach achieves better performance in terms of continuous ranked probability score.
Continuous and Distribution-free Probabilistic Wind Power Forecasting: A Conditional Normalizing Flow Approach
Jun 06, 2022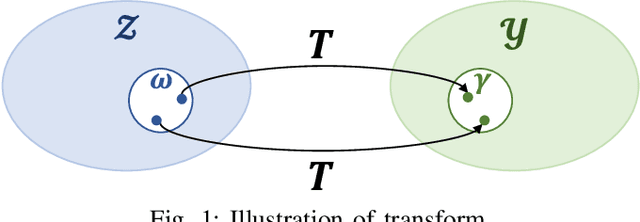
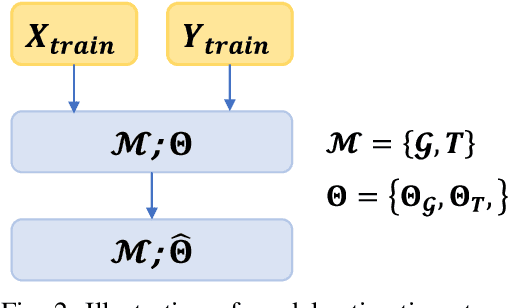
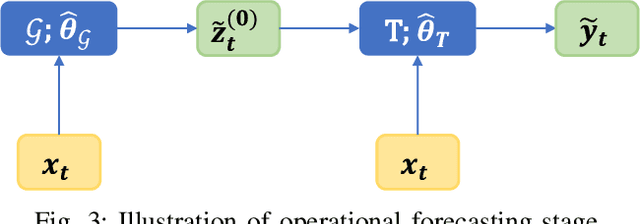
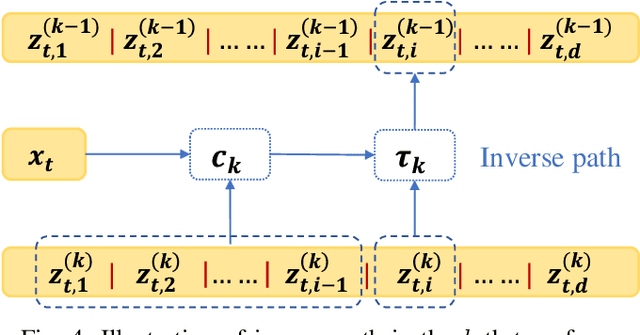
Abstract:We present a data-driven approach for probabilistic wind power forecasting based on conditional normalizing flow (CNF). In contrast with the existing, this approach is distribution-free (as for non-parametric and quantile-based approaches) and can directly yield continuous probability densities, hence avoiding quantile crossing. It relies on a base distribution and a set of bijective mappings. Both the shape parameters of the base distribution and the bijective mappings are approximated with neural networks. Spline-based conditional normalizing flow is considered owing to its non-affine characteristics. Over the training phase, the model sequentially maps input examples onto samples of base distribution, given the conditional contexts, where parameters are estimated through maximum likelihood. To issue probabilistic forecasts, one eventually maps samples of the base distribution into samples of a desired distribution. Case studies based on open datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed model, and allows us to discuss its advantages and caveats with respect to the state of the art.
Automated machine learning for secure key rate in discrete-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution
Jan 24, 2022
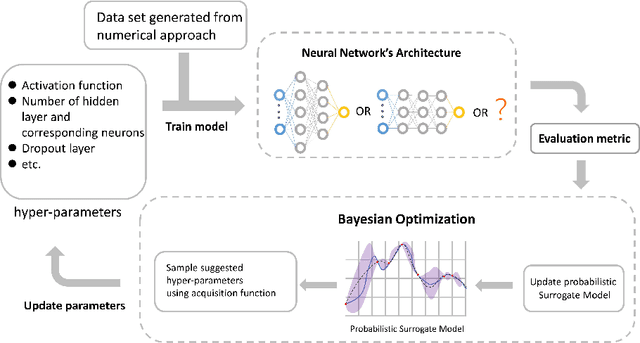
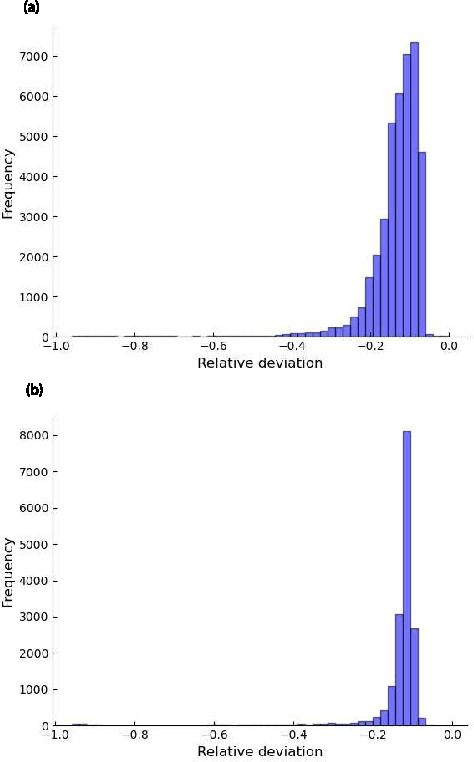
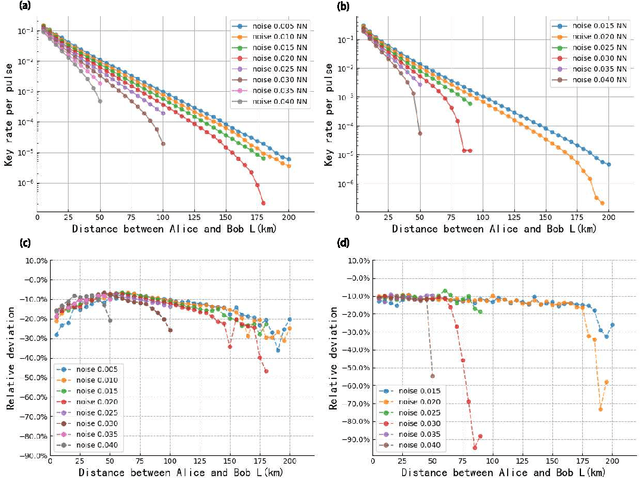
Abstract:Continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CV QKD) with discrete modulation has attracted increasing attention due to its experimental simplicity, lower-cost implementation and compatibility with classical optical communication. Correspondingly, some novel numerical methods have been proposed to analyze the security of these protocols against collective attacks, which promotes key rates over one hundred kilometers of fiber distance. However, numerical methods are limited by their calculation time and resource consumption, for which they cannot play more roles on mobile platforms in quantum networks. To improve this issue, a neural network model predicting key rates in nearly real time has been proposed previously. Here, we go further and show a neural network model combined with Bayesian optimization. This model automatically designs the best architecture of neural network computing key rates in real time. We demonstrate our model with two variants of CV QKD protocols with quaternary modulation. The results show high reliability with secure probability as high as $99.15\%-99.59\%$, considerable tightness and high efficiency with speedup of approximately $10^7$ in both cases. This inspiring model enables the real-time computation of unstructured quantum key distribution protocols' key rate more automatically and efficiently, which has met the growing needs of implementing QKD protocols on moving platforms.
Interest-oriented Universal User Representation via Contrastive Learning
Sep 18, 2021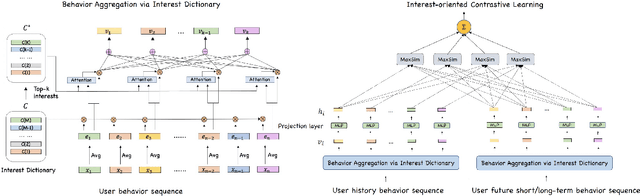
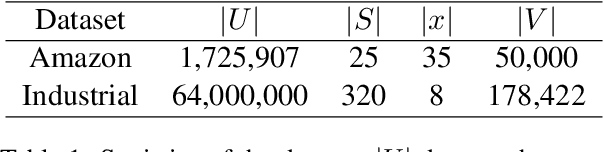
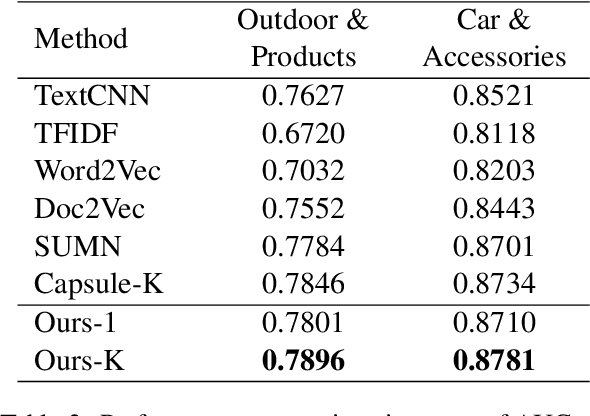
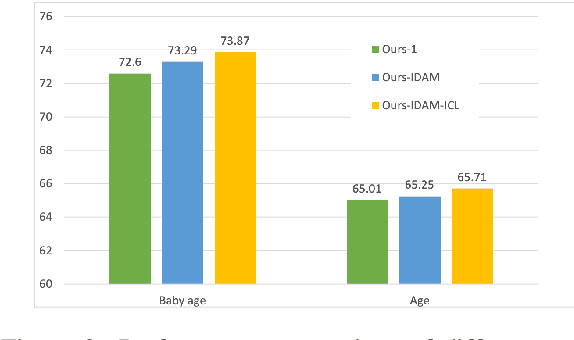
Abstract:User representation is essential for providing high-quality commercial services in industry. Universal user representation has received many interests recently, with which we can be free from the cumbersome work of training a specific model for each downstream application. In this paper, we attempt to improve universal user representation from two points of views. First, a contrastive self-supervised learning paradigm is presented to guide the representation model training. It provides a unified framework that allows for long-term or short-term interest representation learning in a data-driven manner. Moreover, a novel multi-interest extraction module is presented. The module introduces an interest dictionary to capture principal interests of the given user, and then generate his/her interest-oriented representations via behavior aggregation. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and applicability of the learned user representations.
Exploiting Behavioral Consistence for Universal User Representation
Dec 11, 2020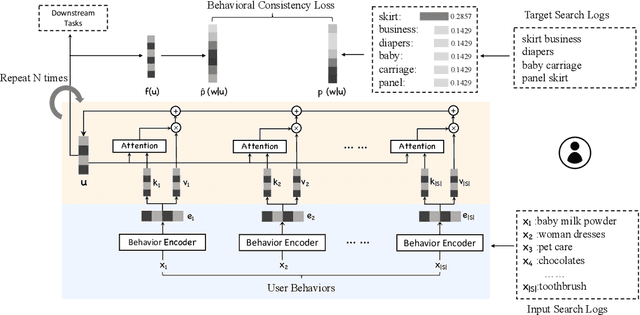
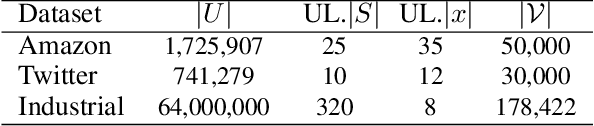
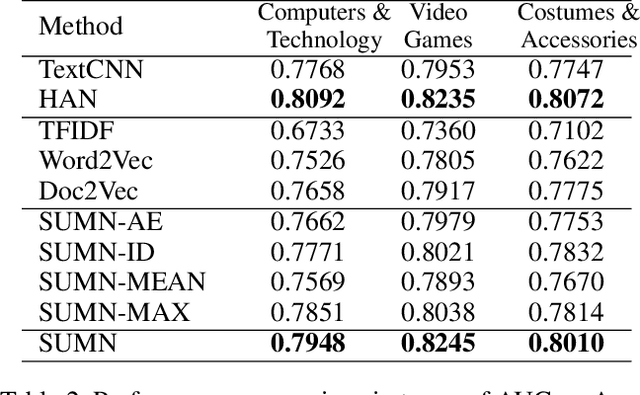
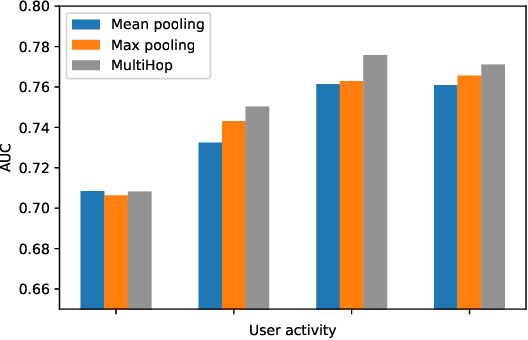
Abstract:User modeling is critical for developing personalized services in industry. A common way for user modeling is to learn user representations that can be distinguished by their interests or preferences. In this work, we focus on developing universal user representation model. The obtained universal representations are expected to contain rich information, and be applicable to various downstream applications without further modifications (e.g., user preference prediction and user profiling). Accordingly, we can be free from the heavy work of training task-specific models for every downstream task as in previous works. In specific, we propose Self-supervised User Modeling Network (SUMN) to encode behavior data into the universal representation. It includes two key components. The first one is a new learning objective, which guides the model to fully identify and preserve valuable user information under a self-supervised learning framework. The other one is a multi-hop aggregation layer, which benefits the model capacity in aggregating diverse behaviors. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets show that our approach can outperform state-of-the-art unsupervised representation methods, and even compete with supervised ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge