Christopher Davis
GaRAGe: A Benchmark with Grounding Annotations for RAG Evaluation
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:We present GaRAGe, a large RAG benchmark with human-curated long-form answers and annotations of each grounding passage, allowing a fine-grained evaluation of whether LLMs can identify relevant grounding when generating RAG answers. Our benchmark contains 2366 questions of diverse complexity, dynamism, and topics, and includes over 35K annotated passages retrieved from both private document sets and the Web, to reflect real-world RAG use cases. This makes it an ideal test bed to evaluate an LLM's ability to identify only the relevant information necessary to compose a response, or provide a deflective response when there is insufficient information. Evaluations of multiple state-of-the-art LLMs on GaRAGe show that the models tend to over-summarise rather than (a) ground their answers strictly on the annotated relevant passages (reaching at most a Relevance-Aware Factuality Score of 60%), or (b) deflect when no relevant grounding is available (reaching at most 31% true positive rate in deflections). The F1 in attribution to relevant sources is at most 58.9%, and we show that performance is particularly reduced when answering time-sensitive questions and when having to draw knowledge from sparser private grounding sources.
Prompting open-source and commercial language models for grammatical error correction of English learner text
Jan 15, 2024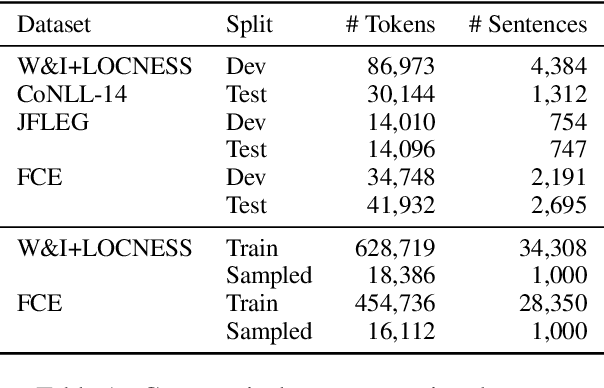
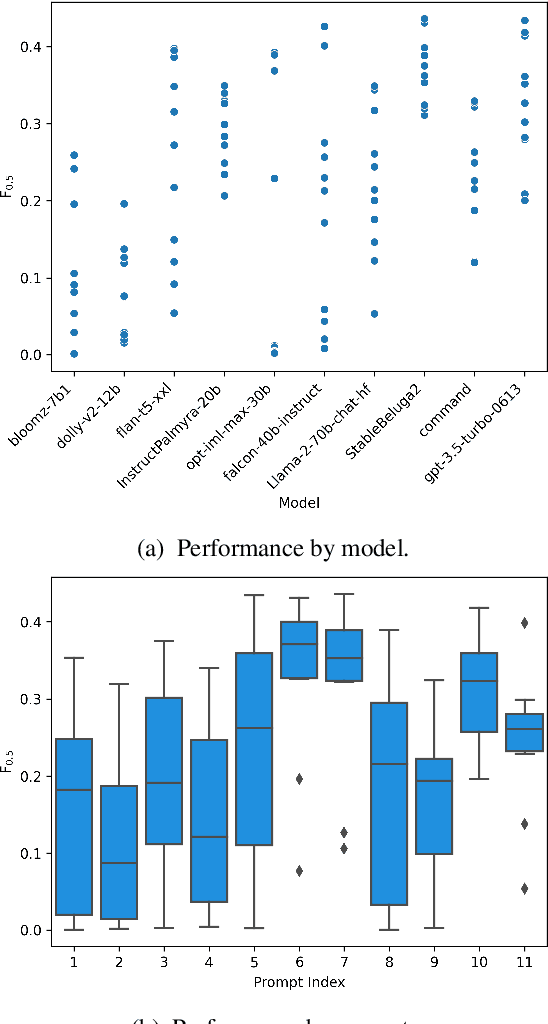

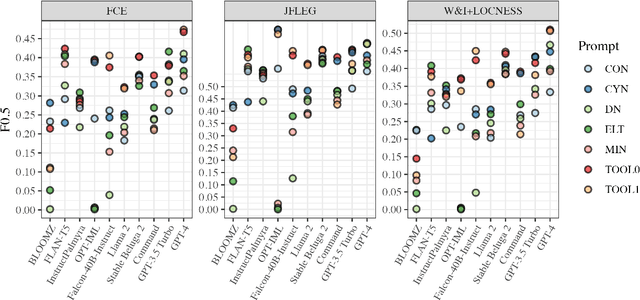
Abstract:Thanks to recent advances in generative AI, we are able to prompt large language models (LLMs) to produce texts which are fluent and grammatical. In addition, it has been shown that we can elicit attempts at grammatical error correction (GEC) from LLMs when prompted with ungrammatical input sentences. We evaluate how well LLMs can perform at GEC by measuring their performance on established benchmark datasets. We go beyond previous studies, which only examined GPT* models on a selection of English GEC datasets, by evaluating seven open-source and three commercial LLMs on four established GEC benchmarks. We investigate model performance and report results against individual error types. Our results indicate that LLMs do not always outperform supervised English GEC models except in specific contexts -- namely commercial LLMs on benchmarks annotated with fluency corrections as opposed to minimal edits. We find that several open-source models outperform commercial ones on minimal edit benchmarks, and that in some settings zero-shot prompting is just as competitive as few-shot prompting.
CLIMB: Curriculum Learning for Infant-inspired Model Building
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:We describe our team's contribution to the STRICT-SMALL track of the BabyLM Challenge. The challenge requires training a language model from scratch using only a relatively small training dataset of ten million words. We experiment with three variants of cognitively-motivated curriculum learning and analyze their effect on the performance of the model on linguistic evaluation tasks. In the vocabulary curriculum, we analyze methods for constraining the vocabulary in the early stages of training to simulate cognitively more plausible learning curves. In the data curriculum experiments, we vary the order of the training instances based on i) infant-inspired expectations and ii) the learning behavior of the model. In the objective curriculum, we explore different variations of combining the conventional masked language modeling task with a more coarse-grained word class prediction task to reinforce linguistic generalization capabilities. Our results did not yield consistent improvements over our own non-curriculum learning baseline across a range of linguistic benchmarks; however, we do find marginal gains on select tasks. Our analysis highlights key takeaways for specific combinations of tasks and settings which benefit from our proposed curricula. We moreover determine that careful selection of model architecture, and training hyper-parameters yield substantial improvements over the default baselines provided by the BabyLM challenge.
On the application of Large Language Models for language teaching and assessment technology
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:The recent release of very large language models such as PaLM and GPT-4 has made an unprecedented impact in the popular media and public consciousness, giving rise to a mixture of excitement and fear as to their capabilities and potential uses, and shining a light on natural language processing research which had not previously received so much attention. The developments offer great promise for education technology, and in this paper we look specifically at the potential for incorporating large language models in AI-driven language teaching and assessment systems. We consider several research areas and also discuss the risks and ethical considerations surrounding generative AI in education technology for language learners. Overall we find that larger language models offer improvements over previous models in text generation, opening up routes toward content generation which had not previously been plausible. For text generation they must be prompted carefully and their outputs may need to be reshaped before they are ready for use. For automated grading and grammatical error correction, tasks whose progress is checked on well-known benchmarks, early investigations indicate that large language models on their own do not improve on state-of-the-art results according to standard evaluation metrics. For grading it appears that linguistic features established in the literature should still be used for best performance, and for error correction it may be that the models can offer alternative feedback styles which are not measured sensitively with existing methods. In all cases, there is work to be done to experiment with the inclusion of large language models in education technology for language learners, in order to properly understand and report on their capacities and limitations, and to ensure that foreseeable risks such as misinformation and harmful bias are mitigated.
Probing for targeted syntactic knowledge through grammatical error detection
Oct 28, 2022



Abstract:Targeted studies testing knowledge of subject-verb agreement (SVA) indicate that pre-trained language models encode syntactic information. We assert that if models robustly encode subject-verb agreement, they should be able to identify when agreement is correct and when it is incorrect. To that end, we propose grammatical error detection as a diagnostic probe to evaluate token-level contextual representations for their knowledge of SVA. We evaluate contextual representations at each layer from five pre-trained English language models: BERT, XLNet, GPT-2, RoBERTa, and ELECTRA. We leverage public annotated training data from both English second language learners and Wikipedia edits, and report results on manually crafted stimuli for subject-verb agreement. We find that masked language models linearly encode information relevant to the detection of SVA errors, while the autoregressive models perform on par with our baseline. However, we also observe a divergence in performance when probes are trained on different training sets, and when they are evaluated on different syntactic constructions, suggesting the information pertaining to SVA error detection is not robustly encoded.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge