Ivana Išgum
Neural Implicit 3D Cardiac Shape Reconstruction from Sparse CT Angiography Slices Mimicking 2D Transthoracic Echocardiography Views
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Accurate 3D representations of cardiac structures allow quantitative analysis of anatomy and function. In this work, we propose a method for reconstructing complete 3D cardiac shapes from segmentations of sparse planes in CT angiography (CTA) for application in 2D transthoracic echocardiography (TTE). Our method uses a neural implicit function to reconstruct the 3D shape of the cardiac chambers and left-ventricle myocardium from sparse CTA planes. To investigate the feasibility of achieving 3D reconstruction from 2D TTE, we select planes that mimic the standard apical 2D TTE views. During training, a multi-layer perceptron learns shape priors from 3D segmentations of the target structures in CTA. At test time, the network reconstructs 3D cardiac shapes from segmentations of TTE-mimicking CTA planes by jointly optimizing the latent code and the rigid transforms that map the observed planes into 3D space. For each heart, we simulate four realistic apical views, and we compare reconstructed multi-class volumes with the reference CTA volumes. On a held-out set of CTA segmentations, our approach achieves an average Dice coefficient of 0.86 $\pm$ 0.04 across all structures. Our method also achieves markedly lower volume errors than the clinical standard, Simpson's biplane rule: 4.88 $\pm$ 4.26 mL vs. 8.14 $\pm$ 6.04 mL, respectively, for the left ventricle; and 6.40 $\pm$ 7.37 mL vs. 37.76 $\pm$ 22.96 mL, respectively, for the left atrium. This suggests that our approach offers a viable route to more accurate 3D chamber quantification in 2D transthoracic echocardiography.
Temporally Consistent Mitral Annulus Measurements from Sparse Annotations in Echocardiographic Videos
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:This work presents a novel approach to achieving temporally consistent mitral annulus landmark localization in echocardiography videos using sparse annotations. Our method introduces a self-supervised loss term that enforces temporal consistency between neighboring frames, which smooths the position of landmarks and enhances measurement accuracy over time. Additionally, we incorporate realistic field-of-view augmentations to improve the recognition of missing anatomical landmarks. We evaluate our approach on both a public and private dataset, and demonstrate significant improvements in Mitral Annular Plane Systolic Excursion (MAPSE) calculations and overall landmark tracking stability. The method achieves a mean absolute MAPSE error of 1.81 $\pm$ 0.14 mm, an annulus size error of 2.46 $\pm$ 0.31 mm, and a landmark localization error of 2.48 $\pm$ 0.07 mm. Finally, it achieves a 0.99 ROC-AUC for recognition of missing landmarks.
Attenuation artifact detection and severity classification in intracoronary OCT using mixed image representations
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:In intracoronary optical coherence tomography (OCT), blood residues and gas bubbles cause attenuation artifacts that can obscure critical vessel structures. The presence and severity of these artifacts may warrant re-acquisition, prolonging procedure time and increasing use of contrast agent. Accurate detection of these artifacts can guide targeted re-acquisition, reducing the amount of repeated scans needed to achieve diagnostically viable images. However, the highly heterogeneous appearance of these artifacts poses a challenge for the automated detection of the affected image regions. To enable automatic detection of the attenuation artifacts caused by blood residues and gas bubbles based on their severity, we propose a convolutional neural network that performs classification of the attenuation lines (A-lines) into three classes: no artifact, mild artifact and severe artifact. Our model extracts and merges features from OCT images in both Cartesian and polar coordinates, where each column of the image represents an A-line. Our method detects the presence of attenuation artifacts in OCT frames reaching F-scores of 0.77 and 0.94 for mild and severe artifacts, respectively. The inference time over a full OCT scan is approximately 6 seconds. Our experiments show that analysis of images represented in both Cartesian and polar coordinate systems outperforms the analysis in polar coordinates only, suggesting that these representations contain complementary features. This work lays the foundation for automated artifact assessment and image acquisition guidance in intracoronary OCT imaging.
Classifier-guided registration of coronary CT angiography and intravascular ultrasound
Dec 22, 2024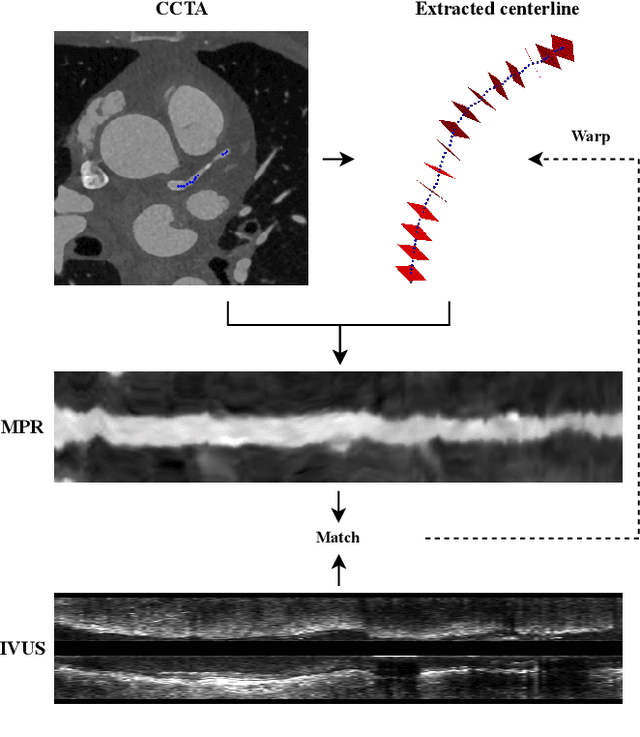
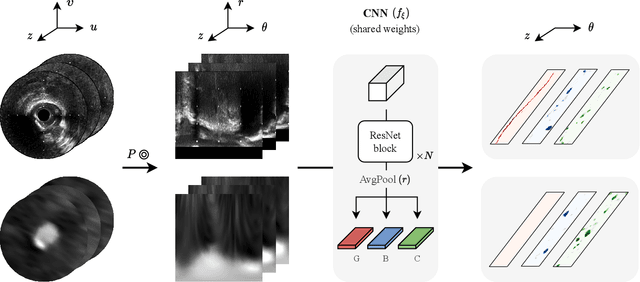
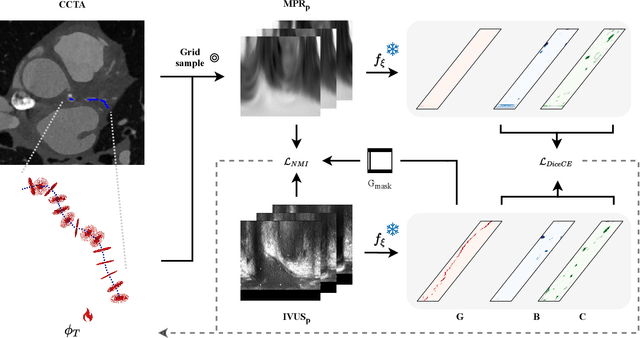
Abstract:Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) provide complementary information for coronary artery disease assessment, making their registration valuable for comprehensive analysis. However, existing registration methods require manual interaction or extensive segmentations, limiting their practical application. In this work, we present a fully automatic framework for CCTA-IVUS registration using deep learning-based feature detection and a differentiable image registration module. Our approach leverages a convolutional neural network trained to identify key anatomical features from polar-transformed multiplanar reformatted CCTA or IVUS data. These detected anatomical featuers subsequently guide a differentiable registration module to optimize transformation parameters of an automatically extracted coronary artery centerline. The method does not require landmark selection or segmentations as input, while accounting for the presence of IVUS guidewire artifacts. Evaluated on 48 clinical cases with reference CCTA centerlines corresponding to IVUS pullback, our method achieved successful registration in 83.3\% of cases, with a median centerline overlap F$_1$-score of 0.982 and median cosine similarities of 0.940 and 0.944 for cross-sectional plane orientation. Our results demonstrate that automatically detected anatomical features can be leveraged for accurate registration. The fully automatic nature of the approach represents a significant step toward streamlined multimodal coronary analysis, potentially facilitating large-scale studies of coronary plaque characteristics across modalities.
Brain age identification from diffusion MRI synergistically predicts neurodegenerative disease
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:Estimated brain age from magnetic resonance image (MRI) and its deviation from chronological age can provide early insights into potential neurodegenerative diseases, supporting early detection and implementation of prevention strategies. Diffusion MRI (dMRI), a widely used modality for brain age estimation, presents an opportunity to build an earlier biomarker for neurodegenerative disease prediction because it captures subtle microstructural changes that precede more perceptible macrostructural changes. However, the coexistence of macro- and micro-structural information in dMRI raises the question of whether current dMRI-based brain age estimation models are leveraging the intended microstructural information or if they inadvertently rely on the macrostructural information. To develop a microstructure-specific brain age, we propose a method for brain age identification from dMRI that minimizes the model's use of macrostructural information by non-rigidly registering all images to a standard template. Imaging data from 13,398 participants across 12 datasets were used for the training and evaluation. We compare our brain age models, trained with and without macrostructural information minimized, with an architecturally similar T1-weighted (T1w) MRI-based brain age model and two state-of-the-art T1w MRI-based brain age models that primarily use macrostructural information. We observe difference between our dMRI-based brain age and T1w MRI-based brain age across stages of neurodegeneration, with dMRI-based brain age being older than T1w MRI-based brain age in participants transitioning from cognitively normal (CN) to mild cognitive impairment (MCI), but younger in participants already diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Approximately 4 years before MCI diagnosis, dMRI-based brain age yields better performance than T1w MRI-based brain ages in predicting transition from CN to MCI.
World of Forms: Deformable Geometric Templates for One-Shot Surface Meshing in Coronary CT Angiography
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:Deep learning-based medical image segmentation and surface mesh generation typically involve a sequential pipeline from image to segmentation to meshes, often requiring large training datasets while making limited use of prior geometric knowledge. This may lead to topological inconsistencies and suboptimal performance in low-data regimes. To address these challenges, we propose a data-efficient deep learning method for direct 3D anatomical object surface meshing using geometric priors. Our approach employs a multi-resolution graph neural network that operates on a prior geometric template which is deformed to fit object boundaries of interest. We show how different templates may be used for the different surface meshing targets, and introduce a novel masked autoencoder pretraining strategy for 3D spherical data. The proposed method outperforms nnUNet in a one-shot setting for segmentation of the pericardium, left ventricle (LV) cavity and the LV myocardium. Similarly, the method outperforms other lumen segmentation operating on multi-planar reformatted images. Results further indicate that mesh quality is on par with or improves upon marching cubes post-processing of voxel mask predictions, while remaining flexible in the choice of mesh triangulation prior, thus paving the way for more accurate and topologically consistent 3D medical object surface meshing.
ATOMMIC: An Advanced Toolbox for Multitask Medical Imaging Consistency to facilitate Artificial Intelligence applications from acquisition to analysis in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:AI is revolutionizing MRI along the acquisition and processing chain. Advanced AI frameworks have been developed to apply AI in various successive tasks, such as image reconstruction, quantitative parameter map estimation, and image segmentation. Existing frameworks are often designed to perform tasks independently or are focused on specific models or datasets, limiting generalization. We introduce ATOMMIC, an open-source toolbox that streamlines AI applications for accelerated MRI reconstruction and analysis. ATOMMIC implements several tasks using DL networks and enables MultiTask Learning (MTL) to perform related tasks integrated, targeting generalization in the MRI domain. We first review the current state of AI frameworks for MRI through a comprehensive literature search and by parsing 12,479 GitHub repositories. We benchmark 25 DL models on eight publicly available datasets to present distinct applications of ATOMMIC on accelerated MRI reconstruction, image segmentation, quantitative parameter map estimation, and joint accelerated MRI reconstruction and image segmentation utilizing MTL. Our findings demonstrate that ATOMMIC is the only MTL framework with harmonized complex-valued and real-valued data support. Evaluations on single tasks show that physics-based models, which enforce data consistency by leveraging the physical properties of MRI, outperform other models in reconstructing highly accelerated acquisitions. Physics-based models that produce high reconstruction quality can accurately estimate quantitative parameter maps. When high-performing reconstruction models are combined with robust segmentation networks utilizing MTL, performance is improved in both tasks. ATOMMIC facilitates MRI reconstruction and analysis by standardizing workflows, enhancing data interoperability, integrating unique features like MTL, and effectively benchmarking DL models.
Deep Learning for Automatic Strain Quantification in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Nov 24, 2023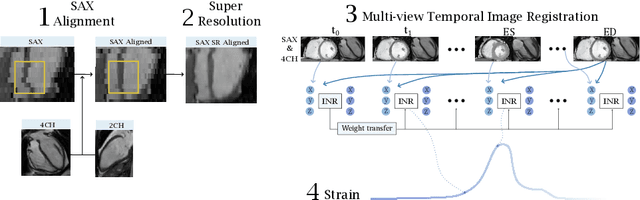
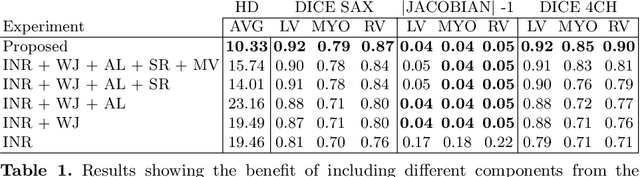
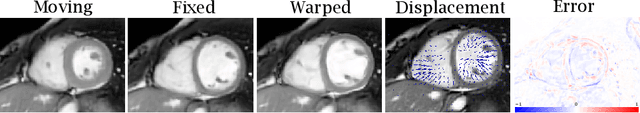
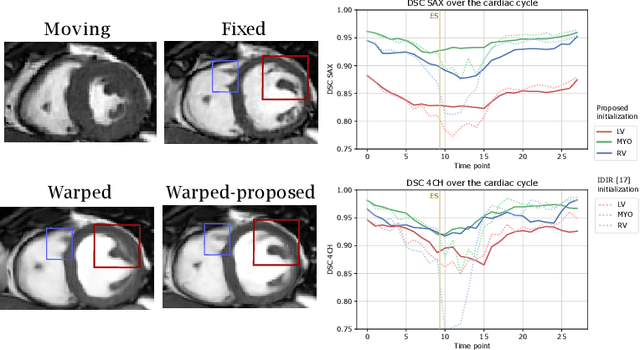
Abstract:Quantification of cardiac motion with cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CMRI) is an integral part of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) diagnosis. Yet, the expert evaluation of motion abnormalities with CMRI is a challenging task. To automatically assess cardiac motion, we register CMRIs from different time points of the cardiac cycle using Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) and perform a biomechanically informed regularization inspired by the myocardial incompressibility assumption. To enhance the registration performance, our method first rectifies the inter-slice misalignment inherent to CMRI by performing a rigid registration guided by the long-axis views, and then increases the through-plane resolution using an unsupervised deep learning super-resolution approach. Finally, we propose to synergically combine information from short-axis and 4-chamber long-axis views, along with an initialization to incorporate information from multiple cardiac time points. Thereafter, to quantify cardiac motion, we calculate global and segmental strain over a cardiac cycle and compute the peak strain. The evaluation of the method is performed on a dataset of cine CMRI scans from 47 ARVC patients and 67 controls. Our results show that inter-slice alignment and generation of super-resolved volumes combined with joint analysis of the two cardiac views, notably improves registration performance. Furthermore, the proposed initialization yields more physiologically plausible registrations. The significant differences in the peak strain, discerned between the ARVC patients and healthy controls suggest that automated motion quantification methods may assist in diagnosis and provide further understanding of disease-specific alterations of cardiac motion.
Predicting Age from White Matter Diffusivity with Residual Learning
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Imaging findings inconsistent with those expected at specific chronological age ranges may serve as early indicators of neurological disorders and increased mortality risk. Estimation of chronological age, and deviations from expected results, from structural MRI data has become an important task for developing biomarkers that are sensitive to such deviations. Complementary to structural analysis, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has proven effective in identifying age-related microstructural changes within the brain white matter, thereby presenting itself as a promising additional modality for brain age prediction. Although early studies have sought to harness DTI's advantages for age estimation, there is no evidence that the success of this prediction is owed to the unique microstructural and diffusivity features that DTI provides, rather than the macrostructural features that are also available in DTI data. Therefore, we seek to develop white-matter-specific age estimation to capture deviations from normal white matter aging. Specifically, we deliberately disregard the macrostructural information when predicting age from DTI scalar images, using two distinct methods. The first method relies on extracting only microstructural features from regions of interest. The second applies 3D residual neural networks (ResNets) to learn features directly from the images, which are non-linearly registered and warped to a template to minimize macrostructural variations. When tested on unseen data, the first method yields mean absolute error (MAE) of 6.11 years for cognitively normal participants and MAE of 6.62 years for cognitively impaired participants, while the second method achieves MAE of 4.69 years for cognitively normal participants and MAE of 4.96 years for cognitively impaired participants. We find that the ResNet model captures subtler, non-macrostructural features for brain age prediction.
Automatic Coronary Artery Plaque Quantification and CAD-RADS Prediction using Mesh Priors
Oct 17, 2023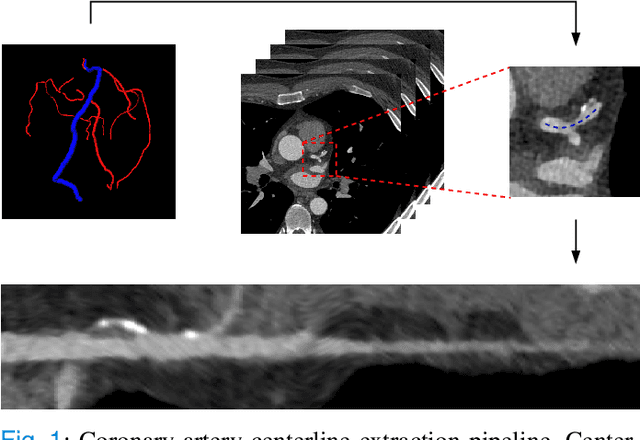
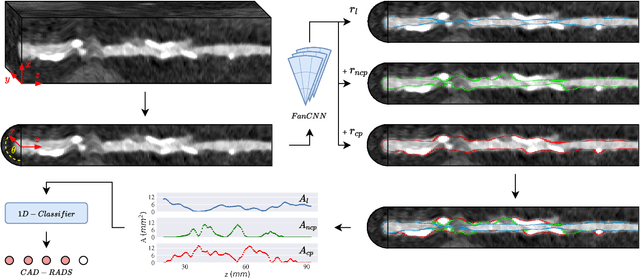
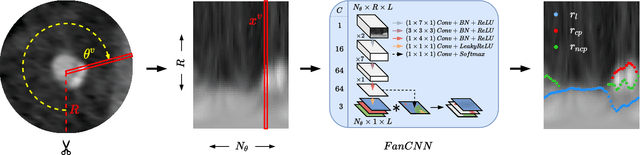
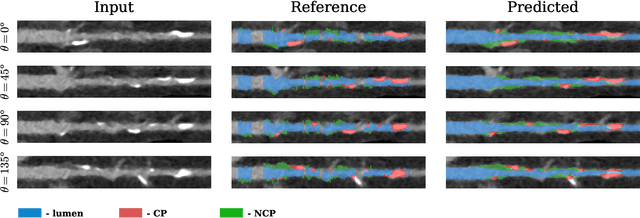
Abstract:Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains the leading cause of death worldwide. Patients with suspected CAD undergo coronary CT angiography (CCTA) to evaluate the risk of cardiovascular events and determine the treatment. Clinical analysis of coronary arteries in CCTA comprises the identification of atherosclerotic plaque, as well as the grading of any coronary artery stenosis typically obtained through the CAD-Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS). This requires analysis of the coronary lumen and plaque. While voxel-wise segmentation is a commonly used approach in various segmentation tasks, it does not guarantee topologically plausible shapes. To address this, in this work, we propose to directly infer surface meshes for coronary artery lumen and plaque based on a centerline prior and use it in the downstream task of CAD-RADS scoring. The method is developed and evaluated using a total of 2407 CCTA scans. Our method achieved lesion-wise volume intraclass correlation coefficients of 0.98, 0.79, and 0.85 for calcified, non-calcified, and total plaque volume respectively. Patient-level CAD-RADS categorization was evaluated on a representative hold-out test set of 300 scans, for which the achieved linearly weighted kappa ($\kappa$) was 0.75. CAD-RADS categorization on the set of 658 scans from another hospital and scanner led to a $\kappa$ of 0.71. The results demonstrate that direct inference of coronary artery meshes for lumen and plaque is feasible, and allows for the automated prediction of routinely performed CAD-RADS categorization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge