Hannah Rashkin
Shammie
Evaluating LLMs for Targeted Concept Simplification forDomain-Specific Texts
Oct 28, 2024


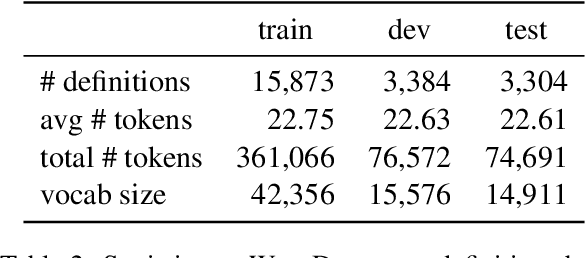
Abstract:One useful application of NLP models is to support people in reading complex text from unfamiliar domains (e.g., scientific articles). Simplifying the entire text makes it understandable but sometimes removes important details. On the contrary, helping adult readers understand difficult concepts in context can enhance their vocabulary and knowledge. In a preliminary human study, we first identify that lack of context and unfamiliarity with difficult concepts is a major reason for adult readers' difficulty with domain-specific text. We then introduce "targeted concept simplification," a simplification task for rewriting text to help readers comprehend text containing unfamiliar concepts. We also introduce WikiDomains, a new dataset of 22k definitions from 13 academic domains paired with a difficult concept within each definition. We benchmark the performance of open-source and commercial LLMs and a simple dictionary baseline on this task across human judgments of ease of understanding and meaning preservation. Interestingly, our human judges preferred explanations about the difficult concept more than simplification of the concept phrase. Further, no single model achieved superior performance across all quality dimensions, and automated metrics also show low correlations with human evaluations of concept simplification ($\sim0.2$), opening up rich avenues for research on personalized human reading comprehension support.
Can Few-shot Work in Long-Context? Recycling the Context to Generate Demonstrations
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Despite recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), their performance on tasks involving long contexts remains sub-optimal. In-Context Learning (ICL) with few-shot examples may be an appealing solution to enhance LLM performance in this scenario; However, naively adding ICL examples with long context introduces challenges, including substantial token overhead added for each few-shot example and context mismatch between the demonstrations and the target query. In this work, we propose to automatically generate few-shot examples for long context QA tasks by recycling contexts. Specifically, given a long input context (1-3k tokens) and a query, we generate additional query-output pairs from the given context as few-shot examples, while introducing the context only once. This ensures that the demonstrations are leveraging the same context as the target query while only adding a small number of tokens to the prompt. We further enhance each demonstration by instructing the model to explicitly identify the relevant paragraphs before the answer, which improves performance while providing fine-grained attribution to the answer source. We apply our method on multiple LLMs and obtain substantial improvements on various QA datasets with long context, especially when the answer lies within the middle of the context. Surprisingly, despite introducing only single-hop ICL examples, LLMs also successfully generalize to multi-hop long-context QA using our approach.
Investigating Content Planning for Navigating Trade-offs in Knowledge-Grounded Dialogue
Feb 03, 2024Abstract:Knowledge-grounded dialogue generation is a challenging task because it requires satisfying two fundamental yet often competing constraints: being responsive in a manner that is specific to what the conversation partner has said while also being attributable to an underlying source document. In this work, we bring this trade-off between these two objectives (specificity and attribution) to light and ask the question: Can explicit content planning before the response generation help the model to address this challenge? To answer this question, we design a framework called PLEDGE, which allows us to experiment with various plan variables explored in prior work, supporting both metric-agnostic and metric-aware approaches. While content planning shows promise, our results on whether it can actually help to navigate this trade-off are mixed -- planning mechanisms that are metric-aware (use automatic metrics during training) are better at automatic evaluations but underperform in human judgment compared to metric-agnostic mechanisms. We discuss how this may be caused by over-fitting to automatic metrics and the need for future work to better calibrate these metrics towards human judgment. We hope the observations from our analysis will inform future work that aims to apply content planning in this context.
Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models
Jun 10, 2022Abstract:Language models demonstrate both quantitative improvement and new qualitative capabilities with increasing scale. Despite their potentially transformative impact, these new capabilities are as yet poorly characterized. In order to inform future research, prepare for disruptive new model capabilities, and ameliorate socially harmful effects, it is vital that we understand the present and near-future capabilities and limitations of language models. To address this challenge, we introduce the Beyond the Imitation Game benchmark (BIG-bench). BIG-bench currently consists of 204 tasks, contributed by 442 authors across 132 institutions. Task topics are diverse, drawing problems from linguistics, childhood development, math, common-sense reasoning, biology, physics, social bias, software development, and beyond. BIG-bench focuses on tasks that are believed to be beyond the capabilities of current language models. We evaluate the behavior of OpenAI's GPT models, Google-internal dense transformer architectures, and Switch-style sparse transformers on BIG-bench, across model sizes spanning millions to hundreds of billions of parameters. In addition, a team of human expert raters performed all tasks in order to provide a strong baseline. Findings include: model performance and calibration both improve with scale, but are poor in absolute terms (and when compared with rater performance); performance is remarkably similar across model classes, though with benefits from sparsity; tasks that improve gradually and predictably commonly involve a large knowledge or memorization component, whereas tasks that exhibit "breakthrough" behavior at a critical scale often involve multiple steps or components, or brittle metrics; social bias typically increases with scale in settings with ambiguous context, but this can be improved with prompting.
Measuring Attribution in Natural Language Generation Models
Dec 23, 2021

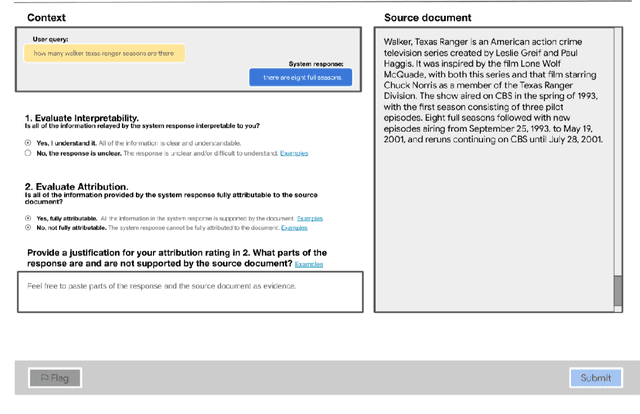
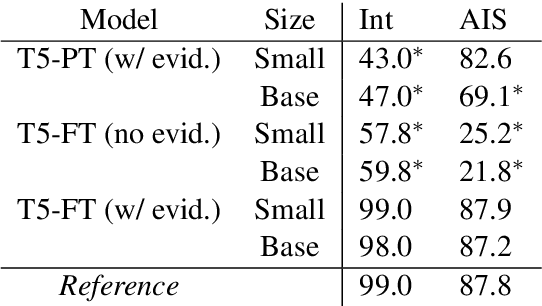
Abstract:With recent improvements in natural language generation (NLG) models for various applications, it has become imperative to have the means to identify and evaluate whether NLG output is only sharing verifiable information about the external world. In this work, we present a new evaluation framework entitled Attributable to Identified Sources (AIS) for assessing the output of natural language generation models, when such output pertains to the external world. We first define AIS and introduce a two-stage annotation pipeline for allowing annotators to appropriately evaluate model output according to AIS guidelines. We empirically validate this approach on three generation datasets (two in the conversational QA domain and one in summarization) via human evaluation studies that suggest that AIS could serve as a common framework for measuring whether model-generated statements are supported by underlying sources. We release guidelines for the human evaluation studies.
CONQRR: Conversational Query Rewriting for Retrieval with Reinforcement Learning
Dec 16, 2021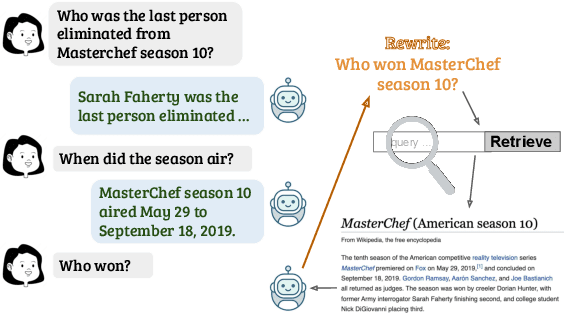
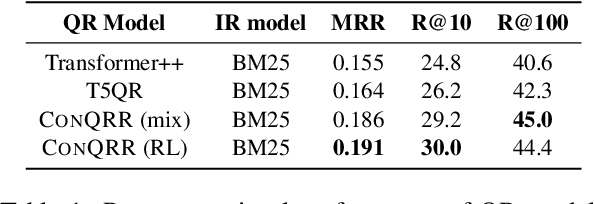
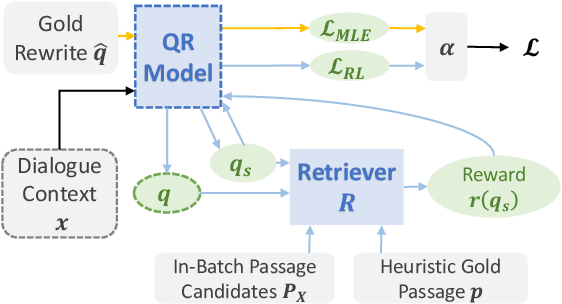
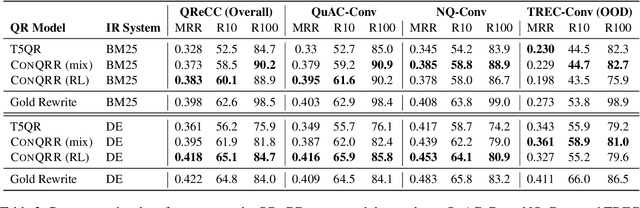
Abstract:For open-domain conversational question answering (CQA), it is important to retrieve the most relevant passages to answer a question, but this is challenging compared with standard passage retrieval because it requires understanding the full dialogue context rather than a single query. Moreover, it can be expensive to re-train well-established retrievers such as search engines that are originally developed for non-conversational queries. To facilitate their use, we develop a query rewriting model CONQRR that rewrites a conversational question in context into a standalone question. It is trained with a novel reward function to directly optimize towards retrieval and can be adapted to any fixed blackbox retriever using reinforcement learning. We show that CONQRR achieves state-of-the-art results on a recent open-domain CQA dataset, a combination of conversations from three different sources. We also conduct extensive experiments to show the effectiveness of CONQRR for any given fixed retriever.
Increasing Faithfulness in Knowledge-Grounded Dialogue with Controllable Features
Jul 14, 2021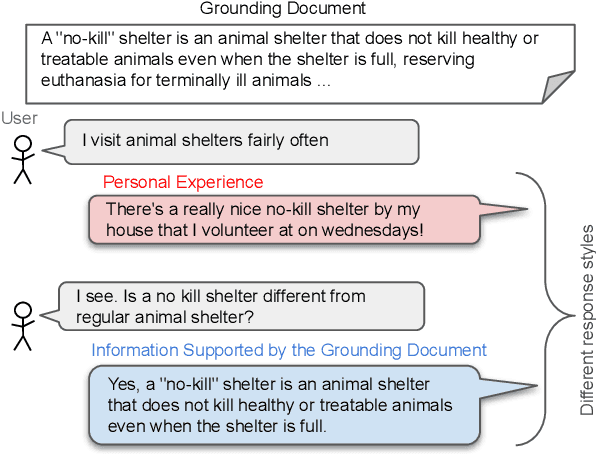
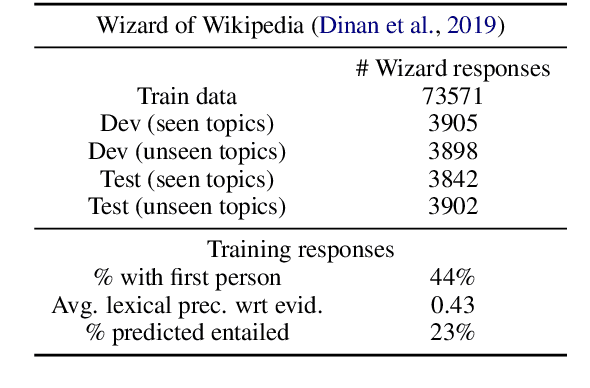
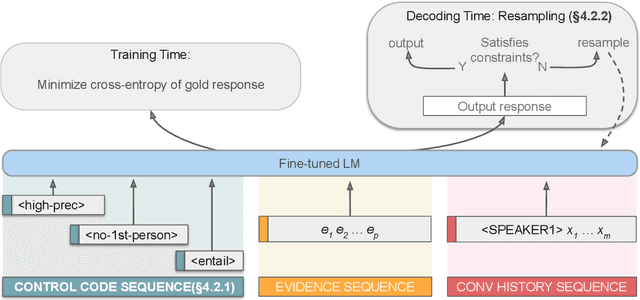
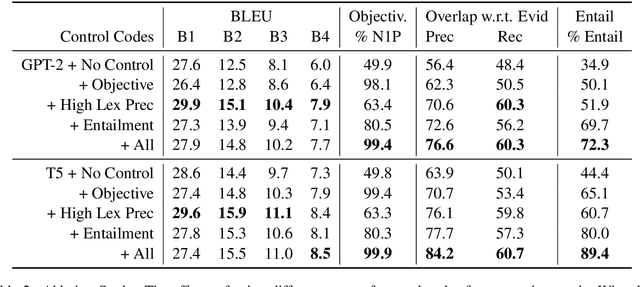
Abstract:Knowledge-grounded dialogue systems are intended to convey information that is based on evidence provided in a given source text. We discuss the challenges of training a generative neural dialogue model for such systems that is controlled to stay faithful to the evidence. Existing datasets contain a mix of conversational responses that are faithful to selected evidence as well as more subjective or chit-chat style responses. We propose different evaluation measures to disentangle these different styles of responses by quantifying the informativeness and objectivity. At training time, additional inputs based on these evaluation measures are given to the dialogue model. At generation time, these additional inputs act as stylistic controls that encourage the model to generate responses that are faithful to the provided evidence. We also investigate the usage of additional controls at decoding time using resampling techniques. In addition to automatic metrics, we perform a human evaluation study where raters judge the output of these controlled generation models to be generally more objective and faithful to the evidence compared to baseline dialogue systems.
Evaluating Groundedness in Dialogue Systems: The BEGIN Benchmark
Apr 30, 2021



Abstract:Knowledge-grounded dialogue agents are systems designed to conduct a conversation based on externally provided background information, such as a Wikipedia page. Such dialogue agents, especially those based on neural network language models, often produce responses that sound fluent but are not justified by the background information. Progress towards addressing this problem requires developing automatic evaluation metrics that can quantify the extent to which responses are grounded in background information. To facilitate evaluation of such metrics, we introduce the Benchmark for Evaluation of Grounded INteraction (BEGIN). BEGIN consists of 8113 dialogue turns generated by language-model-based dialogue systems, accompanied by humans annotations specifying the relationship between the system's response and the background information. These annotations are based on an extension of the natural language inference paradigm. We use the benchmark to demonstrate the effectiveness of adversarially generated data for improving an evaluation metric based on existing natural language inference datasets.
PowerTransformer: Unsupervised Controllable Revision for Biased Language Correction
Oct 26, 2020



Abstract:Unconscious biases continue to be prevalent in modern text and media, calling for algorithms that can assist writers with bias correction. For example, a female character in a story is often portrayed as passive and powerless ("She daydreams about being a doctor") while a man is portrayed as more proactive and powerful ("He pursues his dream of being a doctor"). We formulate *Controllable Debiasing*, a new revision task that aims to rewrite a given text to correct the implicit and potentially undesirable bias in character portrayals. We then introduce PowerTransformer as an approach that debiases text through the lens of connotation frames (Sap et al., 2017), which encode pragmatic knowledge of implied power dynamics with respect to verb predicates. One key challenge of our task is the lack of parallel corpora. To address this challenge, we adopt an unsupervised approach using auxiliary supervision with related tasks such as paraphrasing and self-supervision based on a reconstruction loss, building on pretrained language models. Through comprehensive experiments based on automatic and human evaluations, we demonstrate that our approach outperforms ablations and existing methods from related tasks. Furthermore, we demonstrate the use of PowerTransformer as a step toward mitigating the well-documented gender bias in character portrayal in movie scripts.
PlotMachines: Outline-Conditioned Generation with Dynamic Plot State Tracking
Apr 30, 2020



Abstract:We propose the task of outline-conditioned story generation: given an outline as a set of phrases that describe key characters and events to appear in a story, the task is to generate a coherent narrative that is consistent with the provided outline. This task is challenging as the input only provides a rough sketch of the plot, and thus, models need to generate a story by weaving through the key points provided in the outline. This requires the model to keep track of the dynamic states of the latent plot, conditioning on the input outline while generating the full story. We present PlotMachines, a neural narrative model that learns to transform an outline into a coherent story by tracking the dynamic plot states. In addition, we enrich PlotMachines with high-level discourse structure so that the model can learn different styles of writing corresponding to different parts of the narrative. Comprehensive experiments over three fiction and non-fiction datasets demonstrate that recently introduced large-scale language models, such as GPT-2 and Grover, despite their impressive generation performance, are not sufficient in generating coherent narratives for the given outline, and dynamic plot state tracking is important for composing narratives with tighter, more consistent plots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge