Jane Wu
PBDyG: Position Based Dynamic Gaussians for Motion-Aware Clothed Human Avatars
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel clothed human model that can be learned from multiview RGB videos, with a particular emphasis on recovering physically accurate body and cloth movements. Our method, Position Based Dynamic Gaussians (PBDyG), realizes ``movement-dependent'' cloth deformation via physical simulation, rather than merely relying on ``pose-dependent'' rigid transformations. We model the clothed human holistically but with two distinct physical entities in contact: clothing modeled as 3D Gaussians, which are attached to a skinned SMPL body that follows the movement of the person in the input videos. The articulation of the SMPL body also drives physically-based simulation of the clothes' Gaussians to transform the avatar to novel poses. In order to run position based dynamics simulation, physical properties including mass and material stiffness are estimated from the RGB videos through Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting. Experiments demonstrate that our method not only accurately reproduces appearance but also enables the reconstruction of avatars wearing highly deformable garments, such as skirts or coats, which have been challenging to reconstruct using existing methods.
Hand-Object Interaction Pretraining from Videos
Sep 12, 2024
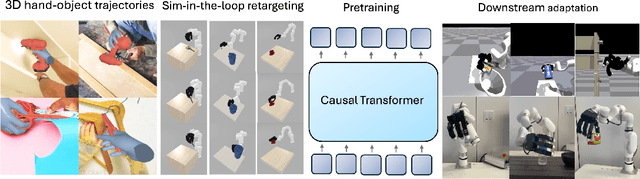

Abstract:We present an approach to learn general robot manipulation priors from 3D hand-object interaction trajectories. We build a framework to use in-the-wild videos to generate sensorimotor robot trajectories. We do so by lifting both the human hand and the manipulated object in a shared 3D space and retargeting human motions to robot actions. Generative modeling on this data gives us a task-agnostic base policy. This policy captures a general yet flexible manipulation prior. We empirically demonstrate that finetuning this policy, with both reinforcement learning (RL) and behavior cloning (BC), enables sample-efficient adaptation to downstream tasks and simultaneously improves robustness and generalizability compared to prior approaches. Qualitative experiments are available at: \url{https://hgaurav2k.github.io/hop/}.
Reconstructing Hand-Held Objects in 3D
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:Objects manipulated by the hand (i.e., manipulanda) are particularly challenging to reconstruct from in-the-wild RGB images or videos. Not only does the hand occlude much of the object, but also the object is often only visible in a small number of image pixels. At the same time, two strong anchors emerge in this setting: (1) estimated 3D hands help disambiguate the location and scale of the object, and (2) the set of manipulanda is small relative to all possible objects. With these insights in mind, we present a scalable paradigm for handheld object reconstruction that builds on recent breakthroughs in large language/vision models and 3D object datasets. Our model, MCC-Hand-Object (MCC-HO), jointly reconstructs hand and object geometry given a single RGB image and inferred 3D hand as inputs. Subsequently, we use GPT-4(V) to retrieve a 3D object model that matches the object in the image and rigidly align the model to the network-inferred geometry; we call this alignment Retrieval-Augmented Reconstruction (RAR). Experiments demonstrate that MCC-HO achieves state-of-the-art performance on lab and Internet datasets, and we show how RAR can be used to automatically obtain 3D labels for in-the-wild images of hand-object interactions.
Inpaint3D: 3D Scene Content Generation using 2D Inpainting Diffusion
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to inpainting 3D regions of a scene, given masked multi-view images, by distilling a 2D diffusion model into a learned 3D scene representation (e.g. a NeRF). Unlike 3D generative methods that explicitly condition the diffusion model on camera pose or multi-view information, our diffusion model is conditioned only on a single masked 2D image. Nevertheless, we show that this 2D diffusion model can still serve as a generative prior in a 3D multi-view reconstruction problem where we optimize a NeRF using a combination of score distillation sampling and NeRF reconstruction losses. Predicted depth is used as additional supervision to encourage accurate geometry. We compare our approach to 3D inpainting methods that focus on object removal. Because our method can generate content to fill any 3D masked region, we additionally demonstrate 3D object completion, 3D object replacement, and 3D scene completion.
Weakly-Supervised 3D Reconstruction of Clothed Humans via Normal Maps
Nov 27, 2023



Abstract:We present a novel deep learning-based approach to the 3D reconstruction of clothed humans using weak supervision via 2D normal maps. Given a single RGB image or multiview images, our network infers a signed distance function (SDF) discretized on a tetrahedral mesh surrounding the body in a rest pose. Subsequently, inferred pose and camera parameters are used to generate a normal map from the SDF. A key aspect of our approach is the use of Marching Tetrahedra to (uniquely) compute a triangulated surface from the SDF on the tetrahedral mesh, facilitating straightforward differentiation (and thus backpropagation). Thus, given only ground truth normal maps (with no volumetric information ground truth information), we can train the network to produce SDF values from corresponding RGB images. Optionally, an additional multiview loss leads to improved results. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach for both network inference and 3D reconstruction.
HazardNet: Road Debris Detection by Augmentation of Synthetic Models
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:We present an algorithm to detect unseen road debris using a small set of synthetic models. Early detection of road debris is critical for safe autonomous or assisted driving, yet the development of a robust road debris detection model has not been widely discussed. There are two main challenges to building a road debris detector: first, data collection of road debris is challenging since hazardous objects on the road are rare to encounter in real driving scenarios; second, the variability of road debris is broad, ranging from a very small brick to a large fallen tree. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel approach to few-shot learning of road debris that uses semantic augmentation and domain randomization to augment real road images with synthetic models. We constrain the problem domain to uncommon objects on the road and allow the deep neural network, HazardNet, to learn the semantic meaning of road debris to eventually detect unseen road debris. Our results demonstrate that HazardNet is able to accurately detect real road debris when only trained on synthetic objects in augmented images.
Skinning a Parameterization of Three-Dimensional Space for Neural Network Cloth
Jun 08, 2020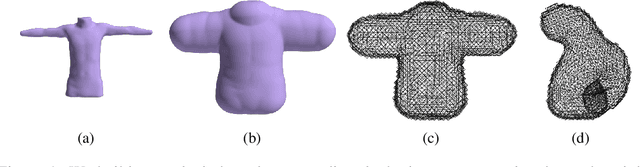

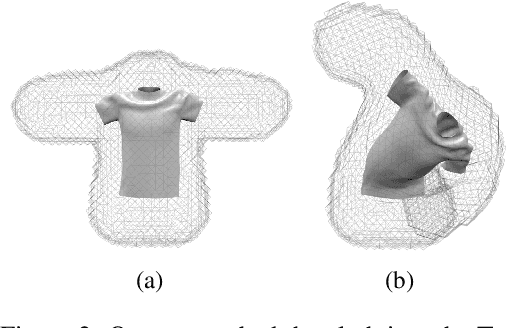
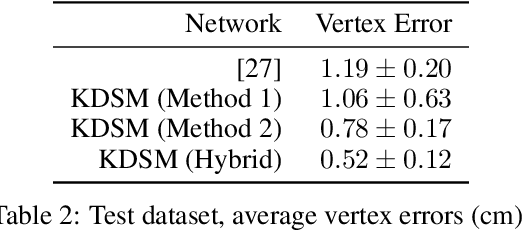
Abstract:We present a novel learning framework for cloth deformation by embedding virtual cloth into a tetrahedral mesh that parametrizes the volumetric region of air surrounding the underlying body. In order to maintain this volumetric parameterization during character animation, the tetrahedral mesh is constrained to follow the body surface as it deforms. We embed the cloth mesh vertices into this parameterization of three-dimensional space in order to automatically capture much of the nonlinear deformation due to both joint rotations and collisions. We then train a convolutional neural network to recover ground truth deformation by learning cloth embedding offsets for each skeletal pose. Our experiments show significant improvement over learning cloth offsets from body surface parameterizations, both quantitatively and visually, with prior state of the art having a mean error five standard deviations higher than ours. Moreover, our results demonstrate the efficacy of a general learning paradigm where high-frequency details can be embedded into low-frequency parameterizations.
Recovering Geometric Information with Learned Texture Perturbations
Jan 20, 2020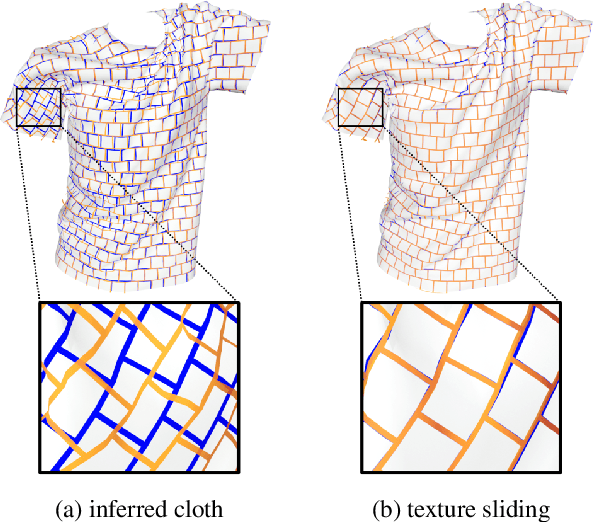
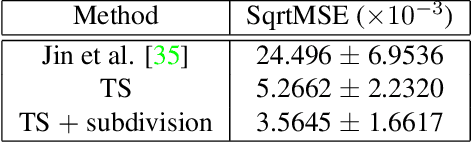
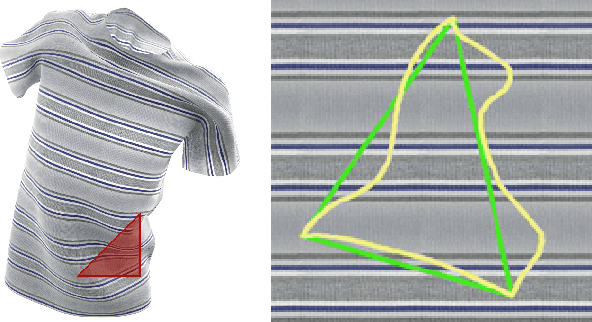
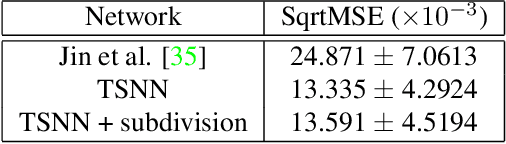
Abstract:Regularization is used to avoid overfitting when training a neural network; unfortunately, this reduces the attainable level of detail hindering the ability to capture high-frequency information present in the training data. Even though various approaches may be used to re-introduce high-frequency detail, it typically does not match the training data and is often not time coherent. In the case of network inferred cloth, these sentiments manifest themselves via either a lack of detailed wrinkles or unnaturally appearing and/or time incoherent surrogate wrinkles. Thus, we propose a general strategy whereby high-frequency information is procedurally embedded into low-frequency data so that when the latter is smeared out by the network the former still retains its high-frequency detail. We illustrate this approach by learning texture coordinates which when smeared do not in turn smear out the high-frequency detail in the texture itself but merely smoothly distort it. Notably, we prescribe perturbed texture coordinates that are subsequently used to correct the over-smoothed appearance of inferred cloth, and correcting the appearance from multiple camera views naturally recovers lost geometric information.
Deep Energies for Estimating Three-Dimensional Facial Pose and Expression
Dec 07, 2018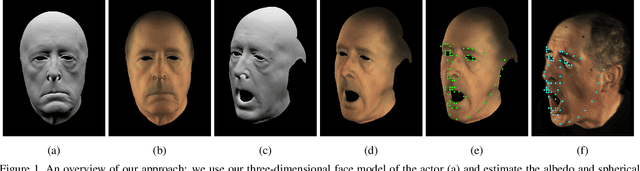
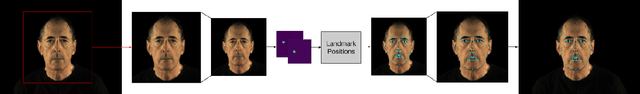

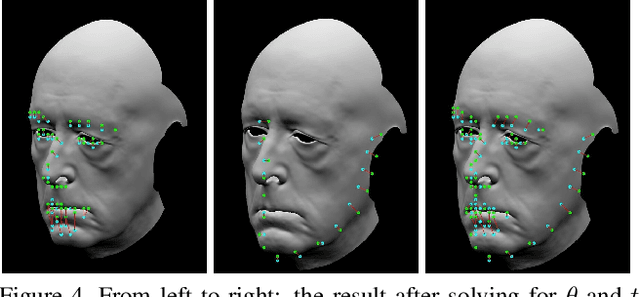
Abstract:While much progress has been made in capturing high-quality facial performances using motion capture markers and shape-from-shading, high-end systems typically also rely on rotoscope curves hand-drawn on the image. These curves are subjective and difficult to draw consistently; moreover, ad-hoc procedural methods are required for generating matching rotoscope curves on synthetic renders embedded in the optimization used to determine three-dimensional facial pose and expression. We propose an alternative approach whereby these curves and other keypoints are detected automatically on both the image and the synthetic renders using trained neural networks, eliminating artist subjectivity and the ad-hoc procedures meant to mimic it. More generally, we propose using machine learning networks to implicitly define deep energies which when minimized using classical optimization techniques lead to three-dimensional facial pose and expression estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge