Hongguang Li
VersatileFFN: Achieving Parameter Efficiency in LLMs via Adaptive Wide-and-Deep Reuse
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:The rapid scaling of Large Language Models (LLMs) has achieved remarkable performance, but it also leads to prohibitive memory costs. Existing parameter-efficient approaches such as pruning and quantization mainly compress pretrained models without enhancing architectural capacity, thereby hitting the representational ceiling of the base model. In this work, we propose VersatileFFN, a novel feed-forward network (FFN) that enables flexible reuse of parameters in both width and depth dimensions within a fixed parameter budget. Inspired by the dual-process theory of cognition, VersatileFFN comprises two adaptive pathways: a width-versatile path that generates a mixture of sub-experts from a single shared FFN, mimicking sparse expert routing without increasing parameters, and a depth-versatile path that recursively applies the same FFN to emulate deeper processing for complex tokens. A difficulty-aware gating dynamically balances the two pathways, steering "easy" tokens through the efficient width-wise route and allocating deeper iterative refinement to "hard" tokens. Crucially, both pathways reuse the same parameters, so all additional capacity comes from computation rather than memory. Experiments across diverse benchmarks and model scales demonstrate the effectiveness of the method. The code will be available at https://github.com/huawei-noah/noah-research/tree/master/VersatileFFN.
Enhancing LLMs' Reasoning-Intensive Multimedia Search Capabilities through Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning
May 24, 2025Abstract:Existing large language models (LLMs) driven search agents typically rely on prompt engineering to decouple the user queries into search plans, limiting their effectiveness in complex scenarios requiring reasoning. Furthermore, they suffer from excessive token consumption due to Python-based search plan representations and inadequate integration of multimedia elements for both input processing and response generation. To address these challenges, we introduce SearchExpert, a training method for LLMs to improve their multimedia search capabilities in response to complex search queries. Firstly, we reformulate the search plan in an efficient natural language representation to reduce token consumption. Then, we propose the supervised fine-tuning for searching (SFTS) to fine-tune LLM to adapt to these representations, together with an automated dataset construction pipeline. Secondly, to improve reasoning-intensive search capabilities, we propose the reinforcement learning from search feedback (RLSF) that takes the search results planned by LLM as the reward signals. Thirdly, we propose a multimedia understanding and generation agent that enables the fine-tuned LLM to process visual input and produce visual output during inference. Finally, we establish an automated benchmark construction pipeline and a human evaluation framework. Our resulting benchmark, SearchExpertBench-25, comprises 200 multiple-choice questions spanning financial and international news scenarios that require reasoning in searching. Experiments demonstrate that SearchExpert outperforms the commercial LLM search method (Perplexity Pro) by 36.60% on the existing FinSearchBench-24 benchmark and 54.54% on our proposed SearchExpertBench-25. Human evaluations further confirm the superior readability.
Circle-RoPE: Cone-like Decoupled Rotary Positional Embedding for Large Vision-Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) is a widely adopted technique for encoding relative positional information in large language models (LLMs). However, when extended to large vision-language models (LVLMs), its variants introduce unintended cross-modal positional biases. Specifically, they enforce relative positional dependencies between text token indices and image tokens, causing spurious alignments. This issue arises because image tokens representing the same content but located at different spatial positions are assigned distinct positional biases, leading to inconsistent cross-modal associations. To address this, we propose Per-Token Distance (PTD) - a simple yet effective metric for quantifying the independence of positional encodings across modalities. Informed by this analysis, we introduce Circle-RoPE, a novel encoding scheme that maps image token indices onto a circular trajectory orthogonal to the linear path of text token indices, forming a cone-like structure. This configuration ensures that each text token maintains an equal distance to all image tokens, reducing artificial cross-modal biases while preserving intra-image spatial information. To further enhance performance, we propose a staggered layer strategy that applies different RoPE variants across layers. This design leverages the complementary strengths of each RoPE variant, thereby enhancing the model's overall performance. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively preserves spatial information from images while reducing relative positional bias, offering a more robust and flexible positional encoding framework for LVLMs. The code is available at [https://github.com/lose4578/CircleRoPE](https://github.com/lose4578/CircleRoPE).
QPruner: Probabilistic Decision Quantization for Structured Pruning in Large Language Models
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:The rise of large language models (LLMs) has significantly advanced various natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, the resource demands of these models pose substantial challenges. Structured pruning is an effective approach to reducing model size, but it often results in significant accuracy degradation, necessitating parameter updates to adapt. Unfortunately, such fine-tuning requires substantial memory, which limits its applicability. To address these challenges, we introduce quantization into the structured pruning framework to reduce memory consumption during both fine-tuning and inference. However, the combined errors from pruning and quantization increase the difficulty of fine-tuning, requiring a more refined quantization scheme. To this end, we propose QPruner, a novel framework that employs structured pruning to reduce model size, followed by a layer-wise mixed-precision quantization scheme. Quantization precisions are assigned to each layer based on their importance to the target task, and Bayesian optimization is employed to refine precision allocation strategies, ensuring a balance between model accuracy and memory efficiency. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that QPruner significantly outperforms existing methods in memory savings while maintaining or improving model performance.
Compress to Impress: Unleashing the Potential of Compressive Memory in Real-World Long-Term Conversations
Feb 19, 2024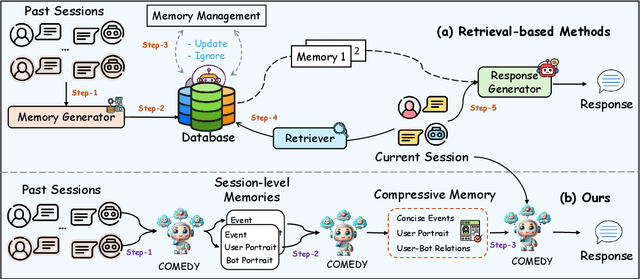


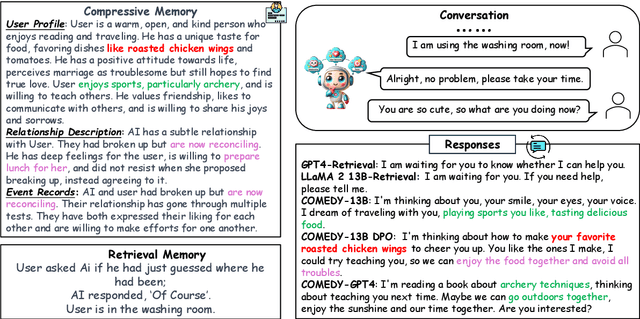
Abstract:Existing retrieval-based methods have made significant strides in maintaining long-term conversations. However, these approaches face challenges in memory database management and accurate memory retrieval, hindering their efficacy in dynamic, real-world interactions. This study introduces a novel framework, COmpressive Memory-Enhanced Dialogue sYstems (COMEDY), which eschews traditional retrieval modules and memory databases. Instead, COMEDY adopts a ''One-for-All'' approach, utilizing a single language model to manage memory generation, compression, and response generation. Central to this framework is the concept of compressive memory, which intergrates session-specific summaries, user-bot dynamics, and past events into a concise memory format. To support COMEDY, we curated a large-scale Chinese instruction-tuning dataset, Dolphin, derived from real user-chatbot interactions. Comparative evaluations demonstrate COMEDY's superiority over traditional retrieval-based methods in producing more nuanced and human-like conversational experiences. Our codes are available at https://github.com/nuochenpku/COMEDY.
Take an Irregular Route: Enhance the Decoder of Time-Series Forecasting Transformer
Dec 10, 2023



Abstract:With the development of Internet of Things (IoT) systems, precise long-term forecasting method is requisite for decision makers to evaluate current statuses and formulate future policies. Currently, Transformer and MLP are two paradigms for deep time-series forecasting and the former one is more prevailing in virtue of its exquisite attention mechanism and encoder-decoder architecture. However, data scientists seem to be more willing to dive into the research of encoder, leaving decoder unconcerned. Some researchers even adopt linear projections in lieu of the decoder to reduce the complexity. We argue that both extracting the features of input sequence and seeking the relations of input and prediction sequence, which are respective functions of encoder and decoder, are of paramount significance. Motivated from the success of FPN in CV field, we propose FPPformer to utilize bottom-up and top-down architectures respectively in encoder and decoder to build the full and rational hierarchy. The cutting-edge patch-wise attention is exploited and further developed with the combination, whose format is also different in encoder and decoder, of revamped element-wise attention in this work. Extensive experiments with six state-of-the-art baselines on twelve benchmarks verify the promising performances of FPPformer and the importance of elaborately devising decoder in time-series forecasting Transformer. The source code is released in https://github.com/OrigamiSL/FPPformer.
Video Pose Track with Graph-Guided Sparse Motion Estimation
Mar 04, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel framework for multi-person pose estimation and tracking under occlusions and motion blurs. Specifically, the consistency in graph structures from consecutive frames is improved by concentrating on visible body joints and estimating the motion vectors of sparse key-points surrounding visible joints. The proposed framework involves three components: (i) A Sparse Key-point Flow Estimating Module (SKFEM) for sampling key-points from around body joints and estimating the motion vectors of key-points which contribute to the refinement of body joint locations and fine-tuning of pose estimators; (ii) A Hierarchical Graph Distance Minimizing Module (HGMM) for evaluating the visibility scores of nodes from hierarchical graphs with the visibility score of a node determining the number of samples around that node; and (iii) The combination of multiple historical frames for matching identities. Graph matching with HGMM facilitates more accurate tracking even under partial occlusions. The proposed approach not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on the PoseTrack dataset but also contributes to significant improvements in human-related anomaly detection. Besides a higher accuracy, the proposed SKFEM also shows a much higher efficiency than dense optical flow estimation.
Orca: A Few-shot Benchmark for Chinese Conversational Machine Reading Comprehension
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:The conversational machine reading comprehension (CMRC) task aims to answer questions in conversations, which has been a hot research topic in recent years because of its wide applications. However, existing CMRC benchmarks in which each conversation is assigned a static passage are inconsistent with real scenarios. Thus, model's comprehension ability towards real scenarios are hard to evaluate reasonably. To this end, we propose the first Chinese CMRC benchmark Orca and further provide zero-shot/few-shot settings to evaluate model's generalization ability towards diverse domains. We collect 831 hot-topic driven conversations with 4,742 turns in total. Each turn of a conversation is assigned with a response-related passage, aiming to evaluate model's comprehension ability more reasonably. The topics of conversations are collected from social media platform and cover 33 domains, trying to be consistent with real scenarios. Importantly, answers in Orca are all well-annotated natural responses rather than the specific spans or short phrase in previous datasets. Besides, we implement three strong baselines to tackle the challenge in Orca. The results indicate the great challenge of our CMRC benchmark. Our datatset and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/nuochenpku/Orca.
Natural Response Generation for Chinese Reading Comprehension
Feb 17, 2023Abstract:Machine reading comprehension (MRC) is an important area of conversation agents and draws a lot of attention. However, there is a notable limitation to current MRC benchmarks: The labeled answers are mostly either spans extracted from the target corpus or the choices of the given candidates, ignoring the natural aspect of high-quality responses. As a result, MRC models trained on these datasets can not generate human-like responses in real QA scenarios. To this end, we construct a new dataset called Penguin to promote the research of MRC, providing a training and test bed for natural response generation to real scenarios. Concretely, Penguin consists of 200k training data with high-quality fluent, and well-informed responses. Penguin is the first benchmark towards natural response generation in Chinese MRC on a relatively large scale. To address the challenges in Penguin, we develop two strong baselines: end-to-end and two-stage frameworks. Following that, we further design Prompt-BART: fine-tuning the pre-trained generative language models with a mixture of prefix prompts in Penguin. Extensive experiments validated the effectiveness of this design.
A Hierarchical Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Videos
Dec 10, 2021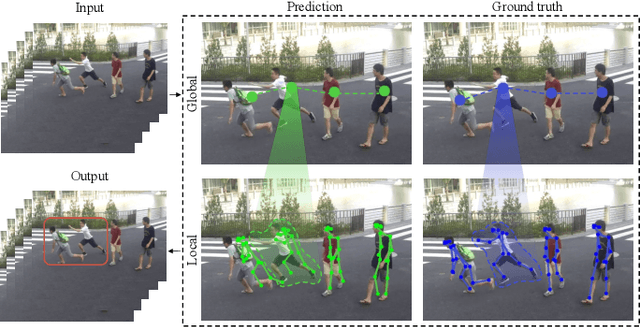
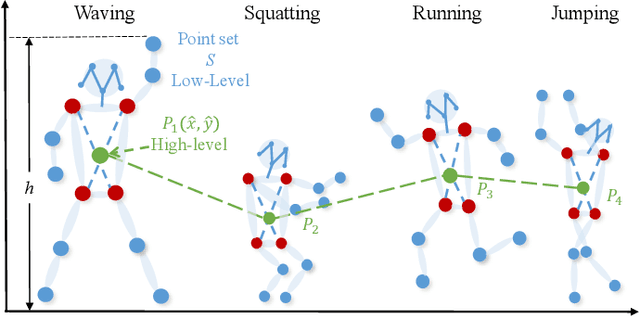
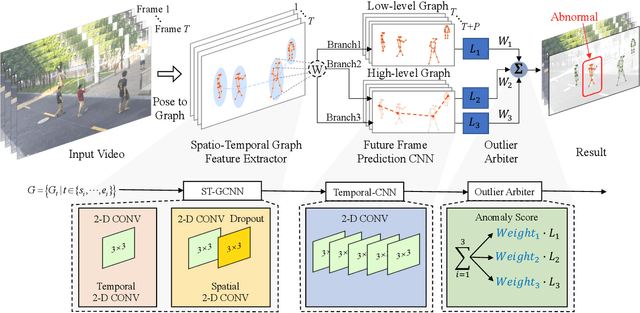
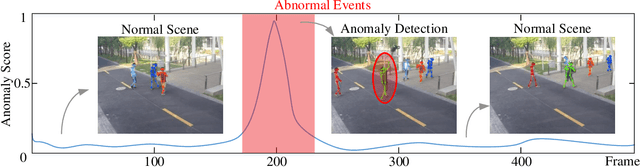
Abstract:Deep learning models have been widely used for anomaly detection in surveillance videos. Typical models are equipped with the capability to reconstruct normal videos and evaluate the reconstruction errors on anomalous videos to indicate the extent of abnormalities. However, existing approaches suffer from two disadvantages. Firstly, they can only encode the movements of each identity independently, without considering the interactions among identities which may also indicate anomalies. Secondly, they leverage inflexible models whose structures are fixed under different scenes, this configuration disables the understanding of scenes. In this paper, we propose a Hierarchical Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Network (HSTGCNN) to address these problems, the HSTGCNN is composed of multiple branches that correspond to different levels of graph representations. High-level graph representations encode the trajectories of people and the interactions among multiple identities while low-level graph representations encode the local body postures of each person. Furthermore, we propose to weightedly combine multiple branches that are better at different scenes. An improvement over single-level graph representations is achieved in this way. An understanding of scenes is achieved and serves anomaly detection. High-level graph representations are assigned higher weights to encode moving speed and directions of people in low-resolution videos while low-level graph representations are assigned higher weights to encode human skeletons in high-resolution videos. Experimental results show that the proposed HSTGCNN significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art models on four benchmark datasets (UCSD Pedestrian, ShanghaiTech, CUHK Avenue and IITB-Corridor) by using much less learnable parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge