Yingqi Qu
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Self-Evaluation of Large Language Model based on Glass-box Features
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:The proliferation of open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) underscores the pressing need for evaluation methods. Existing works primarily rely on external evaluators, focusing on training and prompting strategies. However, a crucial aspect - model-aware glass-box features - is overlooked. In this study, we explore the utility of glass-box features under the scenario of self-evaluation, namely applying an LLM to evaluate its own output. We investigate various glass-box feature groups and discovered that the softmax distribution serves as a reliable indicator for quality evaluation. Furthermore, we propose two strategies to enhance the evaluation by incorporating features derived from references. Experimental results on public benchmarks validate the feasibility of self-evaluation of LLMs using glass-box features.
An Empirical Study of LLM-as-a-Judge for LLM Evaluation: Fine-tuned Judge Models are Task-specific Classifiers
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:Recently, there has been a growing trend of utilizing Large Language Model (LLM) to evaluate the quality of other LLMs. Many studies have employed proprietary close-source models, especially GPT4, as the evaluator. Alternatively, other works have fine-tuned judge models based on open-source LLMs as the evaluator. In this study, we conduct an empirical study of different judge models on their evaluation capability. Our findings indicate that although the fine-tuned judge models achieve high accuracy on in-domain test sets, even surpassing GPT4, they are inherently task-specific classifiers, and their generalizability and fairness severely underperform GPT4.
BASES: Large-scale Web Search User Simulation with Large Language Model based Agents
Feb 27, 2024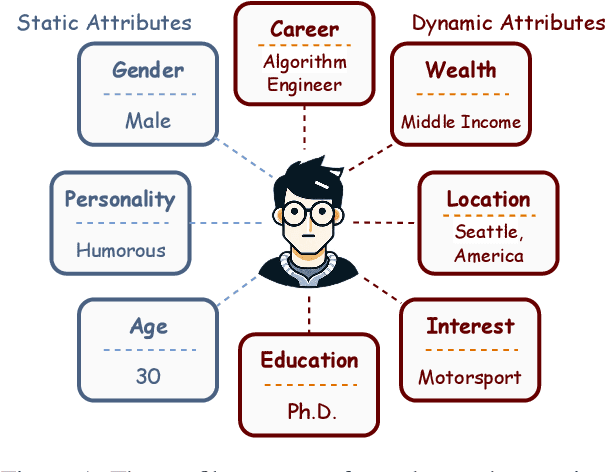
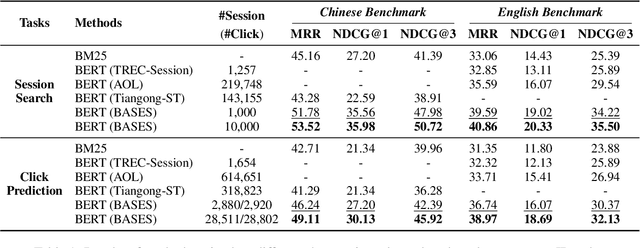
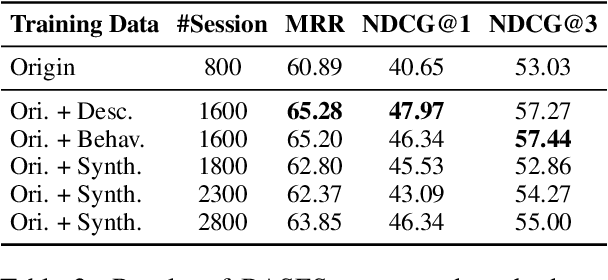
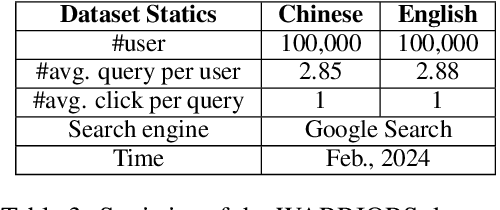
Abstract:Due to the excellent capacities of large language models (LLMs), it becomes feasible to develop LLM-based agents for reliable user simulation. Considering the scarcity and limit (e.g., privacy issues) of real user data, in this paper, we conduct large-scale user simulation for web search, to improve the analysis and modeling of user search behavior. Specially, we propose BASES, a novel user simulation framework with LLM-based agents, designed to facilitate comprehensive simulations of web search user behaviors. Our simulation framework can generate unique user profiles at scale, which subsequently leads to diverse search behaviors. To demonstrate the effectiveness of BASES, we conduct evaluation experiments based on two human benchmarks in both Chinese and English, demonstrating that BASES can effectively simulate large-scale human-like search behaviors. To further accommodate the research on web search, we develop WARRIORS, a new large-scale dataset encompassing web search user behaviors, including both Chinese and English versions, which can greatly bolster research in the field of information retrieval. Our code and data will be publicly released soon.
Investigating the Factual Knowledge Boundary of Large Language Models with Retrieval Augmentation
Jul 23, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge-intensive tasks (e.g., open-domain question answering (QA)) require a substantial amount of factual knowledge and often rely on external information for assistance. Recently, large language models (LLMs) (e.g., ChatGPT), have demonstrated impressive prowess in solving a wide range of tasks with world knowledge, including knowledge-intensive tasks. However, it remains unclear how well LLMs are able to perceive their factual knowledge boundaries, particularly how they behave when incorporating retrieval augmentation. In this study, we present an initial analysis of the factual knowledge boundaries of LLMs and how retrieval augmentation affects LLMs on open-domain QA. Specially, we focus on three primary research questions and analyze them by examining QA performance, priori judgement and posteriori judgement of LLMs. We show evidence that LLMs possess unwavering confidence in their capabilities to respond to questions and the accuracy of their responses. Furthermore, retrieval augmentation proves to be an effective approach in enhancing LLMs' awareness of knowledge boundaries, thereby improving their judgemental abilities. Additionally, we also find that LLMs have a propensity to rely on the provided retrieval results when formulating answers, while the quality of these results significantly impacts their reliance. The code to reproduce this work is available at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/LLM-Knowledge-Boundary.
A Thorough Examination on Zero-shot Dense Retrieval
Apr 27, 2022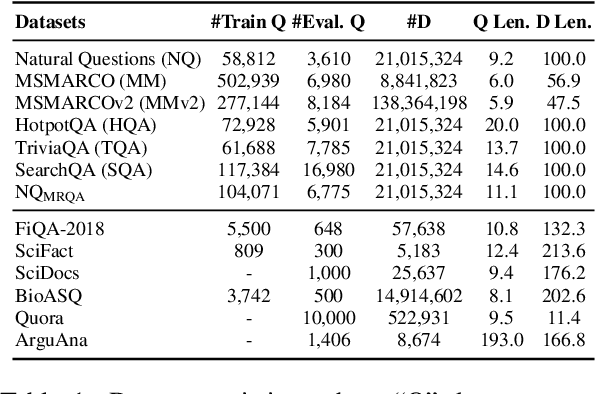
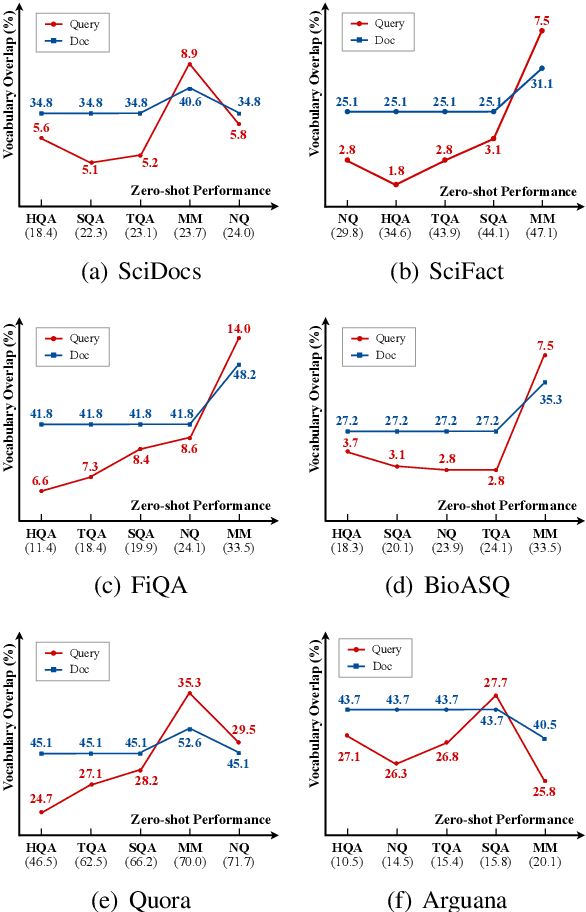
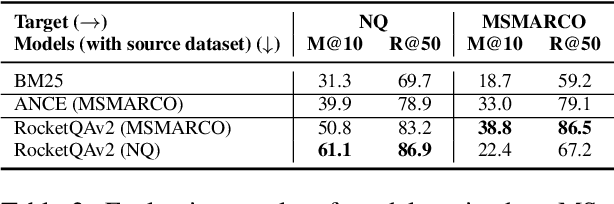
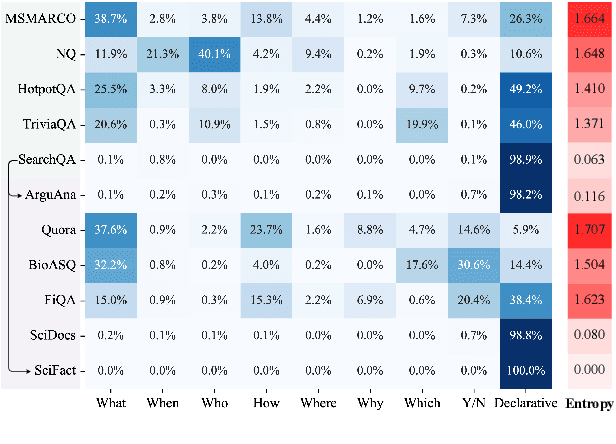
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the significant advance in dense retrieval (DR) based on powerful pre-trained language models (PLM). DR models have achieved excellent performance in several benchmark datasets, while they are shown to be not as competitive as traditional sparse retrieval models (e.g., BM25) in a zero-shot retrieval setting. However, in the related literature, there still lacks a detailed and comprehensive study on zero-shot retrieval. In this paper, we present the first thorough examination of the zero-shot capability of DR models. We aim to identify the key factors and analyze how they affect zero-shot retrieval performance. In particular, we discuss the effect of several key factors related to source training set, analyze the potential bias from the target dataset, and review and compare existing zero-shot DR models. Our findings provide important evidence to better understand and develop zero-shot DR models.
DuReader_retrieval: A Large-scale Chinese Benchmark for Passage Retrieval from Web Search Engine
Mar 19, 2022
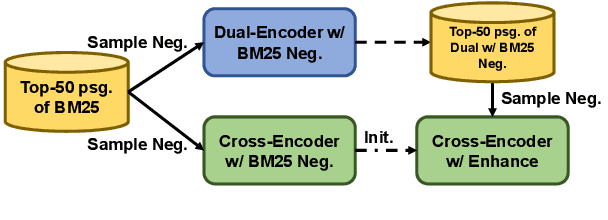
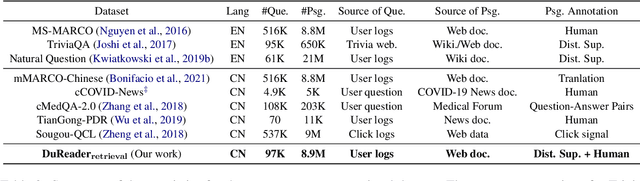
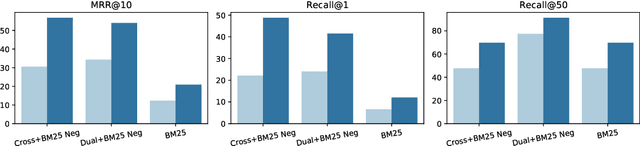
Abstract:In this paper, we present DuReader_retrieval, a large-scale Chinese dataset for passage retrieval. DuReader_retrieval contains more than 90K queries and over 8M unique passages from Baidu search. To ensure the quality of our benchmark and address the shortcomings in other existing datasets, we (1) reduce the false negatives in development and testing sets by pooling the results from multiple retrievers with human annotations, (2) and remove the semantically similar questions between training with development and testing sets. We further introduce two extra out-of-domain testing sets for benchmarking the domain generalization capability. Our experiment results demonstrate that DuReader_retrieval is challenging and there is still plenty of room for the community to improve, e.g. the generalization across domains, salient phrase and syntax mismatch between query and paragraph and robustness. DuReader_retrieval will be publicly available at https://github.com/baidu/DuReader/tree/master/DuReader-Retrieval
RocketQAv2: A Joint Training Method for Dense Passage Retrieval and Passage Re-ranking
Oct 14, 2021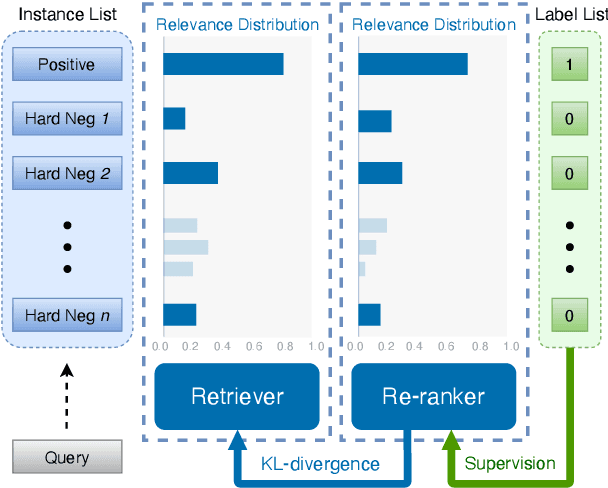
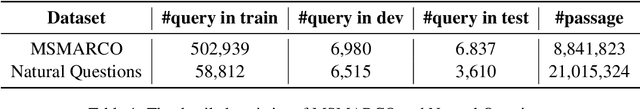
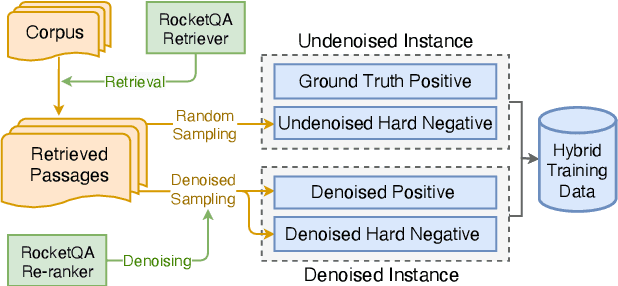
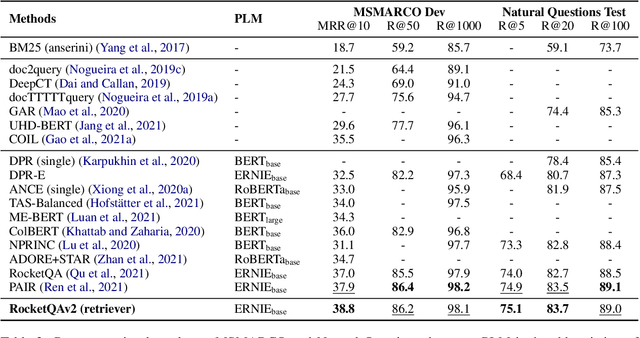
Abstract:In various natural language processing tasks, passage retrieval and passage re-ranking are two key procedures in finding and ranking relevant information. Since both the two procedures contribute to the final performance, it is important to jointly optimize them in order to achieve mutual improvement. In this paper, we propose a novel joint training approach for dense passage retrieval and passage re-ranking. A major contribution is that we introduce the dynamic listwise distillation, where we design a unified listwise training approach for both the retriever and the re-ranker. During the dynamic distillation, the retriever and the re-ranker can be adaptively improved according to each other's relevance information. We also propose a hybrid data augmentation strategy to construct diverse training instances for listwise training approach. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our approach on both MSMARCO and Natural Questions datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/RocketQA.
PAIR: Leveraging Passage-Centric Similarity Relation for Improving Dense Passage Retrieval
Aug 13, 2021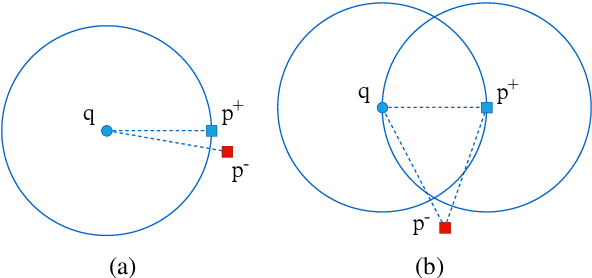
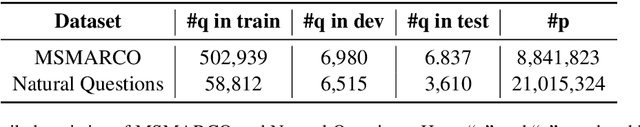
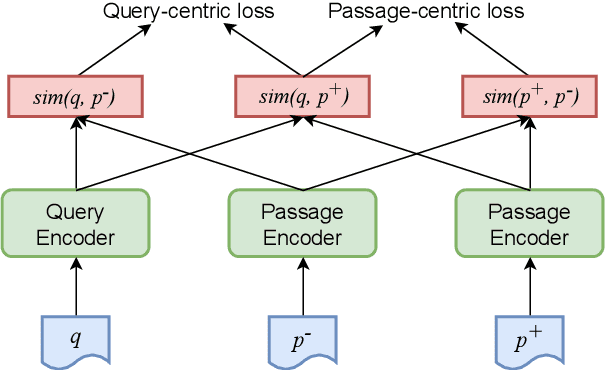
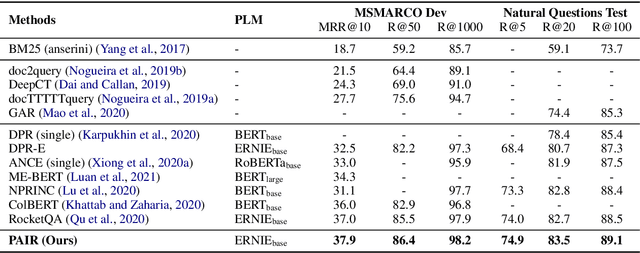
Abstract:Recently, dense passage retrieval has become a mainstream approach to finding relevant information in various natural language processing tasks. A number of studies have been devoted to improving the widely adopted dual-encoder architecture. However, most of the previous studies only consider query-centric similarity relation when learning the dual-encoder retriever. In order to capture more comprehensive similarity relations, we propose a novel approach that leverages both query-centric and PAssage-centric sImilarity Relations (called PAIR) for dense passage retrieval. To implement our approach, we make three major technical contributions by introducing formal formulations of the two kinds of similarity relations, generating high-quality pseudo labeled data via knowledge distillation, and designing an effective two-stage training procedure that incorporates passage-centric similarity relation constraint. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art models on both MSMARCO and Natural Questions datasets.
Question Answering over Freebase via Attentive RNN with Similarity Matrix based CNN
May 27, 2018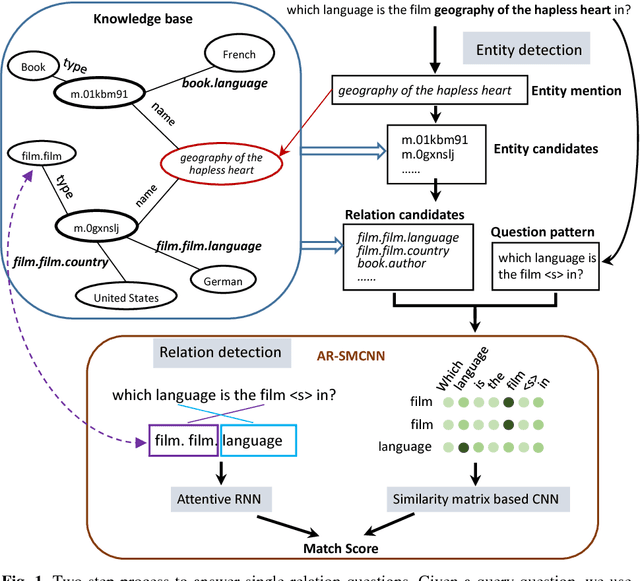
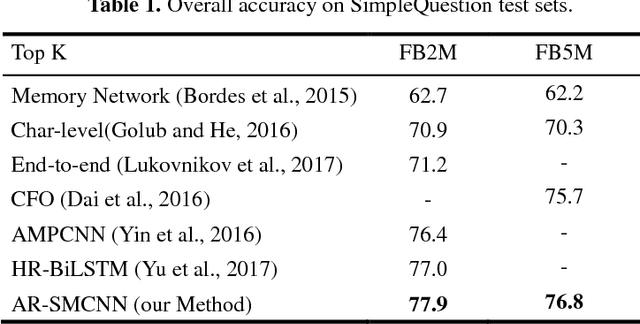
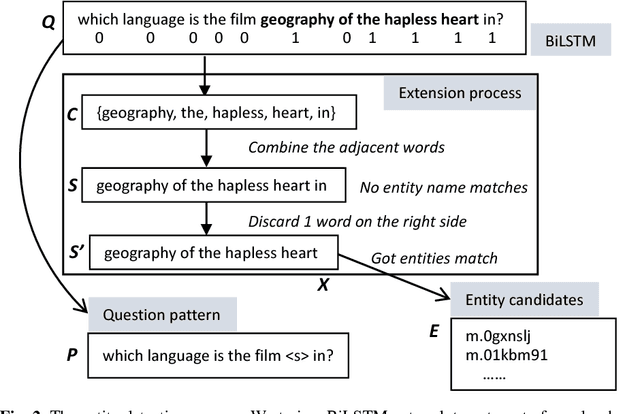
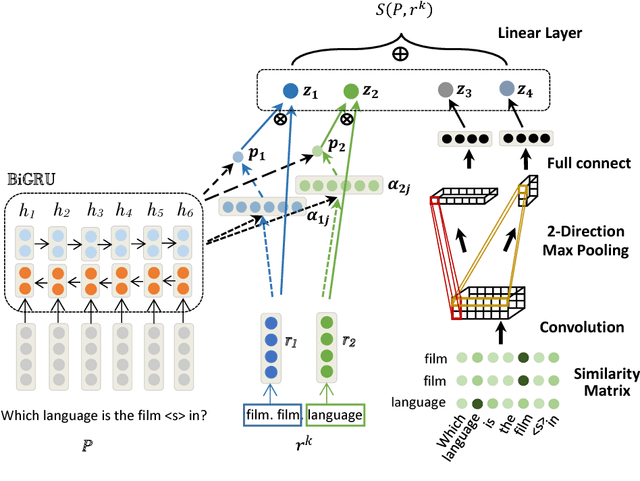
Abstract:With the rapid growth of knowledge bases (KBs), question answering over knowledge base, a.k.a. KBQA has drawn huge attention in recent years. Most of the existing KBQA methods follow so called encoder-compare framework. They map the question and the KB facts to a common embedding space, in which the similarity between the question vector and the fact vectors can be conveniently computed. This, however, inevitably loses original words interaction information. To preserve more original information, we propose an attentive recurrent neural network with similarity matrix based convolutional neural network (AR-SMCNN) model, which is able to capture comprehensive hierarchical information utilizing the advantages of both RNN and CNN. We use RNN to capture semantic-level correlation by its sequential modeling nature, and use an attention mechanism to keep track of the entities and relations simultaneously. Meanwhile, we use a similarity matrix based CNN with two-directions pooling to extract literal-level words interaction matching utilizing CNNs strength of modeling spatial correlation among data. Moreover, we have developed a new heuristic extension method for entity detection, which significantly decreases the effect of noise. Our method has outperformed the state-of-the-arts on SimpleQuestion benchmark in both accuracy and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge