Qianwen Ma
Speaker-Guided Encoder-Decoder Framework for Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Jun 07, 2022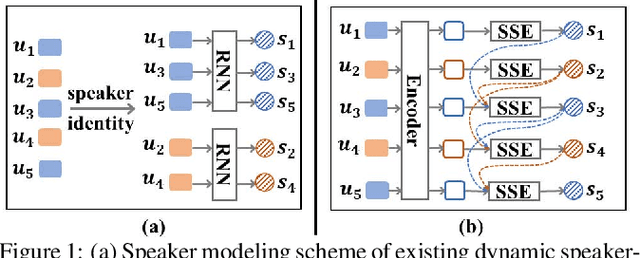
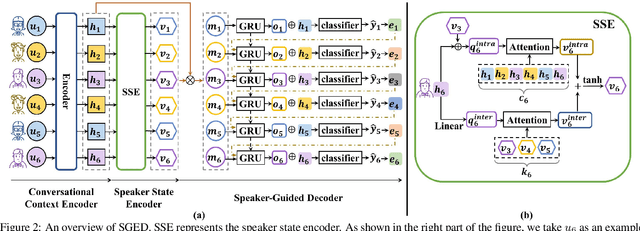
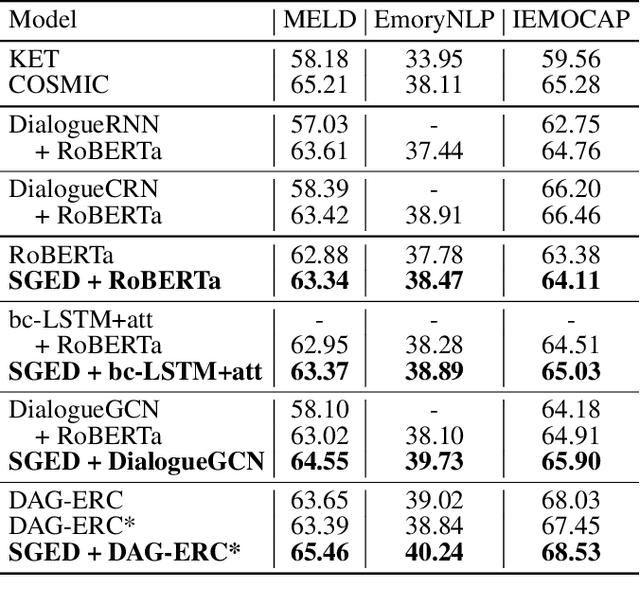
Abstract:The emotion recognition in conversation (ERC) task aims to predict the emotion label of an utterance in a conversation. Since the dependencies between speakers are complex and dynamic, which consist of intra- and inter-speaker dependencies, the modeling of speaker-specific information is a vital role in ERC. Although existing researchers have proposed various methods of speaker interaction modeling, they cannot explore dynamic intra- and inter-speaker dependencies jointly, leading to the insufficient comprehension of context and further hindering emotion prediction. To this end, we design a novel speaker modeling scheme that explores intra- and inter-speaker dependencies jointly in a dynamic manner. Besides, we propose a Speaker-Guided Encoder-Decoder (SGED) framework for ERC, which fully exploits speaker information for the decoding of emotion. We use different existing methods as the conversational context encoder of our framework, showing the high scalability and flexibility of the proposed framework. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of SGED.
Multi-Granularity Semantic Aware Graph Model for Reducing Position Bias in Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction
May 04, 2022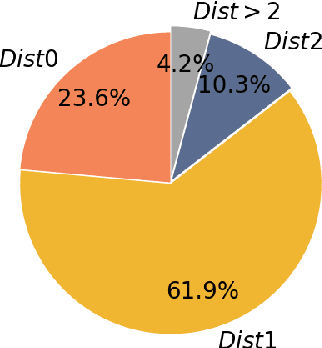
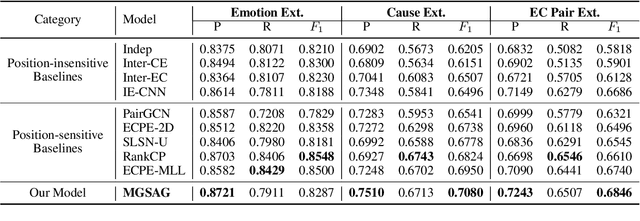
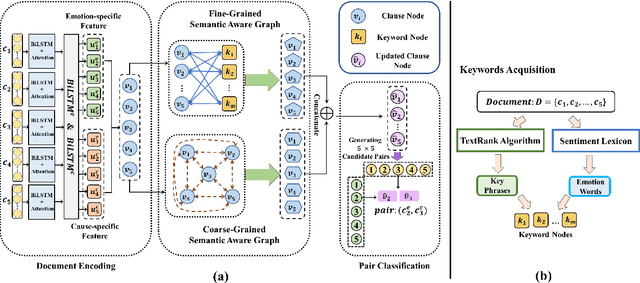
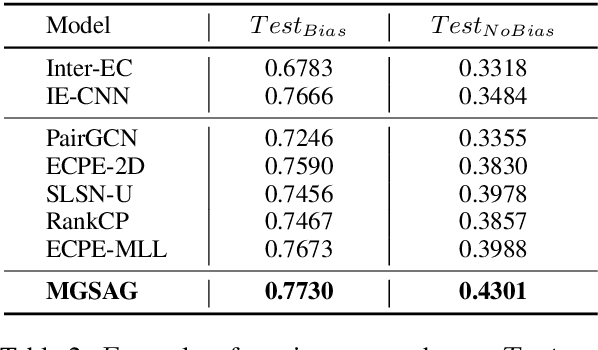
Abstract:The Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction (ECPE) task aims to extract emotions and causes as pairs from documents. We observe that the relative distance distribution of emotions and causes is extremely imbalanced in the typical ECPE dataset. Existing methods have set a fixed size window to capture relations between neighboring clauses. However, they neglect the effective semantic connections between distant clauses, leading to poor generalization ability towards position-insensitive data. To alleviate the problem, we propose a novel \textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{G}ranularity \textbf{S}emantic \textbf{A}ware \textbf{G}raph model (MGSAG) to incorporate fine-grained and coarse-grained semantic features jointly, without regard to distance limitation. In particular, we first explore semantic dependencies between clauses and keywords extracted from the document that convey fine-grained semantic features, obtaining keywords enhanced clause representations. Besides, a clause graph is also established to model coarse-grained semantic relations between clauses. Experimental results indicate that MGSAG surpasses the existing state-of-the-art ECPE models. Especially, MGSAG outperforms other models significantly in the condition of position-insensitive data.
SRLF: A Stance-aware Reinforcement Learning Framework for Content-based Rumor Detection on Social Media
May 10, 2021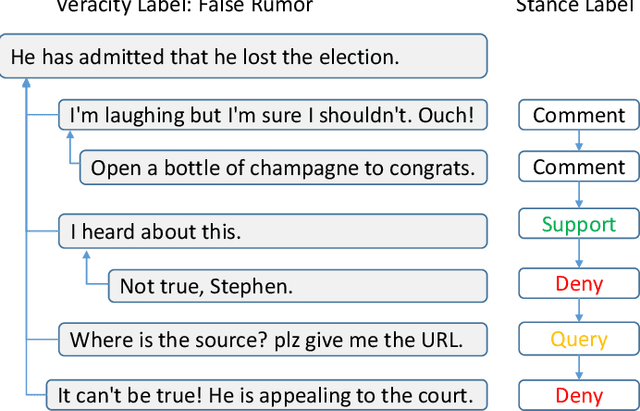
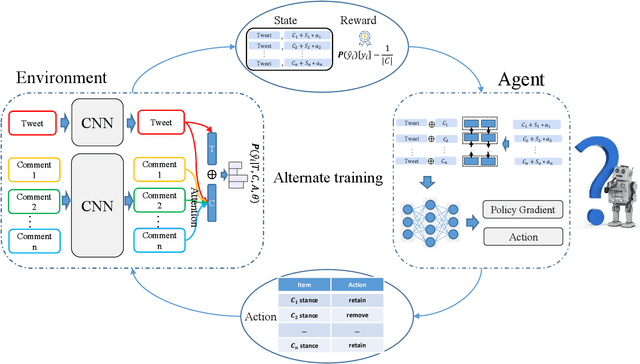
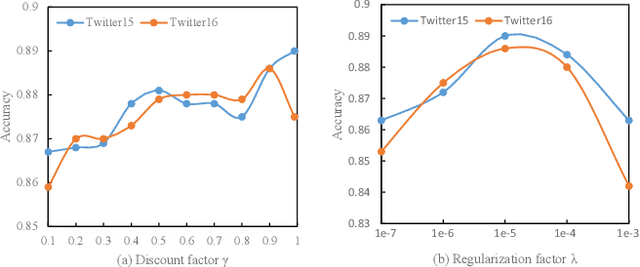
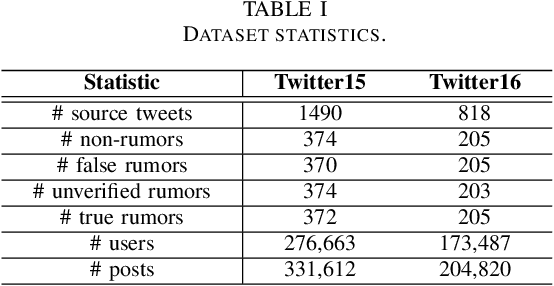
Abstract:The rapid development of social media changes the lifestyle of people and simultaneously provides an ideal place for publishing and disseminating rumors, which severely exacerbates social panic and triggers a crisis of social trust. Early content-based methods focused on finding clues from the text and user profiles for rumor detection. Recent studies combine the stances of users' comments with news content to capture the difference between true and false rumors. Although the user's stance is effective for rumor detection, the manual labeling process is time-consuming and labor-intensive, which limits the application of utilizing it to facilitate rumor detection. In this paper, we first finetune a pre-trained BERT model on a small labeled dataset and leverage this model to annotate weak stance labels for users' comment data to overcome the problem mentioned above. Then, we propose a novel Stance-aware Reinforcement Learning Framework (SRLF) to select high-quality labeled stance data for model training and rumor detection. Both the stance selection and rumor detection tasks are optimized simultaneously to promote both tasks mutually. We conduct experiments on two commonly used real-world datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that our framework outperforms the state-of-the-art models significantly, which confirms the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Early Detection of Fake News by Utilizing the Credibility of News, Publishers, and Users Based on Weakly Supervised Learning
Dec 14, 2020



Abstract:The dissemination of fake news significantly affects personal reputation and public trust. Recently, fake news detection has attracted tremendous attention, and previous studies mainly focused on finding clues from news content or diffusion path. However, the required features of previous models are often unavailable or insufficient in early detection scenarios, resulting in poor performance. Thus, early fake news detection remains a tough challenge. Intuitively, the news from trusted and authoritative sources or shared by many users with a good reputation is more reliable than other news. Using the credibility of publishers and users as prior weakly supervised information, we can quickly locate fake news in massive news and detect them in the early stages of dissemination. In this paper, we propose a novel Structure-aware Multi-head Attention Network (SMAN), which combines the news content, publishing, and reposting relations of publishers and users, to jointly optimize the fake news detection and credibility prediction tasks. In this way, we can explicitly exploit the credibility of publishers and users for early fake news detection. We conducted experiments on three real-world datasets, and the results show that SMAN can detect fake news in 4 hours with an accuracy of over 91%, which is much faster than the state-of-the-art models.
Beyond Statistical Relations: Integrating Knowledge Relations into Style Correlations for Multi-Label Music Style Classification
Nov 09, 2019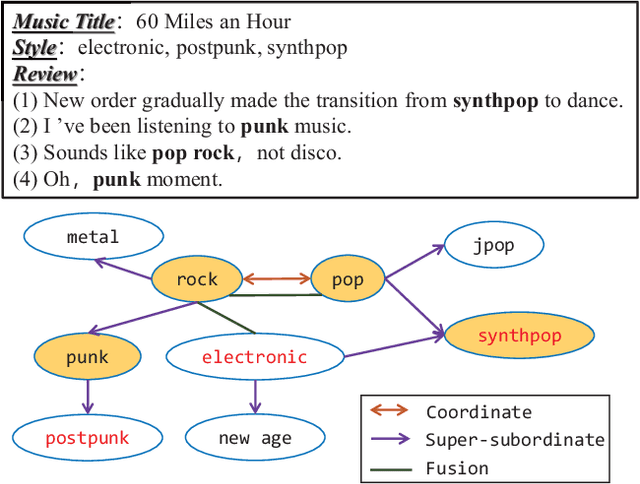
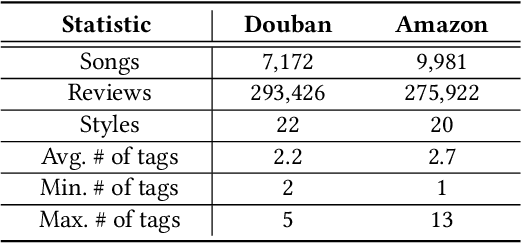
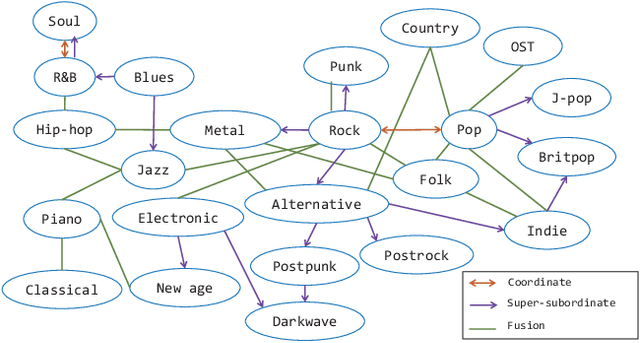
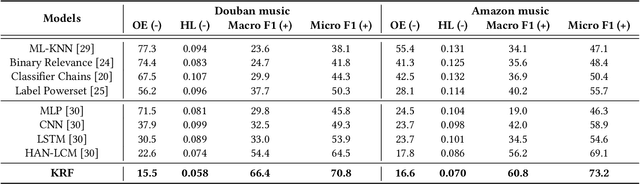
Abstract:Automatically labeling multiple styles for every song is a comprehensive application in all kinds of music websites. Recently, some researches explore review-driven multi-label music style classification and exploit style correlations for this task. However, their methods focus on mining the statistical relations between different music styles and only consider shallow style relations. Moreover, these statistical relations suffer from the underfitting problem because some music styles have little training data. To tackle these problems, we propose a novel knowledge relations integrated framework (KRF) to capture the complete style correlations, which jointly exploits the inherent relations between music styles according to external knowledge and their statistical relations. Based on the two types of relations, we use graph convolutional network to learn the deep correlations between styles automatically. Experimental results show that our framework significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Further studies demonstrate that our framework can effectively alleviate the underfitting problem and learn meaningful style correlations.
Jointly embedding the local and global relations of heterogeneous graph for rumor detection
Sep 11, 2019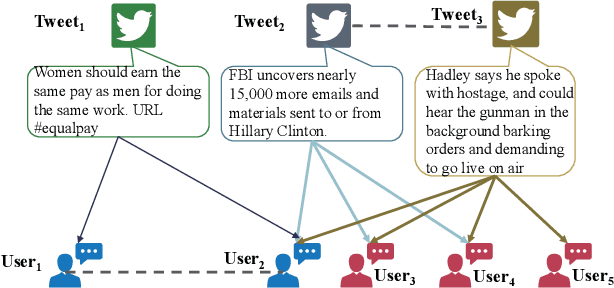
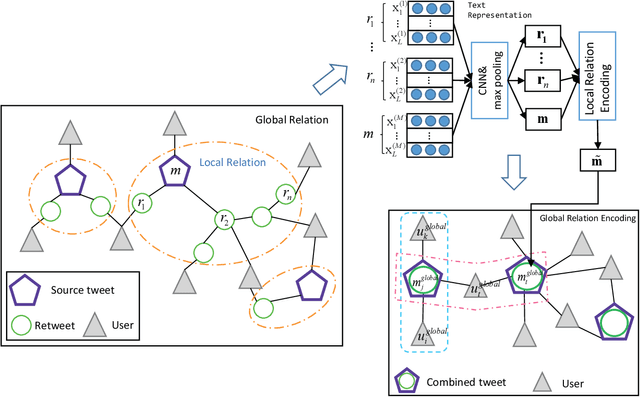
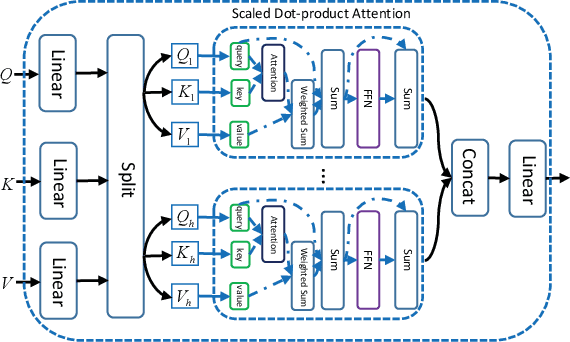
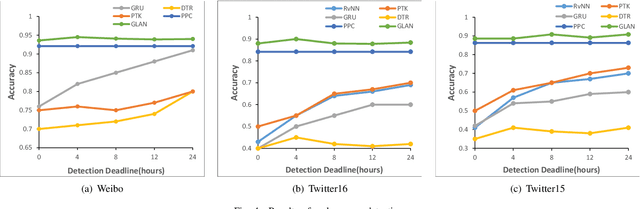
Abstract:The development of social media has revolutionized the way people communicate, share information and make decisions, but it also provides an ideal platform for publishing and spreading rumors. Existing rumor detection methods focus on finding clues from text content, user profiles, and propagation patterns. However, the local semantic relation and global structural information in the message propagation graph have not been well utilized by previous works. In this paper, we present a novel global-local attention network (GLAN) for rumor detection, which jointly encodes the local semantic and global structural information. We first generate a better integrated representation for each source tweet by fusing the semantic information of related retweets with the attention mechanism. Then, we model the global relationships among all source tweets, retweets, and users as a heterogeneous graph to capture the rich structural information for rumor detection. We conduct experiments on three real-world datasets, and the results demonstrate that GLAN significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art models in both rumor detection and early detection scenarios.
Learning review representations from user and product level information for spam detection
Sep 10, 2019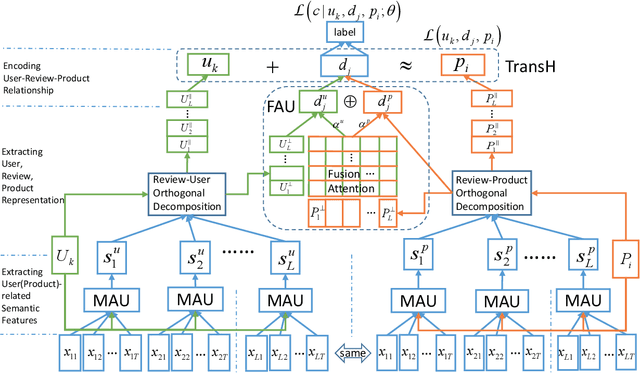

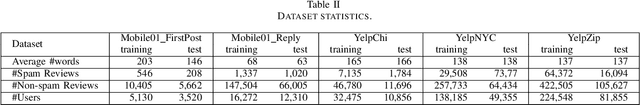
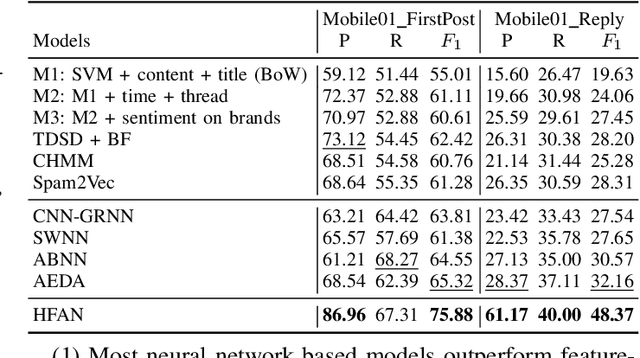
Abstract:Opinion spam has become a widespread problem in social media, where hired spammers write deceptive reviews to promote or demote products to mislead the consumers for profit or fame. Existing works mainly focus on manually designing discrete textual or behavior features, which cannot capture complex semantics of reviews. Although recent works apply deep learning methods to learn review-level semantic features, their models ignore the impact of the user-level and product-level information on learning review semantics and the inherent user-review-product relationship information. In this paper, we propose a Hierarchical Fusion Attention Network (HFAN) to automatically learn the semantics of reviews from the user and product level. Specifically, we design a multi-attention unit to extract user(product)-related review information. Then, we use orthogonal decomposition and fusion attention to learn a user, review, and product representation from the review information. Finally, we take the review as a relation between user and product entity and apply TransH to jointly encode this relationship into review representation. Experimental results obtained more than 10\% absolute precision improvement over the state-of-the-art performances on four real-world datasets, which show the effectiveness and versatility of the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge