Huanjin Yao
R1-SyntheticVL: Is Synthetic Data from Generative Models Ready for Multimodal Large Language Model?
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:In this work, we aim to develop effective data synthesis techniques that autonomously synthesize multimodal training data for enhancing MLLMs in solving complex real-world tasks. To this end, we propose Collective Adversarial Data Synthesis (CADS), a novel and general approach to synthesize high-quality, diverse and challenging multimodal data for MLLMs. The core idea of CADS is to leverage collective intelligence to ensure high-quality and diverse generation, while exploring adversarial learning to synthesize challenging samples for effectively driving model improvement. Specifically, CADS operates with two cyclic phases, i.e., Collective Adversarial Data Generation (CAD-Generate) and Collective Adversarial Data Judgment (CAD-Judge). CAD-Generate leverages collective knowledge to jointly generate new and diverse multimodal data, while CAD-Judge collaboratively assesses the quality of synthesized data. In addition, CADS introduces an Adversarial Context Optimization mechanism to optimize the generation context to encourage challenging and high-value data generation. With CADS, we construct MMSynthetic-20K and train our model R1-SyntheticVL, which demonstrates superior performance on various benchmarks.
DeepResearchEval: An Automated Framework for Deep Research Task Construction and Agentic Evaluation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Deep research systems are widely used for multi-step web research, analysis, and cross-source synthesis, yet their evaluation remains challenging. Existing benchmarks often require annotation-intensive task construction, rely on static evaluation dimensions, or fail to reliably verify facts when citations are missing. To bridge these gaps, we introduce DeepResearchEval, an automated framework for deep research task construction and agentic evaluation. For task construction, we propose a persona-driven pipeline generating realistic, complex research tasks anchored in diverse user profiles, applying a two-stage filter Task Qualification and Search Necessity to retain only tasks requiring multi-source evidence integration and external retrieval. For evaluation, we propose an agentic pipeline with two components: an Adaptive Point-wise Quality Evaluation that dynamically derives task-specific evaluation dimensions, criteria, and weights conditioned on each generated task, and an Active Fact-Checking that autonomously extracts and verifies report statements via web search, even when citations are missing.
R1-ShareVL: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability of Multimodal Large Language Models via Share-GRPO
May 22, 2025Abstract:In this work, we aim to incentivize the reasoning ability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) via reinforcement learning (RL) and develop an effective approach that mitigates the sparse reward and advantage vanishing issues during RL. To this end, we propose Share-GRPO, a novel RL approach that tackle these issues by exploring and sharing diverse reasoning trajectories over expanded question space. Specifically, Share-GRPO first expands the question space for a given question via data transformation techniques, and then encourages MLLM to effectively explore diverse reasoning trajectories over the expanded question space and shares the discovered reasoning trajectories across the expanded questions during RL. In addition, Share-GRPO also shares reward information during advantage computation, which estimates solution advantages hierarchically across and within question variants, allowing more accurate estimation of relative advantages and improving the stability of policy training. Extensive evaluations over six widely-used reasoning benchmarks showcase the superior performance of our method. Code will be available at https://github.com/HJYao00/R1-ShareVL.
R1-Compress: Long Chain-of-Thought Compression via Chunk Compression and Search
May 22, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning enhances large language models (LLMs) by enabling step-by-step problem-solving, yet its extension to Long-CoT introduces substantial computational overhead due to increased token length. Existing compression approaches -- instance-level and token-level -- either sacrifice essential local reasoning signals like reflection or yield incoherent outputs. To address these limitations, we propose R1-Compress, a two-stage chunk-level compression framework that preserves both local information and coherence. Our method segments Long-CoT into manageable chunks, applies LLM-driven inner-chunk compression, and employs an inter-chunk search mechanism to select the short and coherent sequence. Experiments on Qwen2.5-Instruct models across MATH500, AIME24, and GPQA-Diamond demonstrate that R1-Compress significantly reduces token usage while maintaining comparable reasoning accuracy. On MATH500, R1-Compress achieves an accuracy of 92.4%, with only a 0.6% drop compared to the Long-CoT baseline, while reducing token usage by about 20%. Source code will be available at https://github.com/w-yibo/R1-Compress
R1-VL: Learning to Reason with Multimodal Large Language Models via Step-wise Group Relative Policy Optimization
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Recent studies generally enhance MLLMs' reasoning capabilities via supervised fine-tuning on high-quality chain-of-thought reasoning data, which often leads models to merely imitate successful reasoning paths without understanding what the wrong reasoning paths are. In this work, we aim to enhance the MLLMs' reasoning ability beyond passively imitating positive reasoning paths. To this end, we design Step-wise Group Relative Policy Optimization (StepGRPO), a new online reinforcement learning framework that enables MLLMs to self-improve reasoning ability via simple, effective and dense step-wise rewarding. Specifically, StepGRPO introduces two novel rule-based reasoning rewards: Step-wise Reasoning Accuracy Reward (StepRAR) and Step-wise Reasoning Validity Reward (StepRVR). StepRAR rewards the reasoning paths that contain necessary intermediate reasoning steps via a soft key-step matching technique, while StepRAR rewards reasoning paths that follow a well-structured and logically consistent reasoning process through a reasoning completeness and logic evaluation strategy. With the proposed StepGRPO, we introduce R1-VL, a series of MLLMs with outstanding capabilities in step-by-step reasoning. Extensive experiments over 8 benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of our methods.
Panacea: Mitigating Harmful Fine-tuning for Large Language Models via Post-fine-tuning Perturbation
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Harmful fine-tuning attack introduces significant security risks to the fine-tuning services. Mainstream defenses aim to vaccinate the model such that the later harmful fine-tuning attack is less effective. However, our evaluation results show that such defenses are fragile -- with a few fine-tuning steps, the model still can learn the harmful knowledge. To this end, we do further experiment and find that an embarrassingly simple solution -- adding purely random perturbations to the fine-tuned model, can recover the model from harmful behavior, though it leads to a degradation in the model's fine-tuning performance. To address the degradation of fine-tuning performance, we further propose Panacea, which optimizes an adaptive perturbation that will be applied to the model after fine-tuning. Panacea maintains model's safety alignment performance without compromising downstream fine-tuning performance. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on different harmful ratios, fine-tuning tasks and mainstream LLMs, where the average harmful scores are reduced by up-to 21.5%, while maintaining fine-tuning performance. As a by-product, we analyze the optimized perturbation and show that different layers in various LLMs have distinct safety coefficients. Source code available at https://github.com/w-yibo/Panacea
Mulberry: Empowering MLLM with o1-like Reasoning and Reflection via Collective Monte Carlo Tree Search
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we aim to develop an MLLM that understands and solves questions by learning to create each intermediate step of the reasoning involved till the final answer. To this end, we propose Collective Monte Carlo Tree Search (CoMCTS), a new learning-to-reason method for MLLMs, which introduces the concept of collective learning into ``tree search'' for effective and efficient reasoning-path searching and learning. The core idea of CoMCTS is to leverage collective knowledge from multiple models to collaboratively conjecture, search and identify effective reasoning paths toward correct answers via four iterative operations including Expansion, Simulation and Error Positioning, Backpropagation, and Selection. Using CoMCTS, we construct Mulberry-260k, a multimodal dataset with a tree of rich, explicit and well-defined reasoning nodes for each question. With Mulberry-260k, we perform collective SFT to train our model, Mulberry, a series of MLLMs with o1-like step-by-step Reasoning and Reflection capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our proposed methods on various benchmarks. Code will be available at https://github.com/HJYao00/Mulberry
Dense Connector for MLLMs
May 22, 2024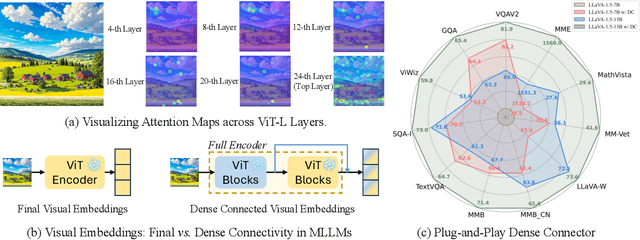
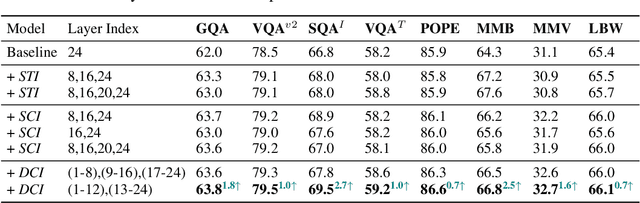
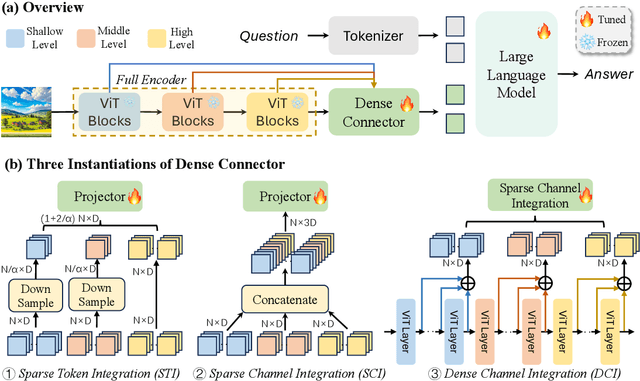
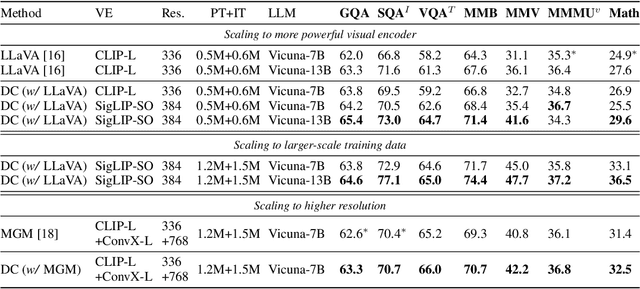
Abstract:Do we fully leverage the potential of visual encoder in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs)? The recent outstanding performance of MLLMs in multimodal understanding has garnered broad attention from both academia and industry. In the current MLLM rat race, the focus seems to be predominantly on the linguistic side. We witness the rise of larger and higher-quality instruction datasets, as well as the involvement of larger-sized LLMs. Yet, scant attention has been directed towards the visual signals utilized by MLLMs, often assumed to be the final high-level features extracted by a frozen visual encoder. In this paper, we introduce the Dense Connector - a simple, effective, and plug-and-play vision-language connector that significantly enhances existing MLLMs by leveraging multi-layer visual features, with minimal additional computational overhead. Furthermore, our model, trained solely on images, showcases remarkable zero-shot capabilities in video understanding as well. Experimental results across various vision encoders, image resolutions, training dataset scales, varying sizes of LLMs (2.7B->70B), and diverse architectures of MLLMs (e.g., LLaVA and Mini-Gemini) validate the versatility and scalability of our approach, achieving state-of-the-art performance on across 19 image and video benchmarks. We hope that this work will provide valuable experience and serve as a basic module for future MLLM development.
GPT4Vis: What Can GPT-4 Do for Zero-shot Visual Recognition?
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:This paper does not present a novel method. Instead, it delves into an essential, yet must-know baseline in light of the latest advancements in Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI): the utilization of GPT-4 for visual understanding. Our study centers on the evaluation of GPT-4's linguistic and visual capabilities in zero-shot visual recognition tasks. Specifically, we explore the potential of its generated rich textual descriptions across various categories to enhance recognition performance without any training. Additionally, we evaluate its visual proficiency in directly recognizing diverse visual content. To achieve this, we conduct an extensive series of experiments, systematically quantifying the performance of GPT-4 across three modalities: images, videos, and point clouds. This comprehensive evaluation encompasses a total of 16 widely recognized benchmark datasets, providing top-1 and top-5 accuracy metrics. Our study reveals that leveraging GPT-4's advanced linguistic knowledge to generate rich descriptions markedly improves zero-shot recognition. In terms of visual proficiency, GPT-4V's average performance across 16 datasets sits roughly between the capabilities of OpenAI-CLIP's ViT-L and EVA-CLIP's ViT-E. We hope that this research will contribute valuable data points and experience for future studies. We release our code at https://github.com/whwu95/GPT4Vis.
Side4Video: Spatial-Temporal Side Network for Memory-Efficient Image-to-Video Transfer Learning
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:Large pre-trained vision models achieve impressive success in computer vision. However, fully fine-tuning large models for downstream tasks, particularly in video understanding, can be prohibitively computationally expensive. Recent studies turn their focus towards efficient image-to-video transfer learning. Nevertheless, existing efficient fine-tuning methods lack attention to training memory usage and exploration of transferring a larger model to the video domain. In this paper, we present a novel Spatial-Temporal Side Network for memory-efficient fine-tuning large image models to video understanding, named Side4Video. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight spatial-temporal side network attached to the frozen vision model, which avoids the backpropagation through the heavy pre-trained model and utilizes multi-level spatial features from the original image model. Extremely memory-efficient architecture enables our method to reduce 75% memory usage than previous adapter-based methods. In this way, we can transfer a huge ViT-E (4.4B) for video understanding tasks which is 14x larger than ViT-L (304M). Our approach achieves remarkable performance on various video datasets across unimodal and cross-modal tasks (i.e., action recognition and text-video retrieval), especially in Something-Something V1&V2 (67.3% & 74.6%), Kinetics-400 (88.6%), MSR-VTT (52.3%), MSVD (56.1%) and VATEX (68.8%). We release our code at https://github.com/HJYao00/Side4Video.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge