Ivan Tarapov
Health AI, Microsoft, Redmond Washington
From Embeddings to Accuracy: Comparing Foundation Models for Radiographic Classification
May 16, 2025Abstract:Foundation models, pretrained on extensive datasets, have significantly advanced machine learning by providing robust and transferable embeddings applicable to various domains, including medical imaging diagnostics. This study evaluates the utility of embeddings derived from both general-purpose and medical domain-specific foundation models for training lightweight adapter models in multi-class radiography classification, focusing specifically on tube placement assessment. A dataset comprising 8842 radiographs classified into seven distinct categories was employed to extract embeddings using six foundation models: DenseNet121, BiomedCLIP, Med-Flamingo, MedImageInsight, Rad-DINO, and CXR-Foundation. Adapter models were subsequently trained using classical machine learning algorithms. Among these combinations, MedImageInsight embeddings paired with an support vector machine adapter yielded the highest mean area under the curve (mAUC) at 93.8%, followed closely by Rad-DINO (91.1%) and CXR-Foundation (89.0%). In comparison, BiomedCLIP and DenseNet121 exhibited moderate performance with mAUC scores of 83.0% and 81.8%, respectively, whereas Med-Flamingo delivered the lowest performance at 75.1%. Notably, most adapter models demonstrated computational efficiency, achieving training within one minute and inference within seconds on CPU, underscoring their practicality for clinical applications. Furthermore, fairness analyses on adapters trained on MedImageInsight-derived embeddings indicated minimal disparities, with gender differences in performance within 2% and standard deviations across age groups not exceeding 3%. These findings confirm that foundation model embeddings-especially those from MedImageInsight-facilitate accurate, computationally efficient, and equitable diagnostic classification using lightweight adapters for radiographic image analysis.
WaveFormer: A 3D Transformer with Wavelet-Driven Feature Representation for Efficient Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Transformer-based architectures have advanced medical image analysis by effectively modeling long-range dependencies, yet they often struggle in 3D settings due to substantial memory overhead and insufficient capture of fine-grained local features. We address these limitations with WaveFormer, a novel 3D-transformer that: i) leverages the fundamental frequency-domain properties of features for contextual representation, and ii) is inspired by the top-down mechanism of the human visual recognition system, making it a biologically motivated architecture. By employing discrete wavelet transformations (DWT) at multiple scales, WaveFormer preserves both global context and high-frequency details while replacing heavy upsampling layers with efficient wavelet-based summarization and reconstruction. This significantly reduces the number of parameters, which is critical for real-world deployment where computational resources and training times are constrained. Furthermore, the model is generic and easily adaptable to diverse applications. Evaluations on BraTS2023, FLARE2021, and KiTS2023 demonstrate performance on par with state-of-the-art methods while offering substantially lower computational complexity.
Multi-Modal Mamba Modeling for Survival Prediction (M4Survive): Adapting Joint Foundation Model Representations
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Accurate survival prediction in oncology requires integrating diverse imaging modalities to capture the complex interplay of tumor biology. Traditional single-modality approaches often fail to leverage the complementary insights provided by radiological and pathological assessments. In this work, we introduce M4Survive (Multi-Modal Mamba Modeling for Survival Prediction), a novel framework that learns joint foundation model representations using efficient adapter networks. Our approach dynamically fuses heterogeneous embeddings from a foundation model repository (e.g., MedImageInsight, BiomedCLIP, Prov-GigaPath, UNI2-h), creating a correlated latent space optimized for survival risk estimation. By leveraging Mamba-based adapters, M4Survive enables efficient multi-modal learning while preserving computational efficiency. Experimental evaluations on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms both unimodal and traditional static multi-modal baselines in survival prediction accuracy. This work underscores the potential of foundation model-driven multi-modal fusion in advancing precision oncology and predictive analytics.
Scalable Drift Monitoring in Medical Imaging AI
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into medical imaging has advanced clinical diagnostics but poses challenges in managing model drift and ensuring long-term reliability. To address these challenges, we develop MMC+, an enhanced framework for scalable drift monitoring, building upon the CheXstray framework that introduced real-time drift detection for medical imaging AI models using multi-modal data concordance. This work extends the original framework's methodologies, providing a more scalable and adaptable solution for real-world healthcare settings and offers a reliable and cost-effective alternative to continuous performance monitoring addressing limitations of both continuous and periodic monitoring methods. MMC+ introduces critical improvements to the original framework, including more robust handling of diverse data streams, improved scalability with the integration of foundation models like MedImageInsight for high-dimensional image embeddings without site-specific training, and the introduction of uncertainty bounds to better capture drift in dynamic clinical environments. Validated with real-world data from Massachusetts General Hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic, MMC+ effectively detects significant data shifts and correlates them with model performance changes. While not directly predicting performance degradation, MMC+ serves as an early warning system, indicating when AI systems may deviate from acceptable performance bounds and enabling timely interventions. By emphasizing the importance of monitoring diverse data streams and evaluating data shifts alongside model performance, this work contributes to the broader adoption and integration of AI solutions in clinical settings.
MedImageInsight: An Open-Source Embedding Model for General Domain Medical Imaging
Oct 09, 2024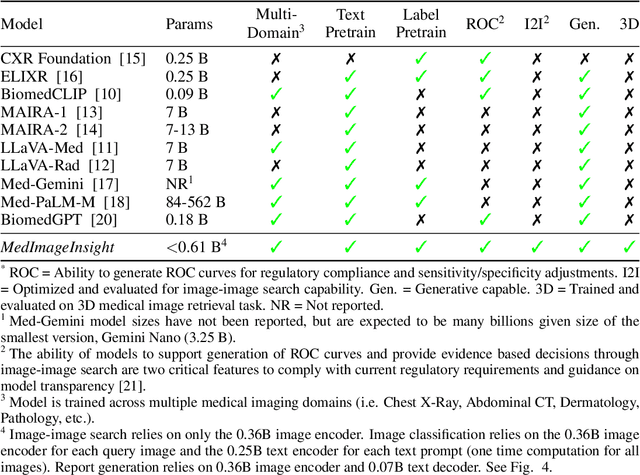
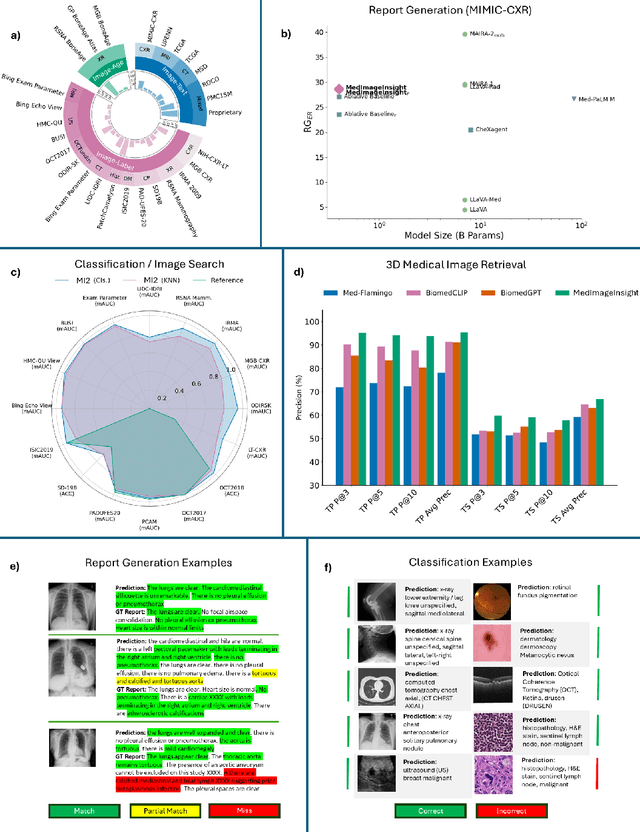
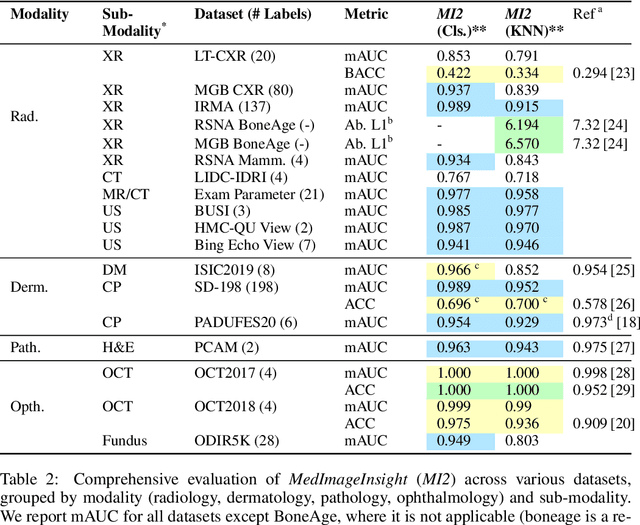
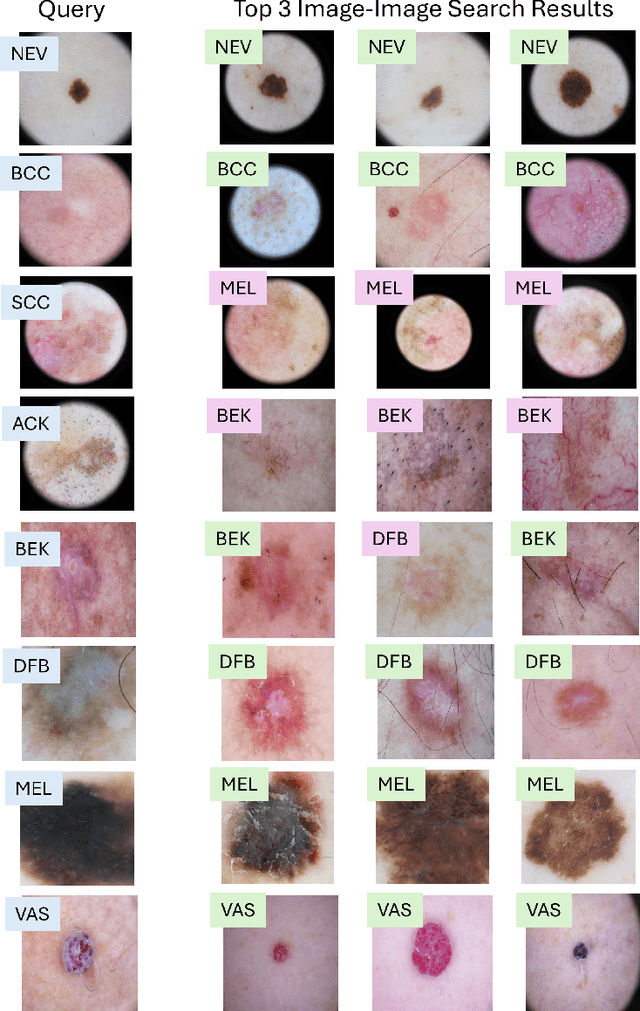
Abstract:In this work, we present MedImageInsight, an open-source medical imaging embedding model. MedImageInsight is trained on medical images with associated text and labels across a diverse collection of domains, including X-Ray, CT, MRI, dermoscopy, OCT, fundus photography, ultrasound, histopathology, and mammography. Rigorous evaluations demonstrate MedImageInsight's ability to achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) or human expert level performance across classification, image-image search, and fine-tuning tasks. Specifically, on public datasets, MedImageInsight achieves SOTA in CT 3D medical image retrieval, as well as SOTA in disease classification and search for chest X-ray, dermatology, and OCT imaging. Furthermore, MedImageInsight achieves human expert performance in bone age estimation (on both public and partner data), as well as AUC above 0.9 in most other domains. When paired with a text decoder, MedImageInsight achieves near SOTA level single image report findings generation with less than 10\% the parameters of other models. Compared to fine-tuning GPT-4o with only MIMIC-CXR data for the same task, MedImageInsight outperforms in clinical metrics, but underperforms on lexical metrics where GPT-4o sets a new SOTA. Importantly for regulatory purposes, MedImageInsight can generate ROC curves, adjust sensitivity and specificity based on clinical need, and provide evidence-based decision support through image-image search (which can also enable retrieval augmented generation). In an independent clinical evaluation of image-image search in chest X-ray, MedImageInsight outperformed every other publicly available foundation model evaluated by large margins (over 6 points AUC), and significantly outperformed other models in terms of AI fairness (across age and gender). We hope releasing MedImageInsight will help enhance collective progress in medical imaging AI research and development.
3D-MIR: A Benchmark and Empirical Study on 3D Medical Image Retrieval in Radiology
Nov 23, 2023



Abstract:The increasing use of medical imaging in healthcare settings presents a significant challenge due to the increasing workload for radiologists, yet it also offers opportunity for enhancing healthcare outcomes if effectively leveraged. 3D image retrieval holds potential to reduce radiologist workloads by enabling clinicians to efficiently search through diagnostically similar or otherwise relevant cases, resulting in faster and more precise diagnoses. However, the field of 3D medical image retrieval is still emerging, lacking established evaluation benchmarks, comprehensive datasets, and thorough studies. This paper attempts to bridge this gap by introducing a novel benchmark for 3D Medical Image Retrieval (3D-MIR) that encompasses four different anatomies imaged with computed tomography. Using this benchmark, we explore a diverse set of search strategies that use aggregated 2D slices, 3D volumes, and multi-modal embeddings from popular multi-modal foundation models as queries. Quantitative and qualitative assessments of each approach are provided alongside an in-depth discussion that offers insight for future research. To promote the advancement of this field, our benchmark, dataset, and code are made publicly available.
Region-based Contrastive Pretraining for Medical Image Retrieval with Anatomic Query
May 09, 2023



Abstract:We introduce a novel Region-based contrastive pretraining for Medical Image Retrieval (RegionMIR) that demonstrates the feasibility of medical image retrieval with similar anatomical regions. RegionMIR addresses two major challenges for medical image retrieval i) standardization of clinically relevant searching criteria (e.g., anatomical, pathology-based), and ii) localization of anatomical area of interests that are semantically meaningful. In this work, we propose an ROI image retrieval image network that retrieves images with similar anatomy by extracting anatomical features (via bounding boxes) and evaluate similarity between pairwise anatomy-categorized features between the query and the database of images using contrastive learning. ROI queries are encoded using a contrastive-pretrained encoder that was fine-tuned for anatomy classification, which generates an anatomical-specific latent space for region-correlated image retrieval. During retrieval, we compare the anatomically encoded query to find similar features within a feature database generated from training samples, and retrieve images with similar regions from training samples. We evaluate our approach on both anatomy classification and image retrieval tasks using the Chest ImaGenome Dataset. Our proposed strategy yields an improvement over state-of-the-art pretraining and co-training strategies, from 92.24 to 94.12 (2.03%) classification accuracy in anatomies. We qualitatively evaluate the image retrieval performance demonstrating generalizability across multiple anatomies with different morphology.
Deep Labeling of fMRI Brain Networks
May 05, 2023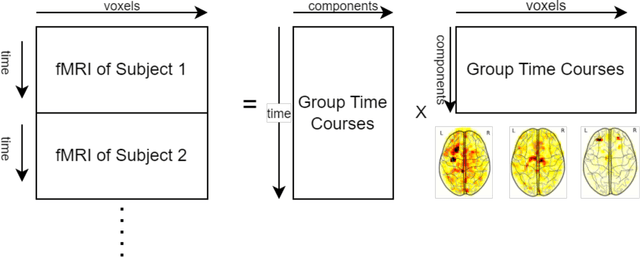
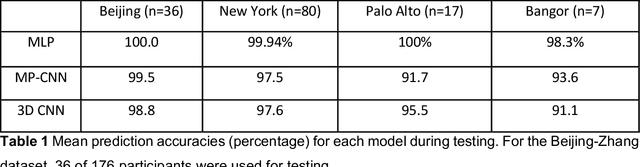
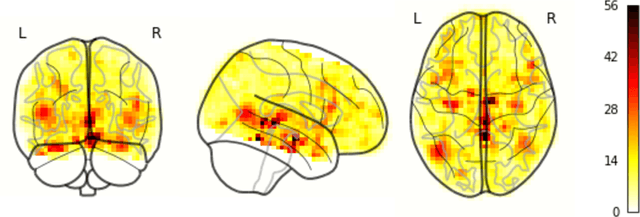
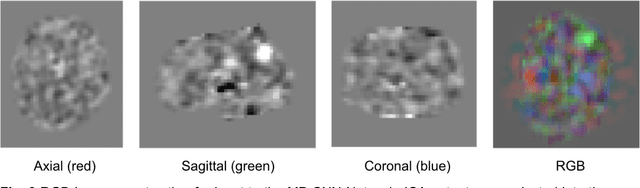
Abstract:Resting State Networks (RSNs) of the brain extracted from Resting State functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (RS-fMRI) are used in the pre-surgical planning to guide the neurosurgeon. This is difficult, though, as expert knowledge is required to label each of the RSNs. There is a lack of efficient and standardized methods to be used in clinical workflows. Additionally, these methods need to be generalizable since the method needs to work well regardless of the acquisition technique. We propose an accurate, fast, and lightweight deep learning approach to label RSNs. Group Independent Component Analysis (ICA) was used to extract large scale functional connectivity patterns in the cohort and dual regression was used to back project them on individual subject RSNs. We compare a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) based method with 2D and 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and find that the MLP is faster and more accurate. The MLP method performs as good or better than other works despite its compact size. We prove the generalizability of our method by showing that the MLP performs at 100% accuracy in the holdout dataset and 98.3% accuracy in three other sites' fMRI acquisitions.
Deep Labeling of fMRI Brain Networks Using Cloud Based Processing
Sep 20, 2022



Abstract:Resting state fMRI is an imaging modality which reveals brain activity localization through signal changes, in what is known as Resting State Networks (RSNs). This technique is gaining popularity in neurosurgical pre-planning to visualize the functional regions and assess regional activity. Labeling of rs-fMRI networks require subject-matter expertise and is time consuming, creating a need for an automated classification algorithm. While the impact of AI in medical diagnosis has shown great progress; deploying and maintaining these in a clinical setting is an unmet need. We propose an end-to-end reproducible pipeline which incorporates image processing of rs-fMRI in a cloud-based workflow while using deep learning to automate the classification of RSNs. We have architected a reproducible Azure Machine Learning cloud-based medical imaging concept pipeline for fMRI analysis integrating the popular FMRIB Software Library (FSL) toolkit. To demonstrate a clinical application using a large dataset, we compare three neural network architectures for classification of deeper RSNs derived from processed rs-fMRI. The three algorithms are: an MLP, a 2D projection-based CNN, and a fully 3D CNN classification networks. Each of the net-works was trained on the rs-fMRI back-projected independent components giving >98% accuracy for each classification method.
CheXstray: Real-time Multi-Modal Data Concordance for Drift Detection in Medical Imaging AI
Feb 06, 2022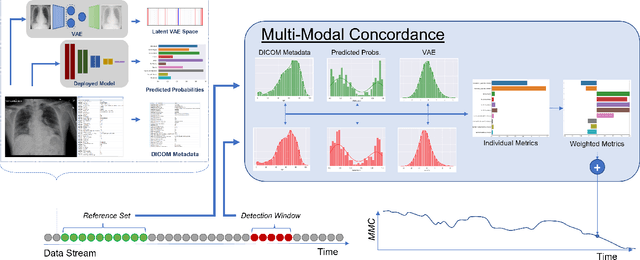
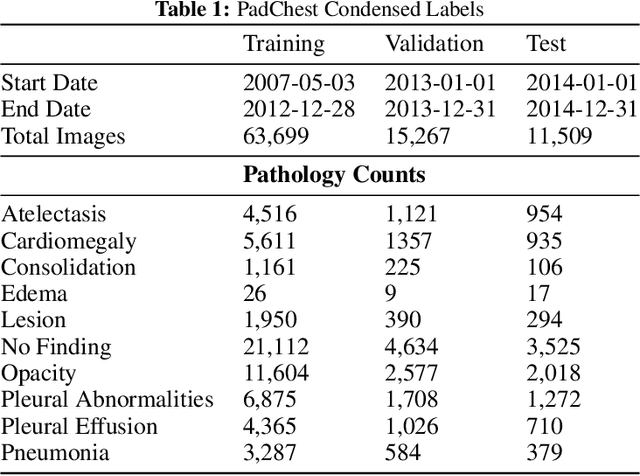
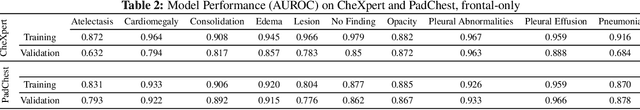
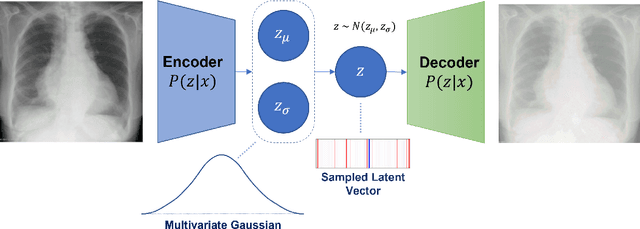
Abstract:Rapidly expanding Clinical AI applications worldwide have the potential to impact to all areas of medical practice. Medical imaging applications constitute a vast majority of approved clinical AI applications. Though healthcare systems are eager to adopt AI solutions a fundamental question remains: \textit{what happens after the AI model goes into production?} We use the CheXpert and PadChest public datasets to build and test a medical imaging AI drift monitoring workflow that tracks data and model drift without contemporaneous ground truth. We simulate drift in multiple experiments to compare model performance with our novel multi-modal drift metric, which uses DICOM metadata, image appearance representation from a variational autoencoder (VAE), and model output probabilities as input. Through experimentation, we demonstrate a strong proxy for ground truth performance using unsupervised distributional shifts in relevant metadata, predicted probabilities, and VAE latent representation. Our key contributions include (1) proof-of-concept for medical imaging drift detection including use of VAE and domain specific statistical methods (2) a multi-modal methodology for measuring and unifying drift metrics (3) new insights into the challenges and solutions for observing deployed medical imaging AI (4) creation of open-source tools enabling others to easily run their own workflows or scenarios. This work has important implications for addressing the translation gap related to continuous medical imaging AI model monitoring in dynamic healthcare environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge