Surya Teja Devarakonda
3D-MIR: A Benchmark and Empirical Study on 3D Medical Image Retrieval in Radiology
Nov 23, 2023



Abstract:The increasing use of medical imaging in healthcare settings presents a significant challenge due to the increasing workload for radiologists, yet it also offers opportunity for enhancing healthcare outcomes if effectively leveraged. 3D image retrieval holds potential to reduce radiologist workloads by enabling clinicians to efficiently search through diagnostically similar or otherwise relevant cases, resulting in faster and more precise diagnoses. However, the field of 3D medical image retrieval is still emerging, lacking established evaluation benchmarks, comprehensive datasets, and thorough studies. This paper attempts to bridge this gap by introducing a novel benchmark for 3D Medical Image Retrieval (3D-MIR) that encompasses four different anatomies imaged with computed tomography. Using this benchmark, we explore a diverse set of search strategies that use aggregated 2D slices, 3D volumes, and multi-modal embeddings from popular multi-modal foundation models as queries. Quantitative and qualitative assessments of each approach are provided alongside an in-depth discussion that offers insight for future research. To promote the advancement of this field, our benchmark, dataset, and code are made publicly available.
FLARe: Forecasting by Learning Anticipated Representations
Apr 17, 2019
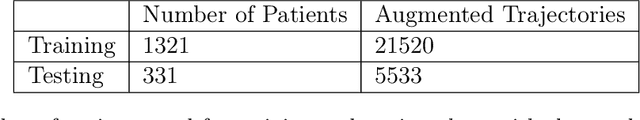
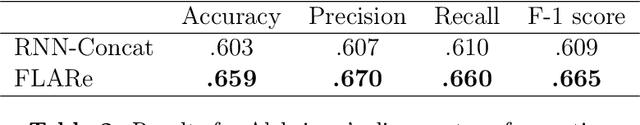
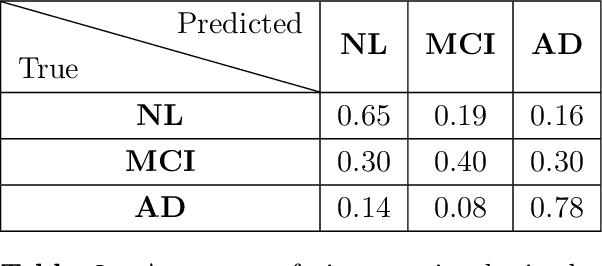
Abstract:Computational models that forecast the progression of Alzheimer's disease at the patient level are extremely useful tools for identifying high risk cohorts for early intervention and treatment planning. The state-of-the-art work in this area proposes models that forecast by using latent representations extracted from the longitudinal data across multiple modalities, including volumetric information extracted from medical scans and demographic info. These models incorporate the time horizon, which is the amount of time between the last recorded visit and the future visit, by directly concatenating a representation of it to the data latent representation. In this paper, we present a model which generates a sequence of latent representations of the patient status across the time horizon, providing more informative modeling of the temporal relationships between the patient's history and future visits. Our proposed model outperforms the baseline in terms of forecasting accuracy and F1 score with the added benefit of robustly handling missing visits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge