Eric Ryan Chan
BAgger: Backwards Aggregation for Mitigating Drift in Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:Autoregressive video models are promising for world modeling via next-frame prediction, but they suffer from exposure bias: a mismatch between training on clean contexts and inference on self-generated frames, causing errors to compound and quality to drift over time. We introduce Backwards Aggregation (BAgger), a self-supervised scheme that constructs corrective trajectories from the model's own rollouts, teaching it to recover from its mistakes. Unlike prior approaches that rely on few-step distillation and distribution-matching losses, which can hurt quality and diversity, BAgger trains with standard score or flow matching objectives, avoiding large teachers and long-chain backpropagation through time. We instantiate BAgger on causal diffusion transformers and evaluate on text-to-video, video extension, and multi-prompt generation, observing more stable long-horizon motion and better visual consistency with reduced drift.
ZeroNVS: Zero-Shot 360-Degree View Synthesis from a Single Real Image
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:We introduce a 3D-aware diffusion model, ZeroNVS, for single-image novel view synthesis for in-the-wild scenes. While existing methods are designed for single objects with masked backgrounds, we propose new techniques to address challenges introduced by in-the-wild multi-object scenes with complex backgrounds. Specifically, we train a generative prior on a mixture of data sources that capture object-centric, indoor, and outdoor scenes. To address issues from data mixture such as depth-scale ambiguity, we propose a novel camera conditioning parameterization and normalization scheme. Further, we observe that Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) tends to truncate the distribution of complex backgrounds during distillation of 360-degree scenes, and propose "SDS anchoring" to improve the diversity of synthesized novel views. Our model sets a new state-of-the-art result in LPIPS on the DTU dataset in the zero-shot setting, even outperforming methods specifically trained on DTU. We further adapt the challenging Mip-NeRF 360 dataset as a new benchmark for single-image novel view synthesis, and demonstrate strong performance in this setting. Our code and data are at http://kylesargent.github.io/zeronvs/
State of the Art on Diffusion Models for Visual Computing
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:The field of visual computing is rapidly advancing due to the emergence of generative artificial intelligence (AI), which unlocks unprecedented capabilities for the generation, editing, and reconstruction of images, videos, and 3D scenes. In these domains, diffusion models are the generative AI architecture of choice. Within the last year alone, the literature on diffusion-based tools and applications has seen exponential growth and relevant papers are published across the computer graphics, computer vision, and AI communities with new works appearing daily on arXiv. This rapid growth of the field makes it difficult to keep up with all recent developments. The goal of this state-of-the-art report (STAR) is to introduce the basic mathematical concepts of diffusion models, implementation details and design choices of the popular Stable Diffusion model, as well as overview important aspects of these generative AI tools, including personalization, conditioning, inversion, among others. Moreover, we give a comprehensive overview of the rapidly growing literature on diffusion-based generation and editing, categorized by the type of generated medium, including 2D images, videos, 3D objects, locomotion, and 4D scenes. Finally, we discuss available datasets, metrics, open challenges, and social implications. This STAR provides an intuitive starting point to explore this exciting topic for researchers, artists, and practitioners alike.
Learning Object-Centric Neural Scattering Functions for Free-viewpoint Relighting and Scene Composition
Mar 10, 2023


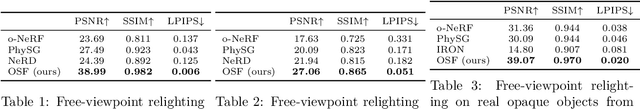
Abstract:Photorealistic object appearance modeling from 2D images is a constant topic in vision and graphics. While neural implicit methods (such as Neural Radiance Fields) have shown high-fidelity view synthesis results, they cannot relight the captured objects. More recent neural inverse rendering approaches have enabled object relighting, but they represent surface properties as simple BRDFs, and therefore cannot handle translucent objects. We propose Object-Centric Neural Scattering Functions (OSFs) for learning to reconstruct object appearance from only images. OSFs not only support free-viewpoint object relighting, but also can model both opaque and translucent objects. While accurately modeling subsurface light transport for translucent objects can be highly complex and even intractable for neural methods, OSFs learn to approximate the radiance transfer from a distant light to an outgoing direction at any spatial location. This approximation avoids explicitly modeling complex subsurface scattering, making learning a neural implicit model tractable. Experiments on real and synthetic data show that OSFs accurately reconstruct appearances for both opaque and translucent objects, allowing faithful free-viewpoint relighting as well as scene composition.
3D Neural Field Generation using Triplane Diffusion
Nov 30, 2022



Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as the state-of-the-art for image generation, among other tasks. Here, we present an efficient diffusion-based model for 3D-aware generation of neural fields. Our approach pre-processes training data, such as ShapeNet meshes, by converting them to continuous occupancy fields and factoring them into a set of axis-aligned triplane feature representations. Thus, our 3D training scenes are all represented by 2D feature planes, and we can directly train existing 2D diffusion models on these representations to generate 3D neural fields with high quality and diversity, outperforming alternative approaches to 3D-aware generation. Our approach requires essential modifications to existing triplane factorization pipelines to make the resulting features easy to learn for the diffusion model. We demonstrate state-of-the-art results on 3D generation on several object classes from ShapeNet.
DiffDreamer: Consistent Single-view Perpetual View Generation with Conditional Diffusion Models
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Perpetual view generation -- the task of generating long-range novel views by flying into a given image -- has been a novel yet promising task. We introduce DiffDreamer, an unsupervised framework capable of synthesizing novel views depicting a long camera trajectory while training solely on internet-collected images of nature scenes. We demonstrate that image-conditioned diffusion models can effectively perform long-range scene extrapolation while preserving both local and global consistency significantly better than prior GAN-based methods. Project page: https://primecai.github.io/diffdreamer .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge