Chaoxu Guo
Hierarchical Masked 3D Diffusion Model for Video Outpainting
Sep 05, 2023
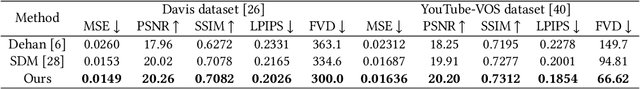
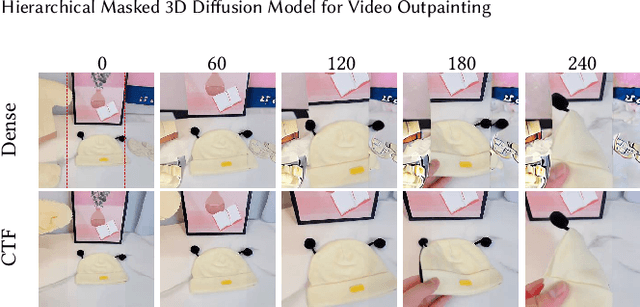
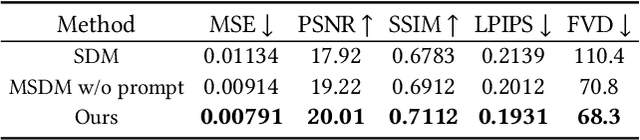
Abstract:Video outpainting aims to adequately complete missing areas at the edges of video frames. Compared to image outpainting, it presents an additional challenge as the model should maintain the temporal consistency of the filled area. In this paper, we introduce a masked 3D diffusion model for video outpainting. We use the technique of mask modeling to train the 3D diffusion model. This allows us to use multiple guide frames to connect the results of multiple video clip inferences, thus ensuring temporal consistency and reducing jitter between adjacent frames. Meanwhile, we extract the global frames of the video as prompts and guide the model to obtain information other than the current video clip using cross-attention. We also introduce a hybrid coarse-to-fine inference pipeline to alleviate the artifact accumulation problem. The existing coarse-to-fine pipeline only uses the infilling strategy, which brings degradation because the time interval of the sparse frames is too large. Our pipeline benefits from bidirectional learning of the mask modeling and thus can employ a hybrid strategy of infilling and interpolation when generating sparse frames. Experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in video outpainting tasks. More results are provided at our https://fanfanda.github.io/M3DDM/.
PV-RCNN++: Point-Voxel Feature Set Abstraction With Local Vector Representation for 3D Object Detection
Jan 31, 2021



Abstract:3D object detection is receiving increasing attention from both industry and academia thanks to its wide applications in various fields. In this paper, we propose the Point-Voxel Region based Convolution Neural Networks (PV-RCNNs) for accurate 3D detection from point clouds. First, we propose a novel 3D object detector, PV-RCNN-v1, which employs the voxel-to-keypoint scene encoding and keypoint-to-grid RoI feature abstraction two novel steps. These two steps deeply incorporate both 3D voxel CNN and PointNet-based set abstraction for learning discriminative point-cloud features. Second, we propose a more advanced framework, PV-RCNN-v2, for more efficient and accurate 3D detection. It consists of two major improvements, where the first one is the sectorized proposal-centric strategy for efficiently producing more representative and uniformly distributed keypoints, and the second one is the VectorPool aggregation to replace set abstraction for better aggregating local point-cloud features with much less resource consumption. With these two major modifications, our PV-RCNN-v2 runs more than twice as fast as the v1 version while still achieving better performance on the large-scale Waymo Open Dataset with 150m * 150m detection range. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed PV-RCNNs significantly outperform previous state-of-the-art 3D detection methods on both the Waymo Open Dataset and the highly-competitive KITTI benchmark.
PV-RCNN: The Top-Performing LiDAR-only Solutions for 3D Detection / 3D Tracking / Domain Adaptation of Waymo Open Dataset Challenges
Aug 28, 2020



Abstract:In this technical report, we present the top-performing LiDAR-only solutions for 3D detection, 3D tracking and domain adaptation three tracks in Waymo Open Dataset Challenges 2020. Our solutions for the competition are built upon our recent proposed PV-RCNN 3D object detection framework. Several variants of our PV-RCNN are explored, including temporal information incorporation, dynamic voxelization, adaptive training sample selection, classification with RoI features, etc. A simple model ensemble strategy with non-maximum-suppression and box voting is adopted to generate the final results. By using only LiDAR point cloud data, our models finally achieve the 1st place among all LiDAR-only methods, and the 2nd place among all multi-modal methods, on the 3D Detection, 3D Tracking and Domain Adaptation three tracks of Waymo Open Dataset Challenges. Our solutions will be available at https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet
PV-RCNN: Point-Voxel Feature Set Abstraction for 3D Object Detection
Dec 31, 2019



Abstract:We present a novel and high-performance 3D object detection framework, named PointVoxel-RCNN (PV-RCNN), for accurate 3D object detection from point clouds. Our proposed method deeply integrates both 3D voxel Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and PointNet-based set abstraction to learn more discriminative point cloud features. It takes advantages of efficient learning and high-quality proposals of the 3D voxel CNN and the flexible receptive fields of the PointNet-based networks. Specifically, the proposed framework summarizes the 3D scene with a 3D voxel CNN into a small set of keypoints via a novel voxel set abstraction module to save follow-up computations and also to encode representative scene features. Given the high-quality 3D proposals generated by the voxel CNN, the RoI-grid pooling is proposed to abstract proposal-specific features from the keypoints to the RoI-grid points via keypoint set abstraction with multiple receptive fields. Compared with conventional pooling operations, the RoI-grid feature points encode much richer context information for accurately estimating object confidences and locations. Extensive experiments on both the KITTI dataset and the Waymo Open dataset show that our proposed PV-RCNN surpasses state-of-the-art 3D detection methods with remarkable margins by using only point clouds.
AugFPN: Improving Multi-scale Feature Learning for Object Detection
Dec 11, 2019



Abstract:Current state-of-the-art detectors typically exploit feature pyramid to detect objects at different scales. Among them, FPN is one of the representative works that build a feature pyramid by multi-scale features summation. However, the design defects behind prevent the multi-scale features from being fully exploited. In this paper, we begin by first analyzing the design defects of feature pyramid in FPN, and then introduce a new feature pyramid architecture named AugFPN to address these problems. Specifically, AugFPN consists of three components: Consistent Supervision, Residual Feature Augmentation, and Soft RoI Selection. AugFPN narrows the semantic gaps between features of different scales before feature fusion through Consistent Supervision. In feature fusion, ratio-invariant context information is extracted by Residual Feature Augmentation to reduce the information loss of feature map at the highest pyramid level. Finally, Soft RoI Selection is employed to learn a better RoI feature adaptively after feature fusion. By replacing FPN with AugFPN in Faster R-CNN, our models achieve 2.3 and 1.6 points higher Average Precision (AP) when using ResNet50 and MobileNet-v2 as backbone respectively. Furthermore, AugFPN improves RetinaNet by 1.6 points AP and FCOS by 0.9 points AP when using ResNet50 as backbone. Codes will be made available.
Exploiting Offset-guided Network for Pose Estimation and Tracking
Jun 04, 2019



Abstract:Human pose estimation has witnessed a significant advance thanks to the development of deep learning. Recent human pose estimation approaches tend to directly predict the location heatmaps, which causes quantization errors and inevitably deteriorates the performance within the reduced network output. Aim at solving it, we revisit the heatmap-offset aggregation method and propose the Offset-guided Network (OGN) with an intuitive but effective fusion strategy for both two-stages pose estimation and Mask R-CNN. For two-stages pose estimation, a greedy box generation strategy is also proposed to keep more necessary candidates while performing person detection. For mask R-CNN, ratio-consistent is adopted to improve the generalization ability of the network. State-of-the-art results on COCO and PoseTrack dataset verify the effectiveness of our offset-guided pose estimation and tracking.
Progressive Sparse Local Attention for Video object detection
Mar 25, 2019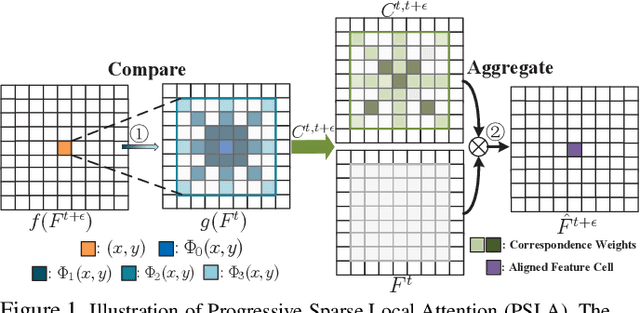
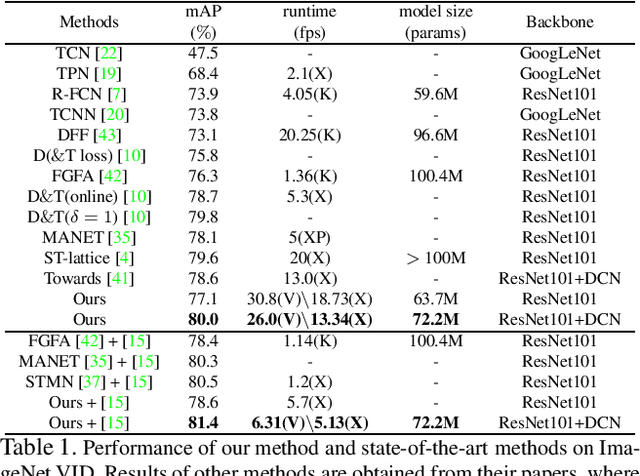
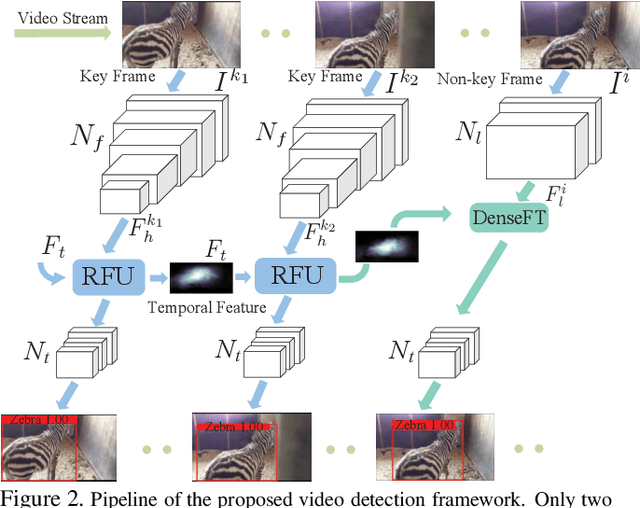
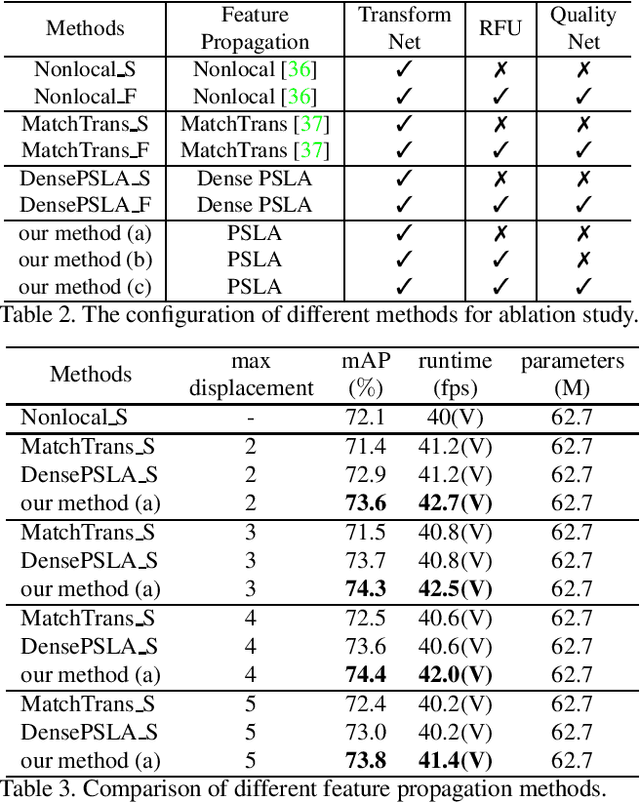
Abstract:Transferring image-based object detectors to the domain of videos remains a challenging problem. Previous efforts mostly exploit optical flow to propagate features across frames, aiming to achieve a good trade-off between accuracy and efficiency. However, introducing an extra model to estimate optical flow would significantly increase the overall model size. The gap between optical flow and high-level features can also hinder it from establishing spatial correspondence accurately. Instead of relying on optical flow, this paper proposes a novel module called Progressive Sparse Local Attention (PSLA), which establishes the spatial correspondence between features across frames in a local region with progressive sparser stride and uses the correspondence to propagate features. Based on PSLA, Recursive Feature Updating (RFU) and Dense Feature Transforming (DFT) are proposed to model temporal appearance and enrich feature representation respectively in a novel video object detection framework. Experiments on ImageNet VID show that our method achieves the best accuracy compared to existing methods with smaller model size and acceptable runtime speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge