Robert Caiming Qiu
Source Localization and Power Estimation through RISs: Performance Analysis and Prototype Validations
Dec 12, 2025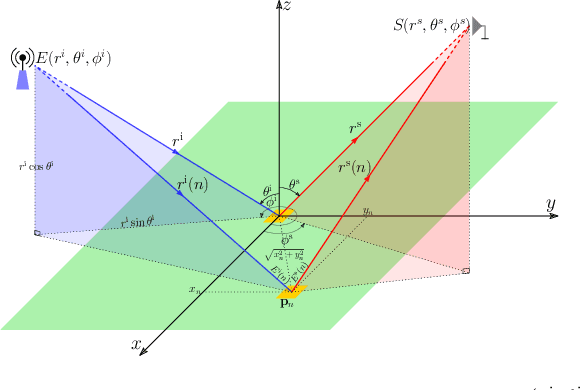
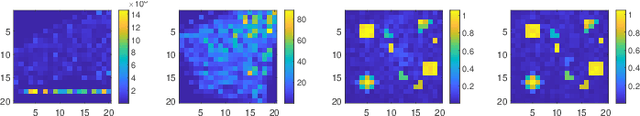
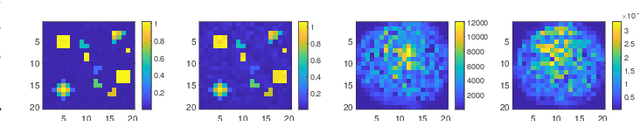
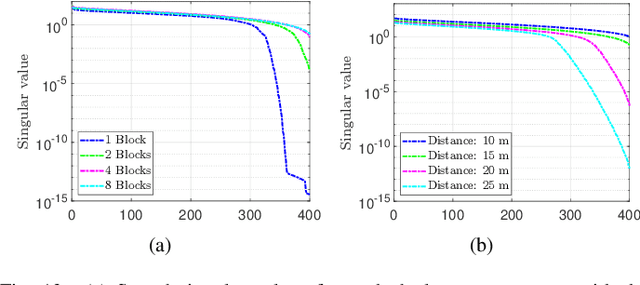
Abstract:This paper investigates the capabilities and effectiveness of backward localization centered on reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs). In the backward sensing paradigm, the region of interest (RoI) is illuminated using a set of diverse radiation patterns. These patterns encode spatial information into a sequence of measurements, which are subsequently processed to reconstruct the RoI. We show that a single RIS can estimate the direction of arrival of incident waves by leveraging configurational diversity, and that the spatial diversity provided by multiple RISs further improves the accuracy of source localization and power estimation. The underlying structure of the sensing operator in the multi-snapshot measurement process is clarified. For single-RIS localization, the sensing operator is decomposed into a product of structured matrices, each corresponding to a specific physical process: wave propagation to and from the RIS, the relative phase offsets of elements with respect to the reference point, and the applied phase configuration of each element. A unified framework for identifying key performance indicators is established by analyzing the conditioning of the sensing operators. In the multi-RIS setting, we derive--via rank analysis--the governing law among the RoI size, the number of elements, and the number of measurements. Upper bounds on the relative error of the least squares reconstruction algorithm are derived. These bounds clarify how key performance indicators affect estimation error and provide valuable guidance for system-level optimization. Numerical experiments confirm that the trend of the relative error is consistent with the theoretical bounds.
WiCAL: Accurate Wi-Fi-Based 3D Localization Enabled by Collaborative Antenna Arrays
May 27, 2025



Abstract:Accurate 3D localization is essential for realizing advanced sensing functionalities in next-generation Wi-Fi communication systems. This study investigates the potential of multistatic localization in Wi-Fi networks through the deployment of multiple cooperative antenna arrays. The collaborative gain offered by these arrays is twofold: (i) intra-array coherent gain at the wavelength scale among antenna elements, and (ii) inter-array cooperative gain across arrays. To evaluate the feasibility and performance of this approach, we develop WiCAL (Wi-Fi Collaborative Antenna Localization), a system built upon commercial Wi-Fi infrastructure equipped with uniform rectangular arrays. These arrays are driven by multiplexing embedded radio frequency chains available in standard access points or user devices, thereby eliminating the need for sophisticated, costly, and power-hungry multi-transceiver modules typically required in multiple-input and multiple-output systems. To address phase offsets introduced by RF chain multiplexing, we propose a three-stage, fine-grained phase alignment scheme to synchronize signals across antenna elements within each array. A bidirectional spatial smoothing MUSIC algorithm is employed to estimate angles of arrival (AoAs) and mitigate performance degradation caused by correlated interference. To further exploit inter-array cooperative gain, we elaborate on the synchronization mechanism among distributed URAs, which enables direct position determination by bypassing intermediate angle estimation. Once synchronized, the distributed URAs effectively form a virtual large-scale array, significantly enhancing spatial resolution and localization accuracy.
Swarm Antenna Arrays: From Deterministic to Stochastic Modeling
May 12, 2025Abstract:Swarm antenna arrays, composed of spatially distributed antennas mounted on unmanned agents, offer unprecedented flexibility and adaptability for wireless sensing and communication. However, their reconfigurable architecture, susceptibility to collisions, and inherently stochastic nature present significant challenges to realizing collaborative gain. It remains unclear how spatial coordination, positional perturbations, and large-scale topological configurations affect coherent signal aggregation and overall system performance. This paper investigates the feasibility of achieving coherent beamforming in such systems from both deterministic and stochastic perspectives. First, we develop a rigorous theoretical framework that characterizes the necessary and sufficient conditions for the emergence of grating lobes in multiple linear configurations. Notably, we show that for dual linear arrays, the classical half-wavelength spacing constraint can be safely relaxed without introducing spatial aliasing. This result challenges traditional array design principles and enables more flexible, collision-aware topologies. Second, we present a theoretical analysis, supported by empirical validation, demonstrating that coherent gain can be approximately preserved under realistic positional perturbations. Our results reveal that spatial perturbations introduce measurable degradation in the main lobe, an effect that cannot be mitigated merely by increasing the number of antennas. Instead, the primary benefit of scaling lies in reducing the variance of perturbation-induced fluctuations.
Group Sparsity Methods for Compressive Space-Frequency Channel Estimation and Spatial Equalization in Fluid Antenna System
Mar 03, 2025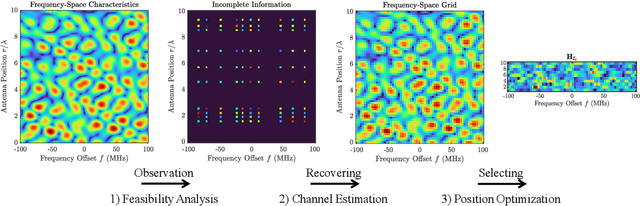



Abstract:Fluid Antenna System (FAS) unlocks unprecedented flexibility in wireless channel optimization through spatial reconfigurability. However, its practical deployment is hindered by the coupled challenges posed by high-dimensional channel estimation and real-time position optimization. This paper bridges wireless propagation physics with compressed sensing theory to address these challenges through three aspects. First, we establish a group-sparse recovery framework for space-frequency characteristics (SFC) in FAS, formally characterizing leakage-induced sparsity degradation from limited aperture and bandwidth as a structured group-sparsity problem. By deriving dictionary-adapted group restricted isometry property (D-GRIP), we prove tight recovery bounds for a convex $\ell_1/\ell_2$-mixed norm optimization formulation that preserves leakage-aware sparsity patterns. Second, we develop a Descending Correlation Group Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (DC-GOMP) algorithm that systematically relaxes leakage constraints to reduce subcoherence. This approach enables robust FSC recovery with accelerated convergence and superior performance compared to conventional compressive sensing methods like OMP or GOMP. Third, we formulate spatial equalization (SE) as a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) problem, ensuring optimality through the branch-and-bound method. To achieve real-time implementability while maintaining near-optimal performance, we complement this with a greedy algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate the proposed channel estimation algorithm effectively resolves energy misallocation and enables recovery of weak details, achieving superior recovery accuracy and convergence rate. The SE framework suppresses deep fading phenomena and reduces hardware deployment overhead while maintaining equivalent link reliability.
Fair Beam Synthesis and Suppression via Transmissive Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Nov 04, 2024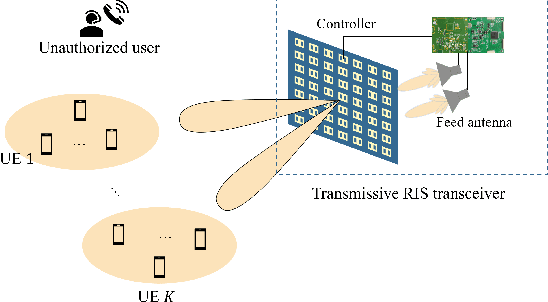
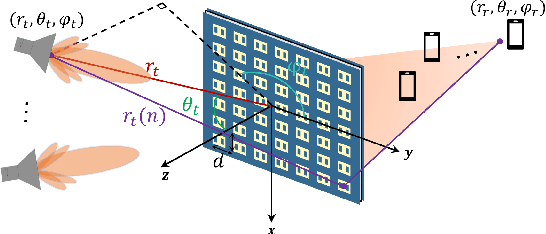
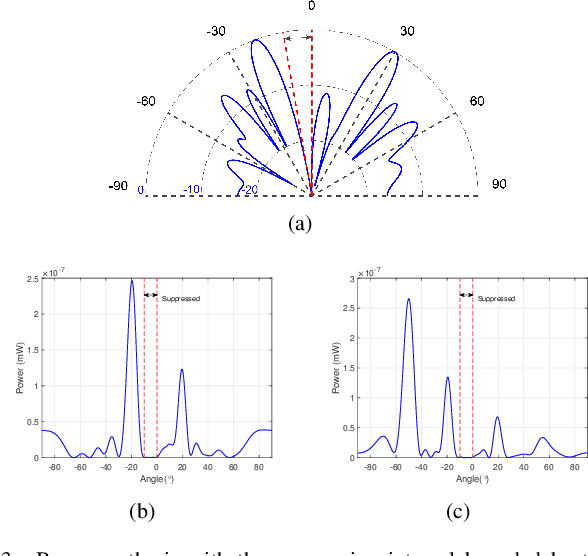
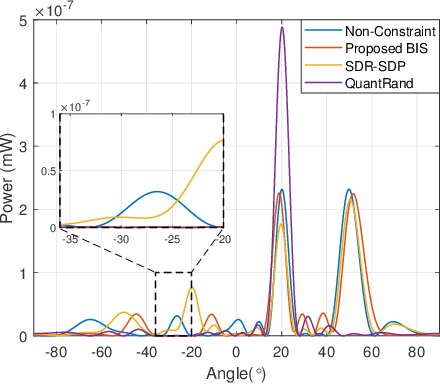
Abstract:Existing phase optimization methods in reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) face significant challenges in achieving flexible beam synthesis, especially for directional beam suppression. This paper introduces a Max-min criterion incorporating non-linear constraints, utilizing optimization techniques to enable multi-beam enhancement and suppression via transmissive RISs. A realistic model grounded in geometrical optics is first presented to characterize the input/output behavior of transmissive RIS, effectively linking explicit beam-forming operations with practical implementation. Subsequently, a highly efficient bisection-based algorithm for constrained Max-min optimization involving quadratic forms is developed, utilizing an auxiliary variable and Moreau envelope to iteratively reach the optimal solution. This approach demonstrates excellent extensibility and is applicable to a wide range of constrained Max-min problems. Numerical simulations validate the proposed methods, confirming that the framework enables beam enhancement or suppression at designated spatial positions.
PoseMamba: Monocular 3D Human Pose Estimation with Bidirectional Global-Local Spatio-Temporal State Space Model
Aug 07, 2024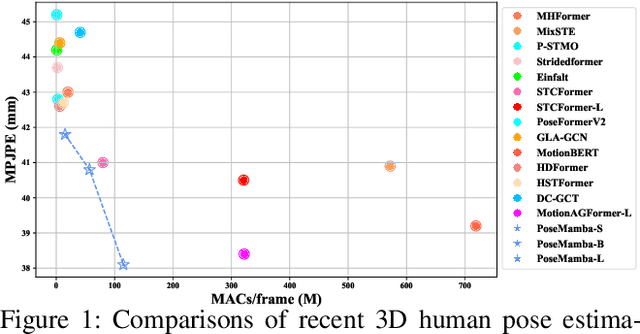

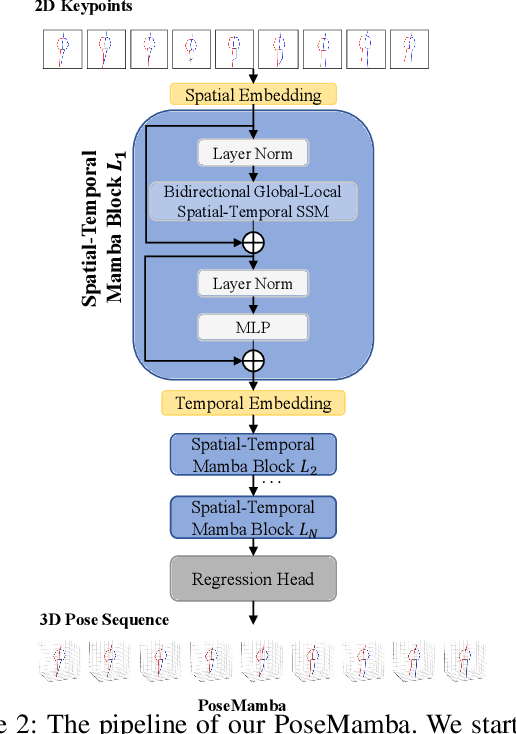

Abstract:Transformers have significantly advanced the field of 3D human pose estimation (HPE). However, existing transformer-based methods primarily use self-attention mechanisms for spatio-temporal modeling, leading to a quadratic complexity, unidirectional modeling of spatio-temporal relationships, and insufficient learning of spatial-temporal correlations. Recently, the Mamba architecture, utilizing the state space model (SSM), has exhibited superior long-range modeling capabilities in a variety of vision tasks with linear complexity. In this paper, we propose PoseMamba, a novel purely SSM-based approach with linear complexity for 3D human pose estimation in monocular video. Specifically, we propose a bidirectional global-local spatio-temporal SSM block that comprehensively models human joint relations within individual frames as well as temporal correlations across frames. Within this bidirectional global-local spatio-temporal SSM block, we introduce a reordering strategy to enhance the local modeling capability of the SSM. This strategy provides a more logical geometric scanning order and integrates it with the global SSM, resulting in a combined global-local spatial scan. We have quantitatively and qualitatively evaluated our approach using two benchmark datasets: Human3.6M and MPI-INF-3DHP. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PoseMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance on both datasets while maintaining a smaller model size and reducing computational costs. The code and models will be released.
TRGR: Transmissive RIS-aided Gait Recognition Through Walls
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Gait recognition with radio frequency (RF) signals enables many potential applications requiring accurate identification. However, current systems require individuals to be within a line-of-sight (LOS) environment and struggle with low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) when signals traverse concrete and thick walls. To address these challenges, we present TRGR, a novel transmissive reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided gait recognition system. TRGR can recognize human identities through walls using only the magnitude measurements of channel state information (CSI) from a pair of transceivers. Specifically, by leveraging transmissive RIS alongside a configuration alternating optimization algorithm, TRGR enhances wall penetration and signal quality, enabling accurate gait recognition. Furthermore, a residual convolution network (RCNN) is proposed as the backbone network to learn robust human information. Experimental results confirm the efficacy of transmissive RIS, highlighting the significant potential of transmissive RIS in enhancing RF-based gait recognition systems. Extensive experiment results show that TRGR achieves an average accuracy of 97.88\% in identifying persons when signals traverse concrete walls, demonstrating the effectiveness and robustness of TRGR.
Toward Wireless Localization Using Multiple Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Jul 30, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates the capabilities and effectiveness of backward sensing centered on reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs). We demonstrate that the direction of arrival (DoA) estimation of incident waves in the far-field regime can be accomplished using a single RIS by leveraging configurational diversity. Furthermore, we identify that the spatial diversity achieved through deploying multiple RISs enables accurate localization of multiple power sources. Physically accurate and mathematically concise models are introduced to characterize forward signal aggregations via RISs. By employing linearized approximations inherent in the far-field region, the measurement process for various configurations can be expressed as a system of linear equations. The mathematical essence of backward sensing lies in solving this system. A theoretical framework for determining key performance indicators is established through condition number analysis of the sensing operators. In the context of localization using multiple RISs, we examine relationships among the rank of sensing operators, the size of the region of interest (RoI), and the number of elements and measurements. For DoA estimations, we provide an upper bound for the relative error of the least squares reconstruction algorithm. These quantitative analyses offer essential insights for system design and optimization. Numerical experiments validate our findings. To demonstrate the practicality of our proposed RIS-centric sensing approach, we develop a proof-of-concept prototype using universal software radio peripherals (USRP) and employ a magnitude-only reconstruction algorithm tailored for this system. To our knowledge, this represents the first trial of its kind.
Dreamer: Dual-RIS-aided Imager in Complementary Modes
Jul 20, 2024Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have emerged as a promising auxiliary technology for radio frequency imaging. However, existing works face challenges of faint and intricate back-scattered waves and the restricted field-of-view (FoV), both resulting from complex target structures and a limited number of antennas. The synergistic benefits of multi-RIS-aided imaging hold promise for addressing these challenges. Here, we propose a dual-RIS-aided imaging system, Dreamer, which operates collaboratively in complementary modes (reflection-mode and transmission-mode). Dreamer significantly expands the FoV and enhances perception by deploying dual-RIS across various spatial and measurement patterns. Specifically, we perform a fine-grained analysis of how radio-frequency (RF) signals encode scene information in the scattered object modeling. Based on this modeling, we design illumination strategies to balance spatial resolution and observation scale, and implement a prototype system in a typical indoor environment. Moreover, we design a novel artificial neural network with a CNN-external-attention mechanism to translate RF signals into high-resolution images of human contours. Our approach achieves an impressive SSIM score exceeding 0.83, validating its effectiveness in broadening perception modes and enhancing imaging capabilities. The code to reproduce our results is available at https://github.com/fuhaiwang/Dreamer.
R-NeRF: Neural Radiance Fields for Modeling RIS-enabled Wireless Environments
May 19, 2024Abstract:Recently, ray tracing has gained renewed interest with the advent of Reflective Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) technology, a key enabler of 6G wireless communications due to its capability of intelligent manipulation of electromagnetic waves. However, accurately modeling RIS-enabled wireless environments poses significant challenges due to the complex variations caused by various environmental factors and the mobility of RISs. In this paper, we propose a novel modeling approach using Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to characterize the dynamics of electromagnetic fields in such environments. Our method utilizes NeRF-based ray tracing to intuitively capture and visualize the complex dynamics of signal propagation, effectively modeling the complete signal pathways from the transmitter to the RIS, and from the RIS to the receiver. This two-stage process accurately characterizes multiple complex transmission paths, enhancing our understanding of signal behavior in real-world scenarios. Our approach predicts the signal field for any specified RIS placement and receiver location, facilitating efficient RIS deployment. Experimental evaluations using both simulated and real-world data validate the significant benefits of our methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge