Helen Yannakoudakis
Not All Code Is Equal: A Data-Centric Study of Code Complexity and LLM Reasoning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly exhibit strong reasoning abilities, often attributed to their capacity to generate chain-of-thought-style intermediate reasoning. Recent work suggests that exposure to code can further enhance these skills, but existing studies largely treat code as a generic training signal, leaving open the question of which properties of code actually contribute to improved reasoning. To address this gap, we study the structural complexity of code, which captures control flow and compositional structure that may shape how models internalise multi-step reasoning during fine-tuning. We examine two complementary settings: solution-driven complexity, where complexity varies across multiple solutions to the same problem, and problem-driven complexity, where complexity reflects variation in the underlying tasks. Using cyclomatic complexity and logical lines of code to construct controlled fine-tuning datasets, we evaluate a range of open-weight LLMs on diverse reasoning benchmarks. Our findings show that although code can improve reasoning, structural properties strongly determine its usefulness. In 83% of experiments, restricting fine-tuning data to a specific structural complexity range outperforms training on structurally diverse code, pointing to a data-centric path for improving reasoning beyond scaling.
KidsArtBench: Multi-Dimensional Children's Art Evaluation with Attribute-Aware MLLMs
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) show remarkable progress across many visual-language tasks; however, their capacity to evaluate artistic expression remains limited. Aesthetic concepts are inherently abstract and open-ended, and multimodal artwork annotations are scarce. We introduce KidsArtBench, a new benchmark of over 1k children's artworks (ages 5-15) annotated by 12 expert educators across 9 rubric-aligned dimensions, together with expert comments for feedback. Unlike prior aesthetic datasets that provide single scalar scores on adult imagery, KidsArtBench targets children's artwork and pairs multi-dimensional annotations with comment supervision to enable both ordinal assessment and formative feedback. Building on this resource, we propose an attribute-specific multi-LoRA approach, where each attribute corresponds to a distinct evaluation dimension (e.g., Realism, Imagination) in the scoring rubric, with Regression-Aware Fine-Tuning (RAFT) to align predictions with ordinal scales. On Qwen2.5-VL-7B, our method increases correlation from 0.468 to 0.653, with the largest gains on perceptual dimensions and narrowed gaps on higher-order attributes. These results show that educator-aligned supervision and attribute-aware training yield pedagogically meaningful evaluations and establish a rigorous testbed for sustained progress in educational AI. We release data and code with ethics documentation.
Donors and Recipients: On Asymmetric Transfer Across Tasks and Languages with Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Nov 17, 2025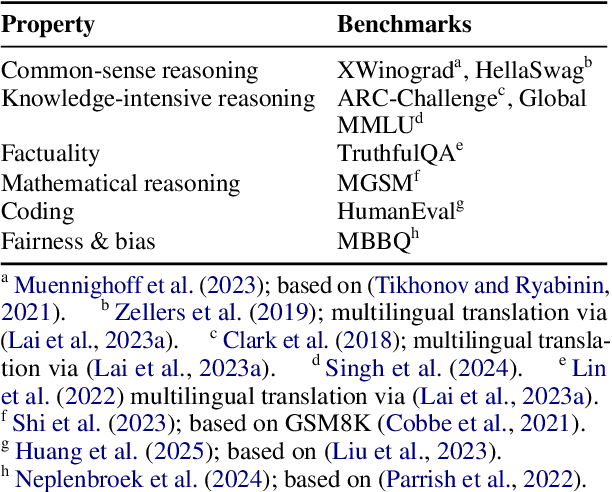
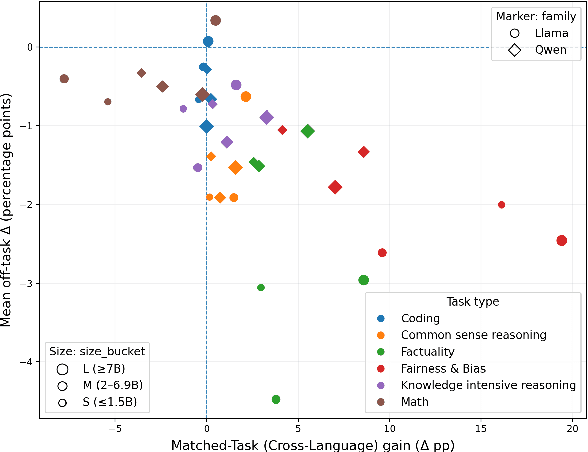
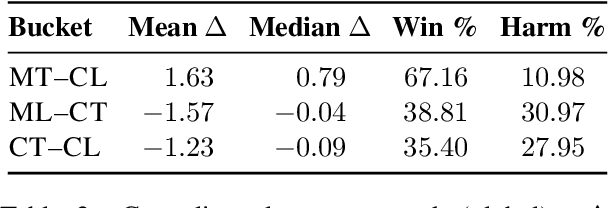
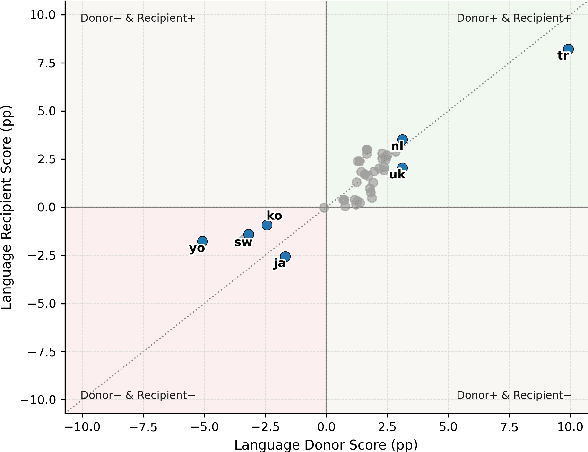
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) perform strongly across tasks and languages, yet how improvements in one task or language affect other tasks and languages and their combinations remains poorly understood. We conduct a controlled PEFT/LoRA study across multiple open-weight LLM families and sizes, treating task and language as transfer axes while conditioning on model family and size; we fine-tune each model on a single task-language source and measure transfer as the percentage-point change versus its baseline score when evaluated on all other task-language target pairs. We decompose transfer into (i) Matched-Task (Cross-Language), (ii) Matched-Language (Cross-Task), and (iii) Cross-Task (Cross-Language) regimes. We uncover two consistent general patterns. First, a pronounced on-task vs. off-task asymmetry: Matched-Task (Cross-Language) transfer is reliably positive, whereas off-task transfer often incurs collateral degradation. Second, a stable donor-recipient structure across languages and tasks (hub donors vs. brittle recipients). We outline implications for risk-aware fine-tuning and model specialisation.
A Function Centric Perspective On Flat and Sharp Minima
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Flat minima are widely believed to correlate with improved generalisation in deep neural networks. However, this connection has proven more nuanced in recent studies, with both theoretical counterexamples and empirical exceptions emerging in the literature. In this paper, we revisit the role of sharpness in model performance, proposing that sharpness is better understood as a function-dependent property rather than a reliable indicator of poor generalisation. We conduct extensive empirical studies, from single-objective optimisation to modern image classification tasks, showing that sharper minima often emerge when models are regularised (e.g., via SAM, weight decay, or data augmentation), and that these sharp minima can coincide with better generalisation, calibration, robustness, and functional consistency. Across a range of models and datasets, we find that baselines without regularisation tend to converge to flatter minima yet often perform worse across all safety metrics. Our findings demonstrate that function complexity, rather than flatness alone, governs the geometry of solutions, and that sharper minima can reflect more appropriate inductive biases (especially under regularisation), calling for a function-centric reappraisal of loss landscape geometry.
Rethinking Knowledge Distillation: A Data Dependent Regulariser With a Negative Asymmetric Payoff
Oct 14, 2025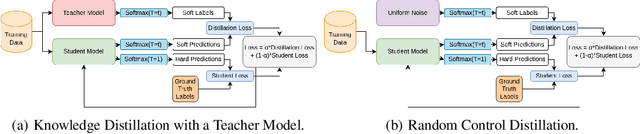

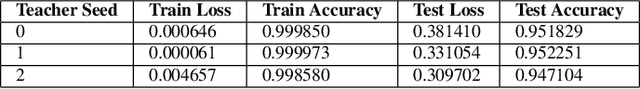
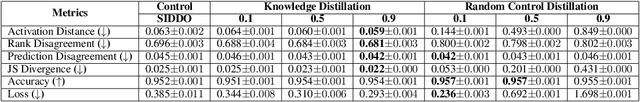
Abstract:Knowledge distillation is often considered a compression mechanism when judged on the resulting student's accuracy and loss, yet its functional impact is poorly understood. In this work, we quantify the compression capacity of knowledge distillation and the resulting knowledge transfer from a functional perspective, decoupling compression from architectural reduction, which provides an improved understanding of knowledge distillation. We employ hypothesis testing, controls, and random control distillation to understand knowledge transfer mechanisms across data modalities. To rigorously test the breadth and limits of our analyses, we explore multiple distillation variants and analyse distillation scaling laws across model sizes. Our findings demonstrate that, while there is statistically significant knowledge transfer in some modalities and architectures, the extent of this transfer is less pronounced than anticipated, even under conditions designed to maximise knowledge sharing. Notably, in cases of significant knowledge transfer, we identify a consistent and severe asymmetric transfer of negative knowledge to the student, raising safety concerns in knowledge distillation applications. Across 12 experimental setups, 9 architectures, and 7 datasets, our findings show that knowledge distillation functions less as a compression mechanism and more as a data-dependent regulariser with a negative asymmetric payoff.
Library Hallucinations in LLMs: Risk Analysis Grounded in Developer Queries
Sep 26, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used to generate code, yet they continue to hallucinate, often inventing non-existent libraries. Such library hallucinations are not just benign errors: they can mislead developers, break builds, and expose systems to supply chain threats such as slopsquatting. Despite increasing awareness of these risks, little is known about how real-world prompt variations affect hallucination rates. Therefore, we present the first systematic study of how user-level prompt variations impact library hallucinations in LLM-generated code. We evaluate six diverse LLMs across two hallucination types: library name hallucinations (invalid imports) and library member hallucinations (invalid calls from valid libraries). We investigate how realistic user language extracted from developer forums and how user errors of varying degrees (one- or multi-character misspellings and completely fake names/members) affect LLM hallucination rates. Our findings reveal systemic vulnerabilities: one-character misspellings in library names trigger hallucinations in up to 26% of tasks, fake library names are accepted in up to 99% of tasks, and time-related prompts lead to hallucinations in up to 84% of tasks. Prompt engineering shows promise for mitigating hallucinations, but remains inconsistent and LLM-dependent. Our results underscore the fragility of LLMs to natural prompt variation and highlight the urgent need for safeguards against library-related hallucinations and their potential exploitation.
A (More) Realistic Evaluation Setup for Generalisation of Community Models on Malicious Content Detection
Apr 02, 2024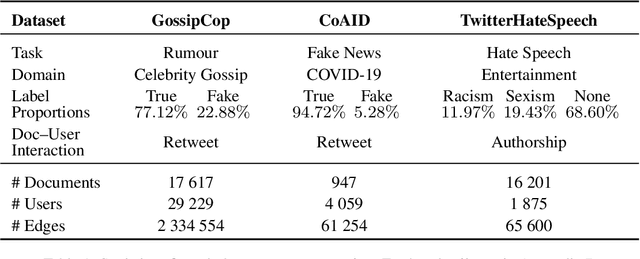
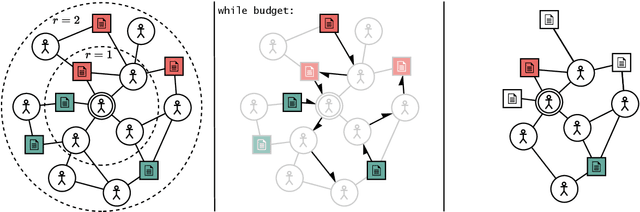
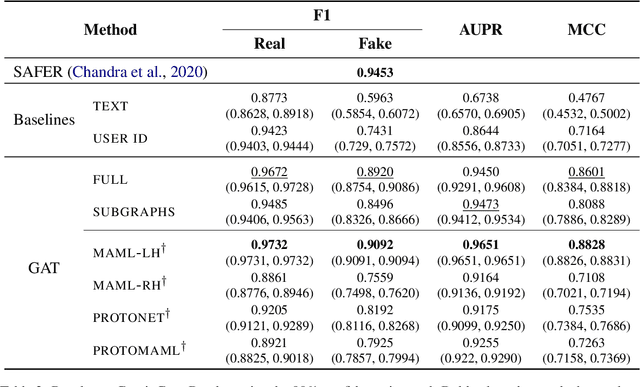
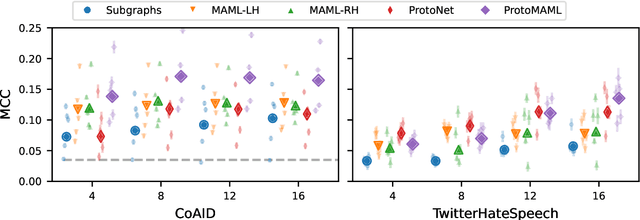
Abstract:Community models for malicious content detection, which take into account the context from a social graph alongside the content itself, have shown remarkable performance on benchmark datasets. Yet, misinformation and hate speech continue to propagate on social media networks. This mismatch can be partially attributed to the limitations of current evaluation setups that neglect the rapid evolution of online content and the underlying social graph. In this paper, we propose a novel evaluation setup for model generalisation based on our few-shot subgraph sampling approach. This setup tests for generalisation through few labelled examples in local explorations of a larger graph, emulating more realistic application settings. We show this to be a challenging inductive setup, wherein strong performance on the training graph is not indicative of performance on unseen tasks, domains, or graph structures. Lastly, we show that graph meta-learners trained with our proposed few-shot subgraph sampling outperform standard community models in the inductive setup. We make our code publicly available.
Prompting open-source and commercial language models for grammatical error correction of English learner text
Jan 15, 2024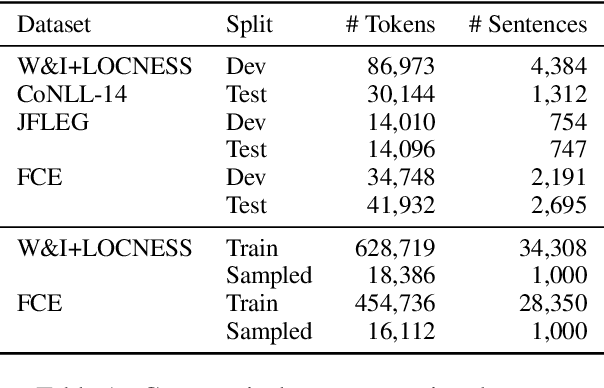
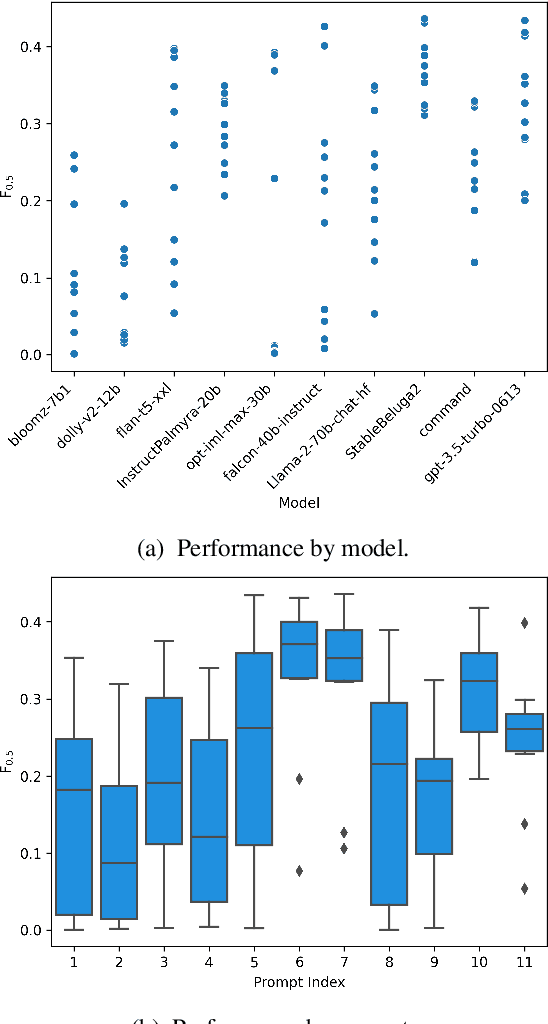

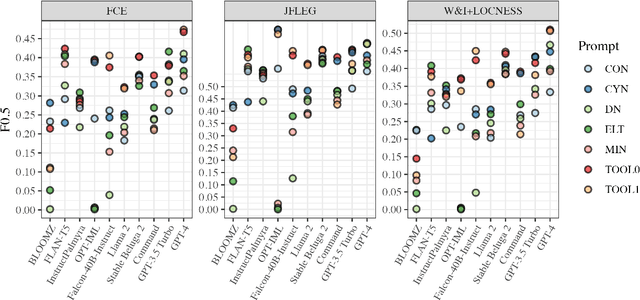
Abstract:Thanks to recent advances in generative AI, we are able to prompt large language models (LLMs) to produce texts which are fluent and grammatical. In addition, it has been shown that we can elicit attempts at grammatical error correction (GEC) from LLMs when prompted with ungrammatical input sentences. We evaluate how well LLMs can perform at GEC by measuring their performance on established benchmark datasets. We go beyond previous studies, which only examined GPT* models on a selection of English GEC datasets, by evaluating seven open-source and three commercial LLMs on four established GEC benchmarks. We investigate model performance and report results against individual error types. Our results indicate that LLMs do not always outperform supervised English GEC models except in specific contexts -- namely commercial LLMs on benchmarks annotated with fluency corrections as opposed to minimal edits. We find that several open-source models outperform commercial ones on minimal edit benchmarks, and that in some settings zero-shot prompting is just as competitive as few-shot prompting.
On the application of Large Language Models for language teaching and assessment technology
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:The recent release of very large language models such as PaLM and GPT-4 has made an unprecedented impact in the popular media and public consciousness, giving rise to a mixture of excitement and fear as to their capabilities and potential uses, and shining a light on natural language processing research which had not previously received so much attention. The developments offer great promise for education technology, and in this paper we look specifically at the potential for incorporating large language models in AI-driven language teaching and assessment systems. We consider several research areas and also discuss the risks and ethical considerations surrounding generative AI in education technology for language learners. Overall we find that larger language models offer improvements over previous models in text generation, opening up routes toward content generation which had not previously been plausible. For text generation they must be prompted carefully and their outputs may need to be reshaped before they are ready for use. For automated grading and grammatical error correction, tasks whose progress is checked on well-known benchmarks, early investigations indicate that large language models on their own do not improve on state-of-the-art results according to standard evaluation metrics. For grading it appears that linguistic features established in the literature should still be used for best performance, and for error correction it may be that the models can offer alternative feedback styles which are not measured sensitively with existing methods. In all cases, there is work to be done to experiment with the inclusion of large language models in education technology for language learners, in order to properly understand and report on their capacities and limitations, and to ensure that foreseeable risks such as misinformation and harmful bias are mitigated.
Finding the Needle in a Haystack: Unsupervised Rationale Extraction from Long Text Classifiers
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Long-sequence transformers are designed to improve the representation of longer texts by language models and their performance on downstream document-level tasks. However, not much is understood about the quality of token-level predictions in long-form models. We investigate the performance of such architectures in the context of document classification with unsupervised rationale extraction. We find standard soft attention methods to perform significantly worse when combined with the Longformer language model. We propose a compositional soft attention architecture that applies RoBERTa sentence-wise to extract plausible rationales at the token-level. We find this method to significantly outperform Longformer-driven baselines on sentiment classification datasets, while also exhibiting significantly lower runtimes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge