Shangwen Lv
PAIR: Leveraging Passage-Centric Similarity Relation for Improving Dense Passage Retrieval
Aug 13, 2021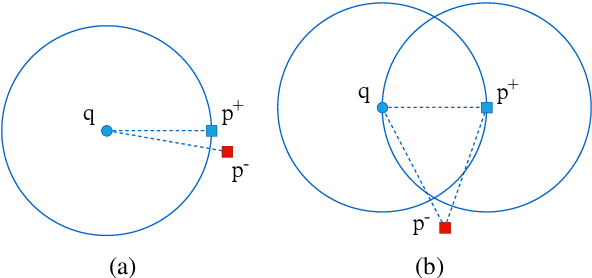
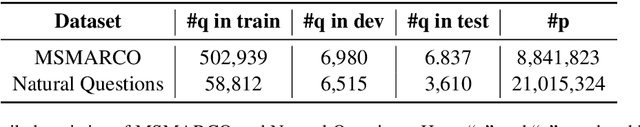
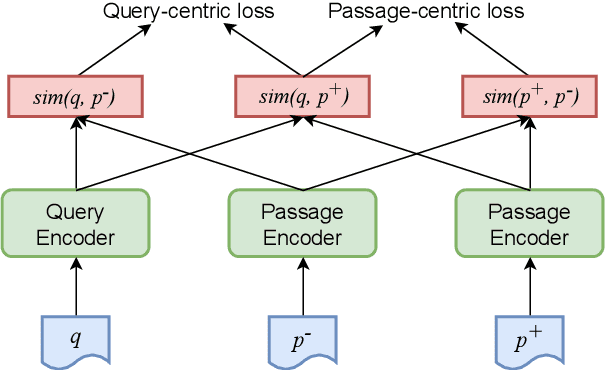
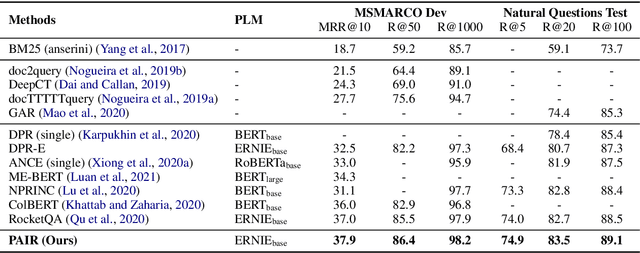
Abstract:Recently, dense passage retrieval has become a mainstream approach to finding relevant information in various natural language processing tasks. A number of studies have been devoted to improving the widely adopted dual-encoder architecture. However, most of the previous studies only consider query-centric similarity relation when learning the dual-encoder retriever. In order to capture more comprehensive similarity relations, we propose a novel approach that leverages both query-centric and PAssage-centric sImilarity Relations (called PAIR) for dense passage retrieval. To implement our approach, we make three major technical contributions by introducing formal formulations of the two kinds of similarity relations, generating high-quality pseudo labeled data via knowledge distillation, and designing an effective two-stage training procedure that incorporates passage-centric similarity relation constraint. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art models on both MSMARCO and Natural Questions datasets.
Pre-training Text Representations as Meta Learning
Apr 12, 2020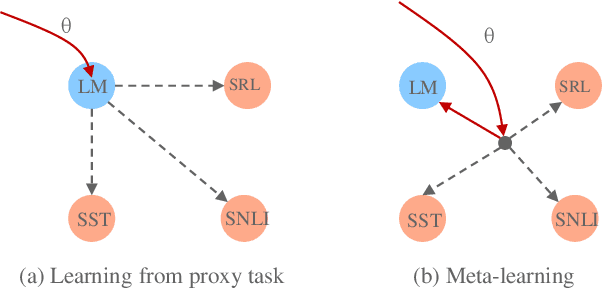
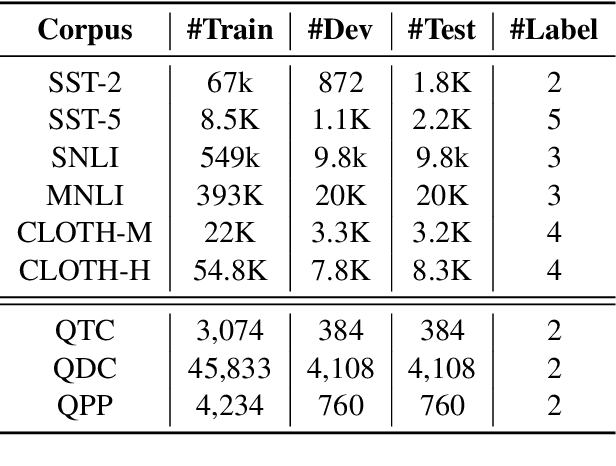
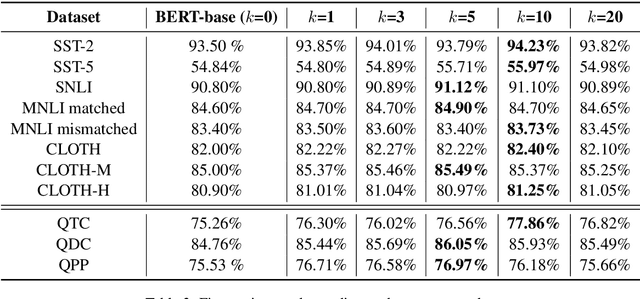
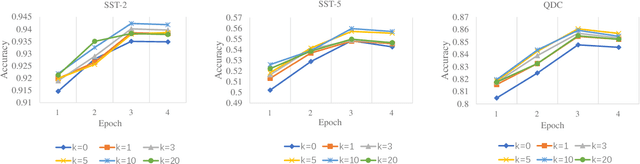
Abstract:Pre-training text representations has recently been shown to significantly improve the state-of-the-art in many natural language processing tasks. The central goal of pre-training is to learn text representations that are useful for subsequent tasks. However, existing approaches are optimized by minimizing a proxy objective, such as the negative log likelihood of language modeling. In this work, we introduce a learning algorithm which directly optimizes model's ability to learn text representations for effective learning of downstream tasks. We show that there is an intrinsic connection between multi-task pre-training and model-agnostic meta-learning with a sequence of meta-train steps. The standard multi-task learning objective adopted in BERT is a special case of our learning algorithm where the depth of meta-train is zero. We study the problem in two settings: unsupervised pre-training and supervised pre-training with different pre-training objects to verify the generality of our approach.Experimental results show that our algorithm brings improvements and learns better initializations for a variety of downstream tasks.
Learning review representations from user and product level information for spam detection
Sep 10, 2019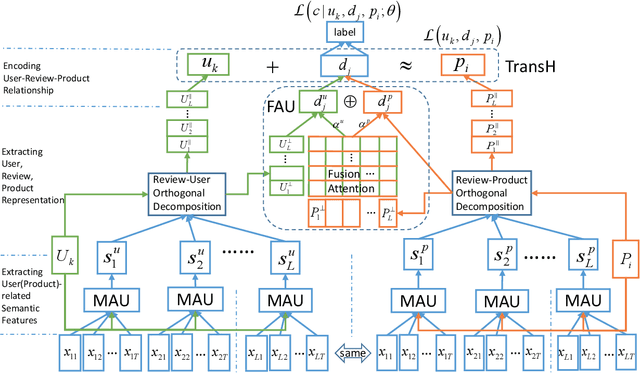

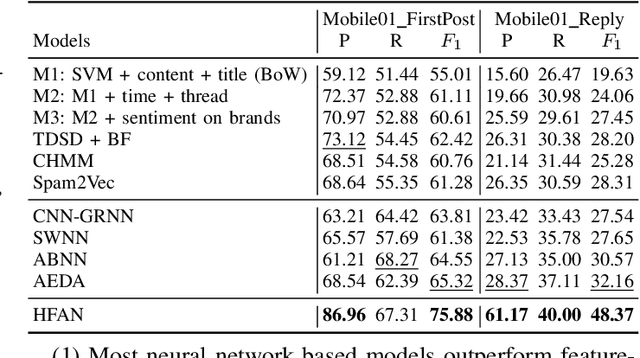
Abstract:Opinion spam has become a widespread problem in social media, where hired spammers write deceptive reviews to promote or demote products to mislead the consumers for profit or fame. Existing works mainly focus on manually designing discrete textual or behavior features, which cannot capture complex semantics of reviews. Although recent works apply deep learning methods to learn review-level semantic features, their models ignore the impact of the user-level and product-level information on learning review semantics and the inherent user-review-product relationship information. In this paper, we propose a Hierarchical Fusion Attention Network (HFAN) to automatically learn the semantics of reviews from the user and product level. Specifically, we design a multi-attention unit to extract user(product)-related review information. Then, we use orthogonal decomposition and fusion attention to learn a user, review, and product representation from the review information. Finally, we take the review as a relation between user and product entity and apply TransH to jointly encode this relationship into review representation. Experimental results obtained more than 10\% absolute precision improvement over the state-of-the-art performances on four real-world datasets, which show the effectiveness and versatility of the model.
Graph-Based Reasoning over Heterogeneous External Knowledge for Commonsense Question Answering
Sep 09, 2019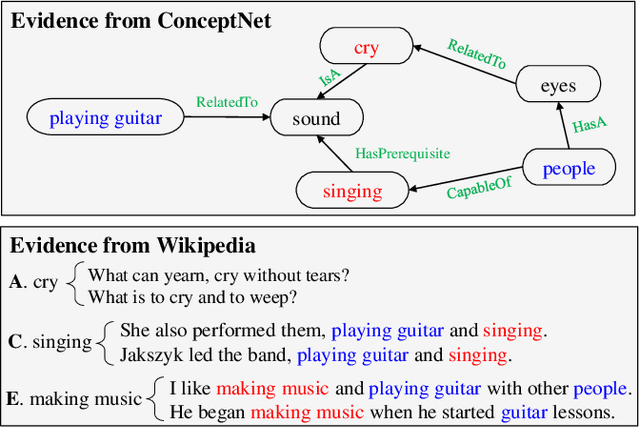
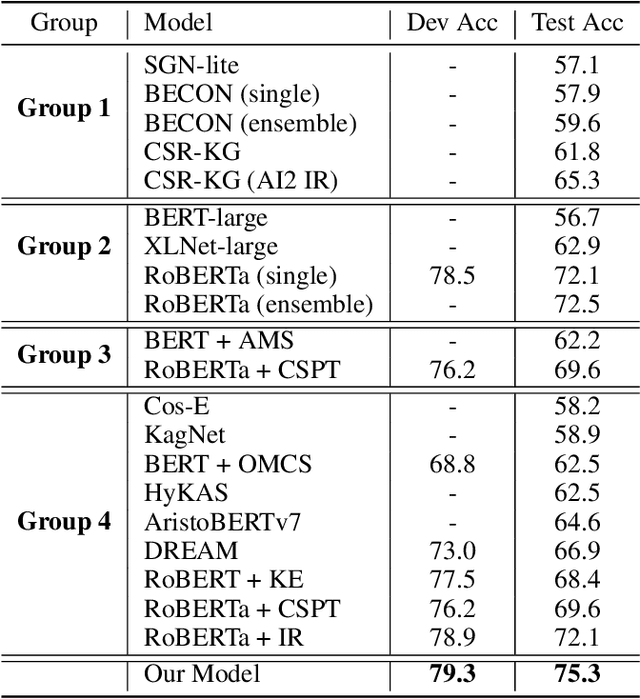
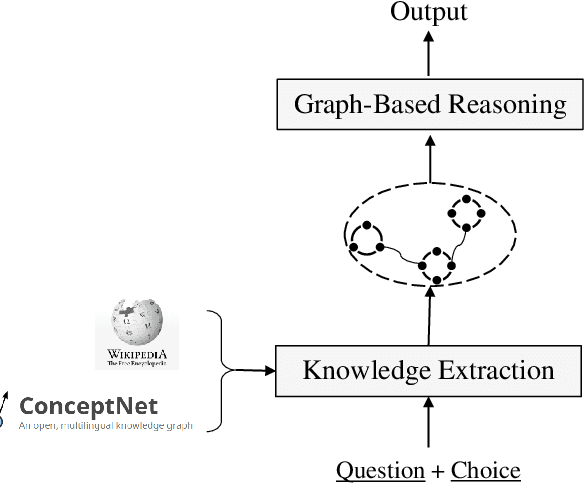

Abstract:Commonsense question answering aims to answer questions which require background knowledge that is not explicitly expressed in the question. The key challenge is how to obtain evidence from external knowledge and make predictions based on the evidence. Recent works either learn to generate evidence from human-annotated evidence which is expensive to collect, or extract evidence from either structured or unstructured knowledge bases which fails to take advantages of both sources. In this work, we propose to automatically extract evidence from heterogeneous knowledge sources, and answer questions based on the extracted evidence. Specifically, we extract evidence from both structured knowledge base (i.e. ConceptNet) and Wikipedia plain texts. We construct graphs for both sources to obtain the relational structures of evidence. Based on these graphs, we propose a graph-based approach consisting of a graph-based contextual word representation learning module and a graph-based inference module. The first module utilizes graph structural information to re-define the distance between words for learning better contextual word representations. The second module adopts graph convolutional network to encode neighbor information into the representations of nodes, and aggregates evidence with graph attention mechanism for predicting the final answer. Experimental results on CommonsenseQA dataset illustrate that our graph-based approach over both knowledge sources brings improvement over strong baselines. Our approach achieves the state-of-the-art accuracy (75.3%) on the CommonsenseQA leaderboard.
Conditional BERT Contextual Augmentation
Dec 17, 2018



Abstract:We propose a novel data augmentation method for labeled sentences called conditional BERT contextual augmentation. Data augmentation methods are often applied to prevent overfitting and improve generalization of deep neural network models. Recently proposed contextual augmentation augments labeled sentences by randomly replacing words with more varied substitutions predicted by language model. BERT demonstrates that a deep bidirectional language model is more powerful than either an unidirectional language model or the shallow concatenation of a forward and backward model. We retrofit BERT to conditional BERT by introducing a new conditional masked language model\footnote{The term "conditional masked language model" appeared once in original BERT paper, which indicates context-conditional, is equivalent to term "masked language model". In our paper, "conditional masked language model" indicates we apply extra label-conditional constraint to the "masked language model".} task. The well trained conditional BERT can be applied to enhance contextual augmentation. Experiments on six various different text classification tasks show that our method can be easily applied to both convolutional or recurrent neural networks classifier to obtain obvious improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge