Guang-Quan Zhou
Efficient MedSAMs: Segment Anything in Medical Images on Laptop
Dec 20, 2024


Abstract:Promptable segmentation foundation models have emerged as a transformative approach to addressing the diverse needs in medical images, but most existing models require expensive computing, posing a big barrier to their adoption in clinical practice. In this work, we organized the first international competition dedicated to promptable medical image segmentation, featuring a large-scale dataset spanning nine common imaging modalities from over 20 different institutions. The top teams developed lightweight segmentation foundation models and implemented an efficient inference pipeline that substantially reduced computational requirements while maintaining state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy. Moreover, the post-challenge phase advanced the algorithms through the design of performance booster and reproducibility tasks, resulting in improved algorithms and validated reproducibility of the winning solution. Furthermore, the best-performing algorithms have been incorporated into the open-source software with a user-friendly interface to facilitate clinical adoption. The data and code are publicly available to foster the further development of medical image segmentation foundation models and pave the way for impactful real-world applications.
TSdetector: Temporal-Spatial Self-correction Collaborative Learning for Colonoscopy Video Detection
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:CNN-based object detection models that strike a balance between performance and speed have been gradually used in polyp detection tasks. Nevertheless, accurately locating polyps within complex colonoscopy video scenes remains challenging since existing methods ignore two key issues: intra-sequence distribution heterogeneity and precision-confidence discrepancy. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Temporal-Spatial self-correction detector (TSdetector), which first integrates temporal-level consistency learning and spatial-level reliability learning to detect objects continuously. Technically, we first propose a global temporal-aware convolution, assembling the preceding information to dynamically guide the current convolution kernel to focus on global features between sequences. In addition, we designed a hierarchical queue integration mechanism to combine multi-temporal features through a progressive accumulation manner, fully leveraging contextual consistency information together with retaining long-sequence-dependency features. Meanwhile, at the spatial level, we advance a position-aware clustering to explore the spatial relationships among candidate boxes for recalibrating prediction confidence adaptively, thus eliminating redundant bounding boxes efficiently. The experimental results on three publicly available polyp video dataset show that TSdetector achieves the highest polyp detection rate and outperforms other state-of-the-art methods. The code can be available at https://github.com/soleilssss/TSdetector.
A Complementary Global and Local Knowledge Network for Ultrasound denoising with Fine-grained Refinement
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Ultrasound imaging serves as an effective and non-invasive diagnostic tool commonly employed in clinical examinations. However, the presence of speckle noise in ultrasound images invariably degrades image quality, impeding the performance of subsequent tasks, such as segmentation and classification. Existing methods for speckle noise reduction frequently induce excessive image smoothing or fail to preserve detailed information adequately. In this paper, we propose a complementary global and local knowledge network for ultrasound denoising with fine-grained refinement. Initially, the proposed architecture employs the L-CSwinTransformer as encoder to capture global information, incorporating CNN as decoder to fuse local features. We expand the resolution of the feature at different stages to extract more global information compared to the original CSwinTransformer. Subsequently, we integrate Fine-grained Refinement Block (FRB) within the skip-connection stage to further augment features. We validate our model on two public datasets, HC18 and BUSI. Experimental results demonstrate that our model can achieve competitive performance in both quantitative metrics and visual performance. Our code will be available at https://github.com/AAlkaid/USDenoising.
FFCNet: Fourier Transform-Based Frequency Learning and Complex Convolutional Network for Colon Disease Classification
Jul 04, 2022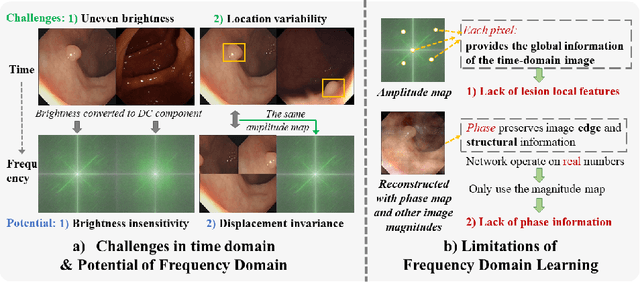
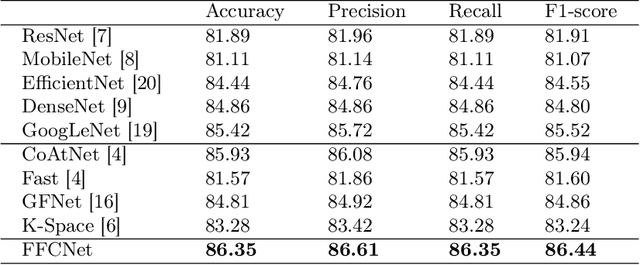
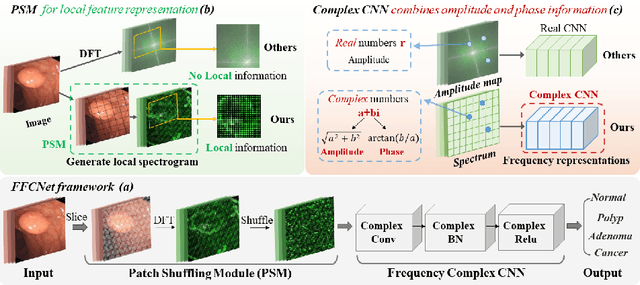
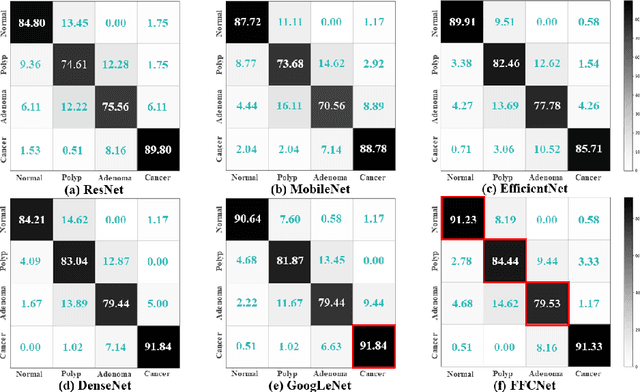
Abstract:Reliable automatic classification of colonoscopy images is of great significance in assessing the stage of colonic lesions and formulating appropriate treatment plans. However, it is challenging due to uneven brightness, location variability, inter-class similarity, and intra-class dissimilarity, affecting the classification accuracy. To address the above issues, we propose a Fourier-based Frequency Complex Network (FFCNet) for colon disease classification in this study. Specifically, FFCNet is a novel complex network that enables the combination of complex convolutional networks with frequency learning to overcome the loss of phase information caused by real convolution operations. Also, our Fourier transform transfers the average brightness of an image to a point in the spectrum (the DC component), alleviating the effects of uneven brightness by decoupling image content and brightness. Moreover, the image patch scrambling module in FFCNet generates random local spectral blocks, empowering the network to learn long-range and local diseasespecific features and improving the discriminative ability of hard samples. We evaluated the proposed FFCNet on an in-house dataset with 2568 colonoscopy images, showing our method achieves high performance outperforming previous state-of-the art methods with an accuracy of 86:35% and an accuracy of 4.46% higher than the backbone. The project page with code is available at https://github.com/soleilssss/FFCNet.
AWSnet: An Auto-weighted Supervision Attention Network for Myocardial Scar and Edema Segmentation in Multi-sequence Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Jan 14, 2022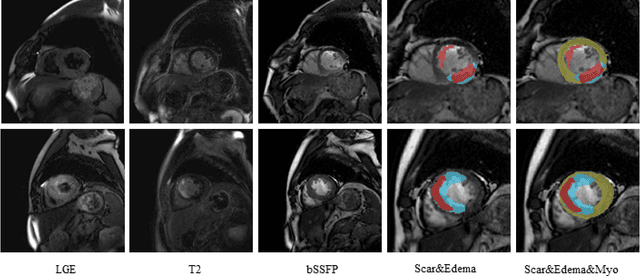
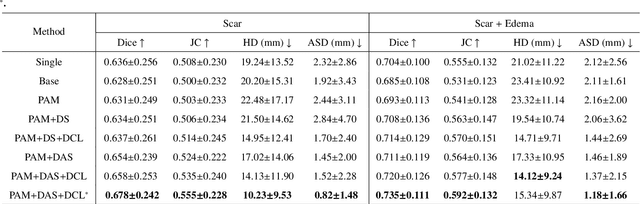
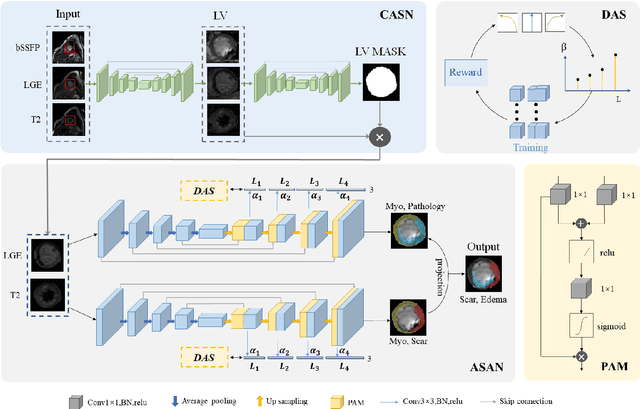
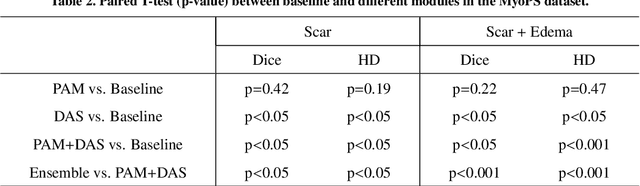
Abstract:Multi-sequence cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) provides essential pathology information (scar and edema) to diagnose myocardial infarction. However, automatic pathology segmentation can be challenging due to the difficulty of effectively exploring the underlying information from the multi-sequence CMR data. This paper aims to tackle the scar and edema segmentation from multi-sequence CMR with a novel auto-weighted supervision framework, where the interactions among different supervised layers are explored under a task-specific objective using reinforcement learning. Furthermore, we design a coarse-to-fine framework to boost the small myocardial pathology region segmentation with shape prior knowledge. The coarse segmentation model identifies the left ventricle myocardial structure as a shape prior, while the fine segmentation model integrates a pixel-wise attention strategy with an auto-weighted supervision model to learn and extract salient pathological structures from the multi-sequence CMR data. Extensive experimental results on a publicly available dataset from Myocardial pathology segmentation combining multi-sequence CMR (MyoPS 2020) demonstrate our method can achieve promising performance compared with other state-of-the-art methods. Our method is promising in advancing the myocardial pathology assessment on multi-sequence CMR data. To motivate the community, we have made our code publicly available via https://github.com/soleilssss/AWSnet/tree/master.
Learn Fine-grained Adaptive Loss for Multiple Anatomical Landmark Detection in Medical Images
May 19, 2021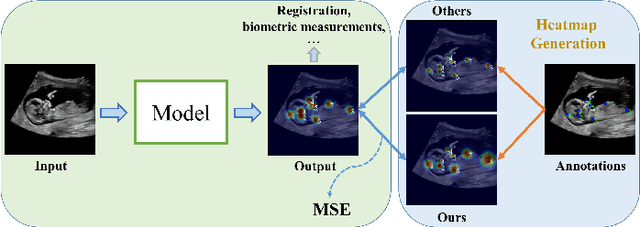
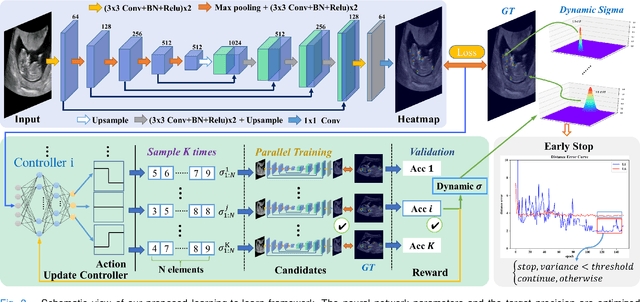
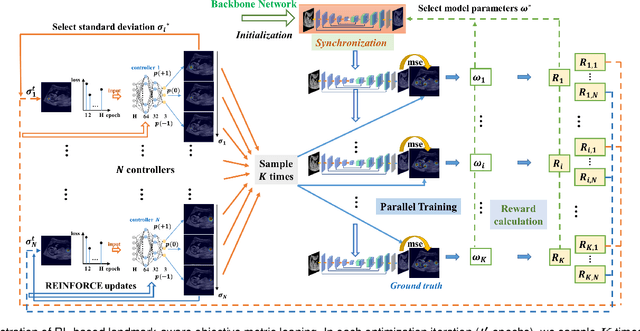
Abstract:Automatic and accurate detection of anatomical landmarks is an essential operation in medical image analysis with a multitude of applications. Recent deep learning methods have improved results by directly encoding the appearance of the captured anatomy with the likelihood maps (i.e., heatmaps). However, most current solutions overlook another essence of heatmap regression, the objective metric for regressing target heatmaps and rely on hand-crafted heuristics to set the target precision, thus being usually cumbersome and task-specific. In this paper, we propose a novel learning-to-learn framework for landmark detection to optimize the neural network and the target precision simultaneously. The pivot of this work is to leverage the reinforcement learning (RL) framework to search objective metrics for regressing multiple heatmaps dynamically during the training process, thus avoiding setting problem-specific target precision. We also introduce an early-stop strategy for active termination of the RL agent's interaction that adapts the optimal precision for separate targets considering exploration-exploitation tradeoffs. This approach shows better stability in training and improved localization accuracy in inference. Extensive experimental results on two different applications of landmark localization: 1) our in-house prenatal ultrasound (US) dataset and 2) the publicly available dataset of cephalometric X-Ray landmark detection, demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. Our proposed framework is general and shows the potential to improve the efficiency of anatomical landmark detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge