Jiaqi Guan
Integrating Protein Dynamics into Structure-Based Drug Design via Full-Atom Stochastic Flows
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:The dynamic nature of proteins, influenced by ligand interactions, is essential for comprehending protein function and progressing drug discovery. Traditional structure-based drug design (SBDD) approaches typically target binding sites with rigid structures, limiting their practical application in drug development. While molecular dynamics simulation can theoretically capture all the biologically relevant conformations, the transition rate is dictated by the intrinsic energy barrier between them, making the sampling process computationally expensive. To overcome the aforementioned challenges, we propose to use generative modeling for SBDD considering conformational changes of protein pockets. We curate a dataset of apo and multiple holo states of protein-ligand complexes, simulated by molecular dynamics, and propose a full-atom flow model (and a stochastic version), named DynamicFlow, that learns to transform apo pockets and noisy ligands into holo pockets and corresponding 3D ligand molecules. Our method uncovers promising ligand molecules and corresponding holo conformations of pockets. Additionally, the resultant holo-like states provide superior inputs for traditional SBDD approaches, playing a significant role in practical drug discovery.
Group Ligands Docking to Protein Pockets
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Molecular docking is a key task in computational biology that has attracted increasing interest from the machine learning community. While existing methods have achieved success, they generally treat each protein-ligand pair in isolation. Inspired by the biochemical observation that ligands binding to the same target protein tend to adopt similar poses, we propose \textsc{GroupBind}, a novel molecular docking framework that simultaneously considers multiple ligands docking to a protein. This is achieved by introducing an interaction layer for the group of ligands and a triangle attention module for embedding protein-ligand and group-ligand pairs. By integrating our approach with diffusion-based docking model, we set a new S performance on the PDBBind blind docking benchmark, demonstrating the effectiveness of our proposed molecular docking paradigm.
Hotspot-Driven Peptide Design via Multi-Fragment Autoregressive Extension
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Peptides, short chains of amino acids, interact with target proteins, making them a unique class of protein-based therapeutics for treating human diseases. Recently, deep generative models have shown great promise in peptide generation. However, several challenges remain in designing effective peptide binders. First, not all residues contribute equally to peptide-target interactions. Second, the generated peptides must adopt valid geometries due to the constraints of peptide bonds. Third, realistic tasks for peptide drug development are still lacking. To address these challenges, we introduce PepHAR, a hot-spot-driven autoregressive generative model for designing peptides targeting specific proteins. Building on the observation that certain hot spot residues have higher interaction potentials, we first use an energy-based density model to fit and sample these key residues. Next, to ensure proper peptide geometry, we autoregressively extend peptide fragments by estimating dihedral angles between residue frames. Finally, we apply an optimization process to iteratively refine fragment assembly, ensuring correct peptide structures. By combining hot spot sampling with fragment-based extension, our approach enables de novo peptide design tailored to a target protein and allows the incorporation of key hot spot residues into peptide scaffolds. Extensive experiments, including peptide design and peptide scaffold generation, demonstrate the strong potential of PepHAR in computational peptide binder design.
Reprogramming Pretrained Target-Specific Diffusion Models for Dual-Target Drug Design
Oct 28, 2024


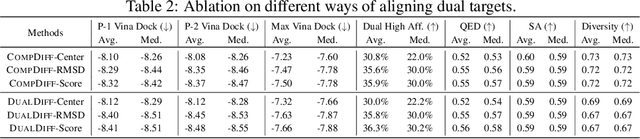
Abstract:Dual-target therapeutic strategies have become a compelling approach and attracted significant attention due to various benefits, such as their potential in overcoming drug resistance in cancer therapy. Considering the tremendous success that deep generative models have achieved in structure-based drug design in recent years, we formulate dual-target drug design as a generative task and curate a novel dataset of potential target pairs based on synergistic drug combinations. We propose to design dual-target drugs with diffusion models that are trained on single-target protein-ligand complex pairs. Specifically, we align two pockets in 3D space with protein-ligand binding priors and build two complex graphs with shared ligand nodes for SE(3)-equivariant composed message passing, based on which we derive a composed drift in both 3D and categorical probability space in the generative process. Our algorithm can well transfer the knowledge gained in single-target pretraining to dual-target scenarios in a zero-shot manner. We also repurpose linker design methods as strong baselines for this task. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method compared with various baselines.
MolDiff: Addressing the Atom-Bond Inconsistency Problem in 3D Molecule Diffusion Generation
May 11, 2023Abstract:Deep generative models have recently achieved superior performance in 3D molecule generation. Most of them first generate atoms and then add chemical bonds based on the generated atoms in a post-processing manner. However, there might be no corresponding bond solution for the temporally generated atoms as their locations are generated without considering potential bonds. We define this problem as the atom-bond inconsistency problem and claim it is the main reason for current approaches to generating unrealistic 3D molecules. To overcome this problem, we propose a new diffusion model called MolDiff which can generate atoms and bonds simultaneously while still maintaining their consistency by explicitly modeling the dependence between their relationships. We evaluated the generation ability of our proposed model and the quality of the generated molecules using criteria related to both geometry and chemical properties. The empirical studies showed that our model outperforms previous approaches, achieving a three-fold improvement in success rate and generating molecules with significantly better quality.
3D Equivariant Diffusion for Target-Aware Molecule Generation and Affinity Prediction
Mar 06, 2023



Abstract:Rich data and powerful machine learning models allow us to design drugs for a specific protein target \textit{in silico}. Recently, the inclusion of 3D structures during targeted drug design shows superior performance to other target-free models as the atomic interaction in the 3D space is explicitly modeled. However, current 3D target-aware models either rely on the voxelized atom densities or the autoregressive sampling process, which are not equivariant to rotation or easily violate geometric constraints resulting in unrealistic structures. In this work, we develop a 3D equivariant diffusion model to solve the above challenges. To achieve target-aware molecule design, our method learns a joint generative process of both continuous atom coordinates and categorical atom types with a SE(3)-equivariant network. Moreover, we show that our model can serve as an unsupervised feature extractor to estimate the binding affinity under proper parameterization, which provides an effective way for drug screening. To evaluate our model, we propose a comprehensive framework to evaluate the quality of sampled molecules from different dimensions. Empirical studies show our model could generate molecules with more realistic 3D structures and better affinities towards the protein targets, and improve binding affinity ranking and prediction without retraining.
Pocket2Mol: Efficient Molecular Sampling Based on 3D Protein Pockets
May 15, 2022



Abstract:Deep generative models have achieved tremendous success in designing novel drug molecules in recent years. A new thread of works have shown the great potential in advancing the specificity and success rate of in silico drug design by considering the structure of protein pockets. This setting posts fundamental computational challenges in sampling new chemical compounds that could satisfy multiple geometrical constraints imposed by pockets. Previous sampling algorithms either sample in the graph space or only consider the 3D coordinates of atoms while ignoring other detailed chemical structures such as bond types and functional groups. To address the challenge, we develop Pocket2Mol, an E(3)-equivariant generative network composed of two modules: 1) a new graph neural network capturing both spatial and bonding relationships between atoms of the binding pockets and 2) a new efficient algorithm which samples new drug candidates conditioned on the pocket representations from a tractable distribution without relying on MCMC. Experimental results demonstrate that molecules sampled from Pocket2Mol achieve significantly better binding affinity and other drug properties such as druglikeness and synthetic accessibility.
Equivariant Point Cloud Analysis via Learning Orientations for Message Passing
Mar 28, 2022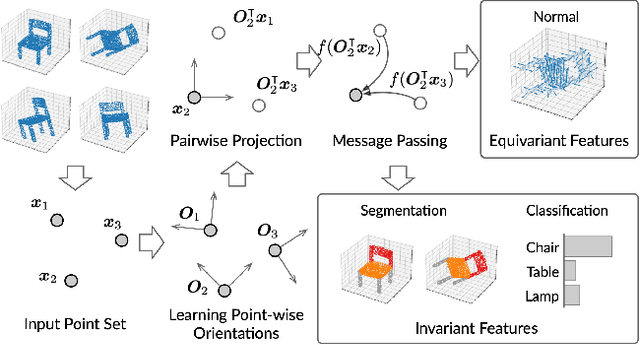
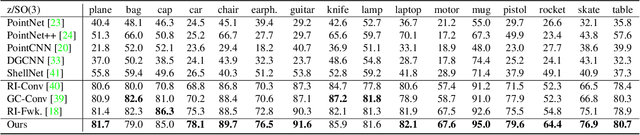
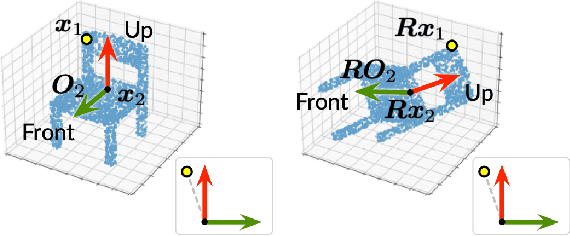
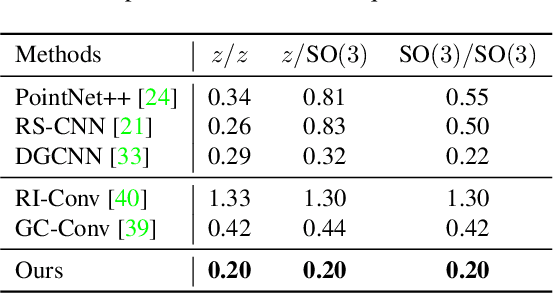
Abstract:Equivariance has been a long-standing concern in various fields ranging from computer vision to physical modeling. Most previous methods struggle with generality, simplicity, and expressiveness -- some are designed ad hoc for specific data types, some are too complex to be accessible, and some sacrifice flexible transformations. In this work, we propose a novel and simple framework to achieve equivariance for point cloud analysis based on the message passing (graph neural network) scheme. We find the equivariant property could be obtained by introducing an orientation for each point to decouple the relative position for each point from the global pose of the entire point cloud. Therefore, we extend current message passing networks with a module that learns orientations for each point. Before aggregating information from the neighbors of a point, the networks transforms the neighbors' coordinates based on the point's learned orientations. We provide formal proofs to show the equivariance of the proposed framework. Empirically, we demonstrate that our proposed method is competitive on both point cloud analysis and physical modeling tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/luost26/Equivariant-OrientedMP .
A 3D Molecule Generative Model for Structure-Based Drug Design
Mar 20, 2022



Abstract:We study a fundamental problem in structure-based drug design -- generating molecules that bind to specific protein binding sites. While we have witnessed the great success of deep generative models in drug design, the existing methods are mostly string-based or graph-based. They are limited by the lack of spatial information and thus unable to be applied to structure-based design tasks. Particularly, such models have no or little knowledge of how molecules interact with their target proteins exactly in 3D space. In this paper, we propose a 3D generative model that generates molecules given a designated 3D protein binding site. Specifically, given a binding site as the 3D context, our model estimates the probability density of atom's occurrences in 3D space -- positions that are more likely to have atoms will be assigned higher probability. To generate 3D molecules, we propose an auto-regressive sampling scheme -- atoms are sampled sequentially from the learned distribution until there is no room for new atoms. Combined with this sampling scheme, our model can generate valid and diverse molecules, which could be applicable to various structure-based molecular design tasks such as molecule sampling and linker design. Experimental results demonstrate that molecules sampled from our model exhibit high binding affinity to specific targets and good drug properties such as drug-likeness even if the model is not explicitly optimized for them.
Directed Weight Neural Networks for Protein Structure Representation Learning
Jan 28, 2022



Abstract:A protein performs biological functions by folding to a particular 3D structure. To accurately model the protein structures, both the overall geometric topology and local fine-grained relations between amino acids (e.g. side-chain torsion angles and inter-amino-acid orientations) should be carefully considered. In this work, we propose the Directed Weight Neural Network for better capturing geometric relations among different amino acids. Extending a single weight from a scalar to a 3D directed vector, our new framework supports a rich set of geometric operations on both classical and SO(3)--representation features, on top of which we construct a perceptron unit for processing amino-acid information. In addition, we introduce an equivariant message passing paradigm on proteins for plugging the directed weight perceptrons into existing Graph Neural Networks, showing superior versatility in maintaining SO(3)-equivariance at the global scale. Experiments show that our network has remarkably better expressiveness in representing geometric relations in comparison to classical neural networks and the (globally) equivariant networks. It also achieves state-of-the-art performance on various computational biology applications related to protein 3D structures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge