Haoran Huang
DACO: Towards Application-Driven and Comprehensive Data Analysis via Code Generation
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Data analysis is a crucial analytical process to generate in-depth studies and conclusive insights to comprehensively answer a given user query for tabular data. In this work, we aim to propose new resources and benchmarks to inspire future research on this crucial yet challenging and under-explored task. However, collecting data analysis annotations curated by experts can be prohibitively expensive. We propose to automatically generate high-quality answer annotations leveraging the code-generation capabilities of LLMs with a multi-turn prompting technique. We construct the DACO dataset, containing (1) 440 databases (of tabular data) collected from real-world scenarios, (2) ~2k query-answer pairs that can serve as weak supervision for model training, and (3) a concentrated but high-quality test set with human refined annotations that serves as our main evaluation benchmark. We train a 6B supervised fine-tuning (SFT) model on DACO dataset, and find that the SFT model learns reasonable data analysis capabilities. To further align the models with human preference, we use reinforcement learning to encourage generating analysis perceived by human as helpful, and design a set of dense rewards to propagate the sparse human preference reward to intermediate code generation steps. Our DACO-RL algorithm is evaluated by human annotators to produce more helpful answers than SFT model in 57.72% cases, validating the effectiveness of our proposed algorithm. Data and code are released at https://github.com/shirley-wu/daco
Improving Generalization of Alignment with Human Preferences through Group Invariant Learning
Oct 19, 2023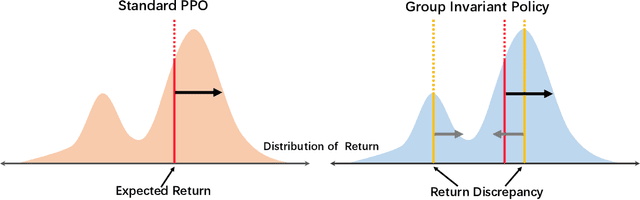


Abstract:The success of AI assistants based on language models (LLMs) hinges crucially on Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), which enables the generation of responses more aligned with human preferences. As universal AI assistants, there's a growing expectation for them to perform consistently across various domains. However, previous work shows that Reinforcement Learning (RL) often exploits shortcuts to attain high rewards and overlooks challenging samples. This focus on quick reward gains undermines both the stability in training and the model's ability to generalize to new, unseen data. In this work, we propose a novel approach that can learn a consistent policy via RL across various data groups or domains. Given the challenges associated with acquiring group annotations, our method automatically classifies data into different groups, deliberately maximizing performance variance. Then, we optimize the policy to perform well on challenging groups. Lastly, leveraging the established groups, our approach adaptively adjusts the exploration space, allocating more learning capacity to more challenging data and preventing the model from over-optimizing on simpler data. Experimental results indicate that our approach significantly enhances training stability and model generalization.
Secrets of RLHF in Large Language Models Part I: PPO
Jul 18, 2023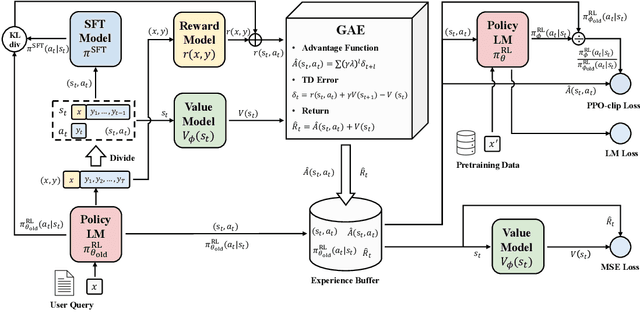



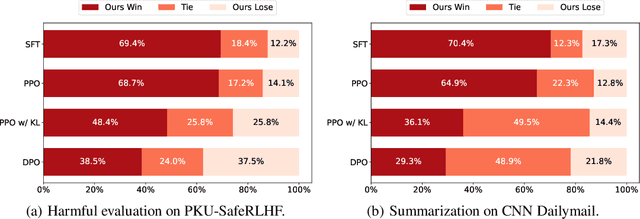
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have formulated a blueprint for the advancement of artificial general intelligence. Its primary objective is to function as a human-centric (helpful, honest, and harmless) assistant. Alignment with humans assumes paramount significance, and reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) emerges as the pivotal technological paradigm underpinning this pursuit. Current technical routes usually include \textbf{reward models} to measure human preferences, \textbf{Proximal Policy Optimization} (PPO) to optimize policy model outputs, and \textbf{process supervision} to improve step-by-step reasoning capabilities. However, due to the challenges of reward design, environment interaction, and agent training, coupled with huge trial and error cost of large language models, there is a significant barrier for AI researchers to motivate the development of technical alignment and safe landing of LLMs. The stable training of RLHF has still been a puzzle. In the first report, we dissect the framework of RLHF, re-evaluate the inner workings of PPO, and explore how the parts comprising PPO algorithms impact policy agent training. We identify policy constraints being the key factor for the effective implementation of the PPO algorithm. Therefore, we explore the PPO-max, an advanced version of PPO algorithm, to efficiently improve the training stability of the policy model. Based on our main results, we perform a comprehensive analysis of RLHF abilities compared with SFT models and ChatGPT. The absence of open-source implementations has posed significant challenges to the investigation of LLMs alignment. Therefore, we are eager to release technical reports, reward models and PPO codes, aiming to make modest contributions to the advancement of LLMs.
Two-Level Supervised Contrastive Learning for Response Selection in Multi-Turn Dialogue
Mar 01, 2022


Abstract:Selecting an appropriate response from many candidates given the utterances in a multi-turn dialogue is the key problem for a retrieval-based dialogue system. Existing work formalizes the task as matching between the utterances and a candidate and uses the cross-entropy loss in learning of the model. This paper applies contrastive learning to the problem by using the supervised contrastive loss. In this way, the learned representations of positive examples and representations of negative examples can be more distantly separated in the embedding space, and the performance of matching can be enhanced. We further develop a new method for supervised contrastive learning, referred to as two-level supervised contrastive learning, and employ the method in response selection in multi-turn dialogue. Our method exploits two techniques: sentence token shuffling (STS) and sentence re-ordering (SR) for supervised contrastive learning. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the contrastive learning baseline and the state-of-the-art methods for the task.
Spelling Error Correction with Soft-Masked BERT
May 15, 2020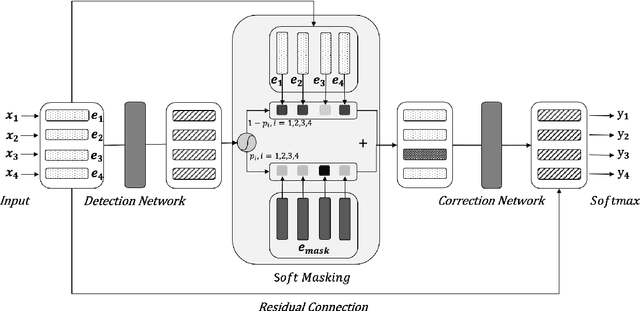
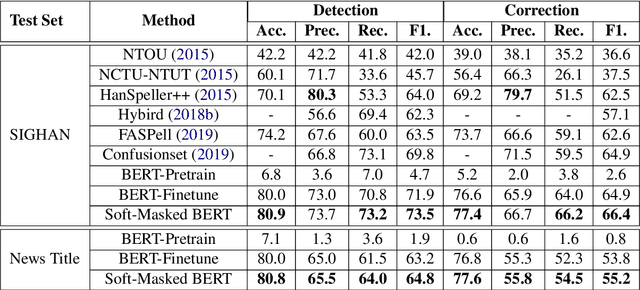
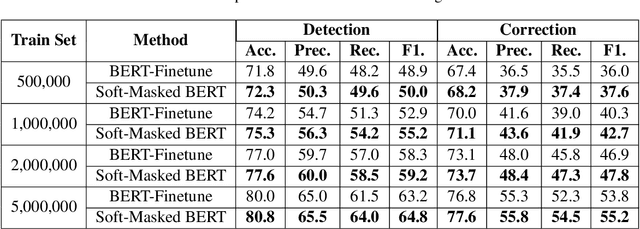
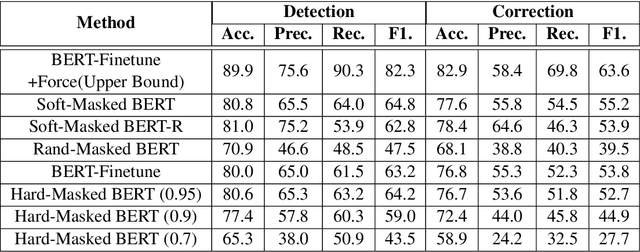
Abstract:Spelling error correction is an important yet challenging task because a satisfactory solution of it essentially needs human-level language understanding ability. Without loss of generality we consider Chinese spelling error correction (CSC) in this paper. A state-of-the-art method for the task selects a character from a list of candidates for correction (including non-correction) at each position of the sentence on the basis of BERT, the language representation model. The accuracy of the method can be sub-optimal, however, because BERT does not have sufficient capability to detect whether there is an error at each position, apparently due to the way of pre-training it using mask language modeling. In this work, we propose a novel neural architecture to address the aforementioned issue, which consists of a network for error detection and a network for error correction based on BERT, with the former being connected to the latter with what we call soft-masking technique. Our method of using `Soft-Masked BERT' is general, and it may be employed in other language detection-correction problems. Experimental results on two datasets demonstrate that the performance of our proposed method is significantly better than the baselines including the one solely based on BERT.
Query Answering with Inconsistent Existential Rules under Stable Model Semantics
Feb 18, 2016

Abstract:Traditional inconsistency-tolerent query answering in ontology-based data access relies on selecting maximal components of an ABox/database which are consistent with the ontology. However, some rules in ontologies might be unreliable if they are extracted from ontology learning or written by unskillful knowledge engineers. In this paper we present a framework of handling inconsistent existential rules under stable model semantics, which is defined by a notion called rule repairs to select maximal components of the existential rules. Surprisingly, for R-acyclic existential rules with R-stratified or guarded existential rules with stratified negations, both the data complexity and combined complexity of query answering under the rule {repair semantics} remain the same as that under the conventional query answering semantics. This leads us to propose several approaches to handle the rule {repair semantics} by calling answer set programming solvers. An experimental evaluation shows that these approaches have good scalability of query answering under rule repairs on realistic cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge