Yinan Bao
Supervised Adversarial Contrastive Learning for Emotion Recognition in Conversations
Jun 02, 2023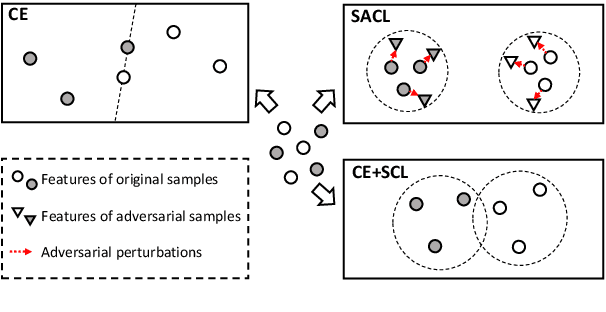
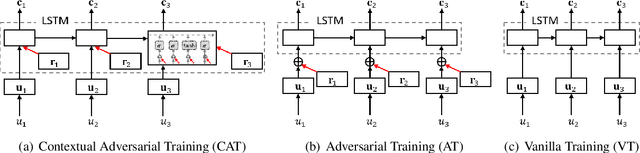
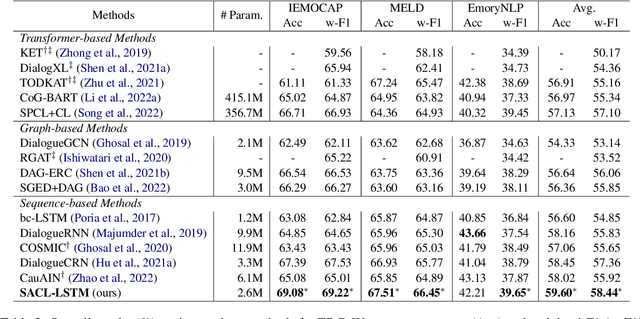
Abstract:Extracting generalized and robust representations is a major challenge in emotion recognition in conversations (ERC). To address this, we propose a supervised adversarial contrastive learning (SACL) framework for learning class-spread structured representations. The framework applies contrast-aware adversarial training to generate worst-case samples and uses a joint class-spread contrastive learning objective on both original and adversarial samples. It can effectively utilize label-level feature consistency and retain fine-grained intra-class features. To avoid the negative impact of adversarial perturbations on context-dependent data, we design a contextual adversarial training strategy to learn more diverse features from context and enhance the model's context robustness. We develop a sequence-based method SACL-LSTM under this framework, to learn label-consistent and context-robust emotional features for ERC. Experiments on three datasets demonstrate that SACL-LSTM achieves state-of-the-art performance on ERC. Extended experiments prove the effectiveness of the SACL framework.
Orca: A Few-shot Benchmark for Chinese Conversational Machine Reading Comprehension
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:The conversational machine reading comprehension (CMRC) task aims to answer questions in conversations, which has been a hot research topic in recent years because of its wide applications. However, existing CMRC benchmarks in which each conversation is assigned a static passage are inconsistent with real scenarios. Thus, model's comprehension ability towards real scenarios are hard to evaluate reasonably. To this end, we propose the first Chinese CMRC benchmark Orca and further provide zero-shot/few-shot settings to evaluate model's generalization ability towards diverse domains. We collect 831 hot-topic driven conversations with 4,742 turns in total. Each turn of a conversation is assigned with a response-related passage, aiming to evaluate model's comprehension ability more reasonably. The topics of conversations are collected from social media platform and cover 33 domains, trying to be consistent with real scenarios. Importantly, answers in Orca are all well-annotated natural responses rather than the specific spans or short phrase in previous datasets. Besides, we implement three strong baselines to tackle the challenge in Orca. The results indicate the great challenge of our CMRC benchmark. Our datatset and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/nuochenpku/Orca.
Natural Response Generation for Chinese Reading Comprehension
Feb 17, 2023Abstract:Machine reading comprehension (MRC) is an important area of conversation agents and draws a lot of attention. However, there is a notable limitation to current MRC benchmarks: The labeled answers are mostly either spans extracted from the target corpus or the choices of the given candidates, ignoring the natural aspect of high-quality responses. As a result, MRC models trained on these datasets can not generate human-like responses in real QA scenarios. To this end, we construct a new dataset called Penguin to promote the research of MRC, providing a training and test bed for natural response generation to real scenarios. Concretely, Penguin consists of 200k training data with high-quality fluent, and well-informed responses. Penguin is the first benchmark towards natural response generation in Chinese MRC on a relatively large scale. To address the challenges in Penguin, we develop two strong baselines: end-to-end and two-stage frameworks. Following that, we further design Prompt-BART: fine-tuning the pre-trained generative language models with a mixture of prefix prompts in Penguin. Extensive experiments validated the effectiveness of this design.
Speaker-Guided Encoder-Decoder Framework for Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Jun 07, 2022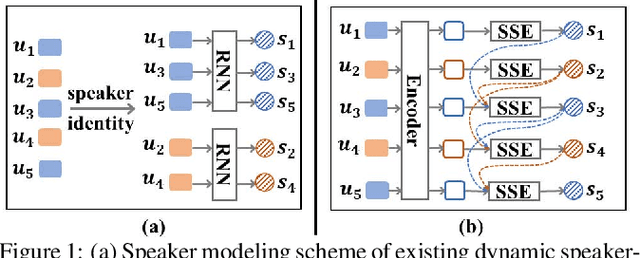
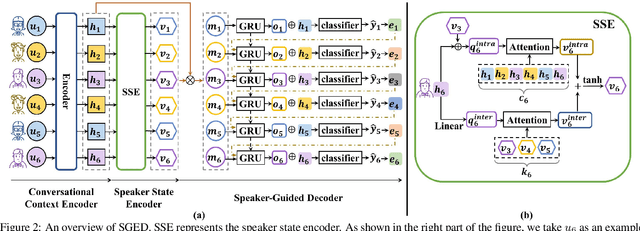
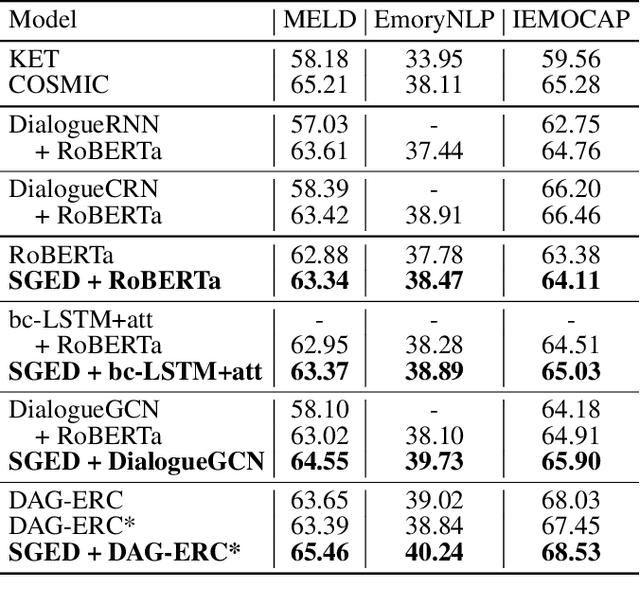
Abstract:The emotion recognition in conversation (ERC) task aims to predict the emotion label of an utterance in a conversation. Since the dependencies between speakers are complex and dynamic, which consist of intra- and inter-speaker dependencies, the modeling of speaker-specific information is a vital role in ERC. Although existing researchers have proposed various methods of speaker interaction modeling, they cannot explore dynamic intra- and inter-speaker dependencies jointly, leading to the insufficient comprehension of context and further hindering emotion prediction. To this end, we design a novel speaker modeling scheme that explores intra- and inter-speaker dependencies jointly in a dynamic manner. Besides, we propose a Speaker-Guided Encoder-Decoder (SGED) framework for ERC, which fully exploits speaker information for the decoding of emotion. We use different existing methods as the conversational context encoder of our framework, showing the high scalability and flexibility of the proposed framework. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of SGED.
Multi-Granularity Semantic Aware Graph Model for Reducing Position Bias in Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction
May 04, 2022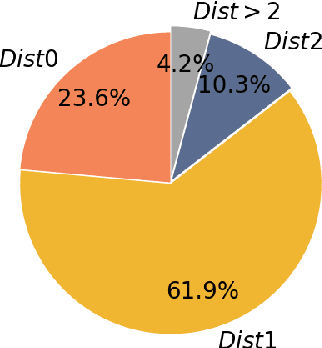
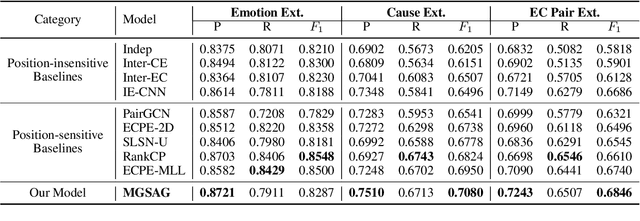
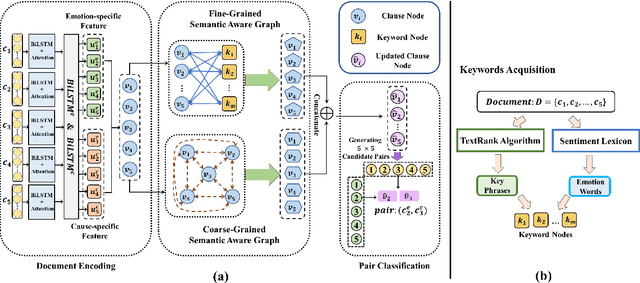
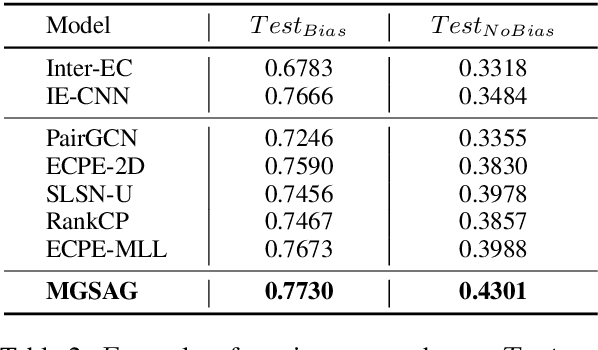
Abstract:The Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction (ECPE) task aims to extract emotions and causes as pairs from documents. We observe that the relative distance distribution of emotions and causes is extremely imbalanced in the typical ECPE dataset. Existing methods have set a fixed size window to capture relations between neighboring clauses. However, they neglect the effective semantic connections between distant clauses, leading to poor generalization ability towards position-insensitive data. To alleviate the problem, we propose a novel \textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{G}ranularity \textbf{S}emantic \textbf{A}ware \textbf{G}raph model (MGSAG) to incorporate fine-grained and coarse-grained semantic features jointly, without regard to distance limitation. In particular, we first explore semantic dependencies between clauses and keywords extracted from the document that convey fine-grained semantic features, obtaining keywords enhanced clause representations. Besides, a clause graph is also established to model coarse-grained semantic relations between clauses. Experimental results indicate that MGSAG surpasses the existing state-of-the-art ECPE models. Especially, MGSAG outperforms other models significantly in the condition of position-insensitive data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge