Dongsoo Lee
PrefillShare: A Shared Prefill Module for KV Reuse in Multi-LLM Disaggregated Serving
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent systems increasingly orchestrate multiple specialized language models to solve complex real-world problems, often invoking them over a shared context. This execution pattern repeatedly processes the same prompt prefix across models. Consequently, each model redundantly executes the prefill stage and maintains its own key-value (KV) cache, increasing aggregate prefill load and worsening tail latency by intensifying prefill-decode interference in existing LLM serving stacks. Disaggregated serving reduces such interference by placing prefill and decode on separate GPUs, but disaggregation does not fundamentally eliminate inter-model redundancy in computation and KV storage for the same prompt. To address this issue, we propose PrefillShare, a novel algorithm that enables sharing the prefill stage across multiple models in a disaggregated setting. PrefillShare factorizes the model into prefill and decode modules, freezes the prefill module, and fine-tunes only the decode module. This design allows multiple task-specific models to share a prefill module and the KV cache generated for the same prompt. We further introduce a routing mechanism that enables effective prefill sharing across heterogeneous models in a vLLM-based disaggregated system. PrefillShare not only matches full fine-tuning accuracy on a broad range of tasks and models, but also delivers 4.5x lower p95 latency and 3.9x higher throughput in multi-model agent workloads.
CodeGEMM: A Codebook-Centric Approach to Efficient GEMM in Quantized LLMs
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Weight-only quantization is widely used to mitigate the memory-bound nature of LLM inference. Codebook-based methods extend this trend by achieving strong accuracy in the extremely low-bit regime (e.g., 2-bit). However, current kernels rely on dequantization, which repeatedly fetches centroids and reconstructs weights, incurring substantial latency and cache pressure. We present CodeGEMM, a codebook-centric GEMM kernel that replaces dequantization with precomputed inner products between centroids and activations stored in a lightweight Psumbook. At inference, code indices directly gather these partial sums, eliminating per-element lookups and reducing the on-chip footprint. The kernel supports the systematic exploration of latency-memory-accuracy trade-offs under a unified implementation. On Llama-3 models, CodeGEMM delivers 1.83x (8B) and 8.93x (70B) speedups in the 2-bit configuration compared to state-of-the-art codebook-based quantization at comparable accuracy and further improves computing efficiency and memory subsystem utilization.
Unifying Uniform and Binary-coding Quantization for Accurate Compression of Large Language Models
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:How can we quantize large language models while preserving accuracy? Quantization is essential for deploying large language models (LLMs) efficiently. Binary-coding quantization (BCQ) and uniform quantization (UQ) are promising quantization schemes that have strong expressiveness and optimizability, respectively. However, neither scheme leverages both advantages. In this paper, we propose UniQuanF (Unified Quantization with Flexible Mapping), an accurate quantization method for LLMs. UniQuanF harnesses both strong expressiveness and optimizability by unifying the flexible mapping technique in UQ and non-uniform quantization levels of BCQ. We propose unified initialization, and local and periodic mapping techniques to optimize the parameters in UniQuanF precisely. After optimization, our unification theorem removes computational and memory overhead, allowing us to utilize the superior accuracy of UniQuanF without extra deployment costs induced by the unification. Experimental results demonstrate that UniQuanF outperforms existing UQ and BCQ methods, achieving up to 4.60% higher accuracy on GSM8K benchmark.
An Investigation of FP8 Across Accelerators for LLM Inference
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:The introduction of 8-bit floating-point (FP8) computation units in modern AI accelerators has generated significant interest in FP8-based large language model (LLM) inference. Unlike 16-bit floating-point formats, FP8 in deep learning requires a shared scaling factor. Additionally, while E4M3 and E5M2 are well-defined at the individual value level, their scaling and accumulation methods remain unspecified and vary across hardware and software implementations. As a result, FP8 behaves more like a quantization format than a standard numeric representation. In this work, we provide the first comprehensive analysis of FP8 computation and acceleration on two AI accelerators: the NVIDIA H100 and Intel Gaudi 2. Our findings highlight that the Gaudi 2, by leveraging FP8, achieves higher throughput-to-power efficiency during LLM inference, offering valuable insights into the practical implications of FP8 adoption for datacenter-scale LLM serving.
Debunking the CUDA Myth Towards GPU-based AI Systems
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:With the rise of AI, NVIDIA GPUs have become the de facto standard for AI system design. This paper presents a comprehensive evaluation of Intel Gaudi NPUs as an alternative to NVIDIA GPUs for AI model serving. First, we create a suite of microbenchmarks to compare Intel Gaudi-2 with NVIDIA A100, showing that Gaudi-2 achieves competitive performance not only in primitive AI compute, memory, and communication operations but also in executing several important AI workloads end-to-end. We then assess Gaudi NPU's programmability by discussing several software-level optimization strategies to employ for implementing critical FBGEMM operators and vLLM, evaluating their efficiency against GPU-optimized counterparts. Results indicate that Gaudi-2 achieves energy efficiency comparable to A100, though there are notable areas for improvement in terms of software maturity. Overall, we conclude that, with effective integration into high-level AI frameworks, Gaudi NPUs could challenge NVIDIA GPU's dominance in the AI server market, though further improvements are necessary to fully compete with NVIDIA's robust software ecosystem.
LRQ: Optimizing Post-Training Quantization for Large Language Models by Learning Low-Rank Weight-Scaling Matrices
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:With the commercialization of large language models (LLMs), weight-activation quantization has emerged to compress and accelerate LLMs, achieving high throughput while reducing inference costs. However, existing post-training quantization (PTQ) techniques for quantizing weights and activations of LLMs still suffer from non-negligible accuracy drops, especially on massive multitask language understanding. To address this issue, we propose Low-Rank Quantization (LRQ) $-$ a simple yet effective post-training weight quantization method for LLMs that reconstructs the outputs of an intermediate Transformer block by leveraging low-rank weight-scaling matrices, replacing the conventional full weight-scaling matrices that entail as many learnable scales as their associated weights. Thanks to parameter sharing via low-rank structure, LRQ only needs to learn significantly fewer parameters while enabling the individual scaling of weights, thus boosting the generalization capability of quantized LLMs. We show the superiority of LRQ over prior LLM PTQ works under (i) $8$-bit weight and per-tensor activation quantization, (ii) $4$-bit weight and $8$-bit per-token activation quantization, and (iii) low-bit weight-only quantization schemes. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/onliwad101/FlexRound_LRQ} to inspire LLM researchers and engineers.
To FP8 and Back Again: Quantifying the Effects of Reducing Precision on LLM Training Stability
May 29, 2024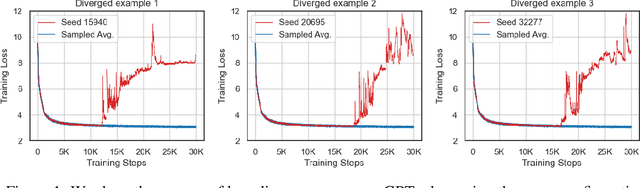
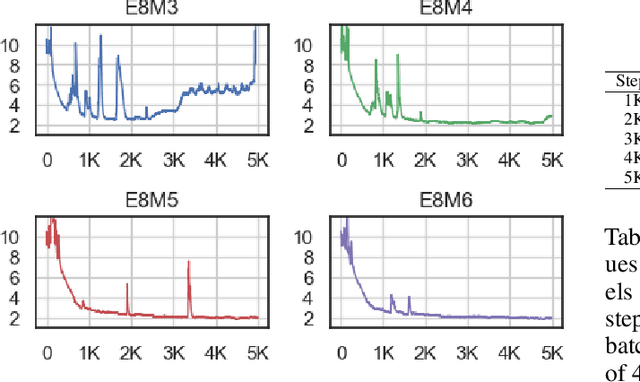
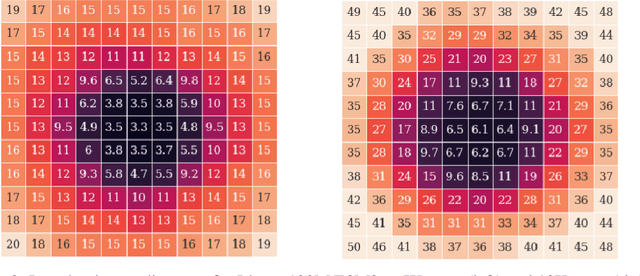
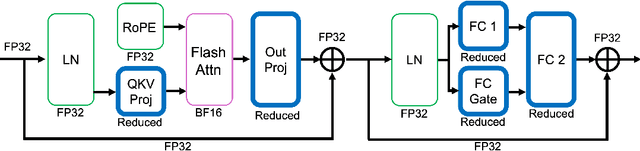
Abstract:The massive computational costs associated with large language model (LLM) pretraining have spurred great interest in reduced-precision floating-point representations to accelerate the process. As a result, the BrainFloat16 (BF16) precision has become the de facto standard for LLM training, with hardware support included in recent accelerators. This trend has gone even further in the latest processors, where FP8 has recently been introduced. However, prior experience with FP16, which was found to be less stable than BF16, raises concerns as to whether FP8, with even fewer bits than FP16, can be a cost-effective option for LLM training. We argue that reduced-precision training schemes must have similar training stability and hyperparameter sensitivities to their higher-precision counterparts in order to be cost-effective. However, we find that currently available methods for FP8 training are not robust enough to allow their use as economical replacements. This prompts us to investigate the stability of reduced-precision LLM training in terms of robustness across random seeds and learning rates. To this end, we propose new evaluation techniques and a new metric for quantifying loss landscape sharpness in autoregressive language models. By simulating incremental bit reductions in floating-point representations, we analyze the relationship between representational power and training stability with the intent of aiding future research into the field.
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
No Token Left Behind: Reliable KV Cache Compression via Importance-Aware Mixed Precision Quantization
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Key-Value (KV) Caching has become an essential technique for accelerating the inference speed and throughput of generative Large Language Models~(LLMs). However, the memory footprint of the KV cache poses a critical bottleneck in LLM deployment as the cache size grows with batch size and sequence length, often surpassing even the size of the model itself. Although recent methods were proposed to select and evict unimportant KV pairs from the cache to reduce memory consumption, the potential ramifications of eviction on the generative process are yet to be thoroughly examined. In this paper, we examine the detrimental impact of cache eviction and observe that unforeseen risks arise as the information contained in the KV pairs is exhaustively discarded, resulting in safety breaches, hallucinations, and context loss. Surprisingly, we find that preserving even a small amount of information contained in the evicted KV pairs via reduced precision quantization substantially recovers the incurred degradation. On the other hand, we observe that the important KV pairs must be kept at a relatively higher precision to safeguard the generation quality. Motivated by these observations, we propose \textit{Mixed-precision KV cache}~(MiKV), a reliable cache compression method that simultaneously preserves the context details by retaining the evicted KV pairs in low-precision and ensure generation quality by keeping the important KV pairs in high-precision. Experiments on diverse benchmarks and LLM backbones show that our proposed method offers a state-of-the-art trade-off between compression ratio and performance, compared to other baselines.
DropBP: Accelerating Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models by Dropping Backward Propagation
Feb 27, 2024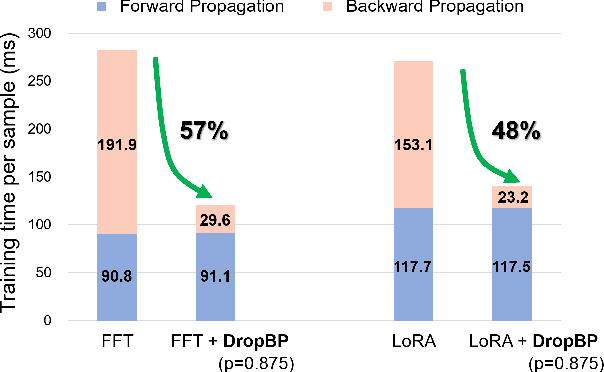

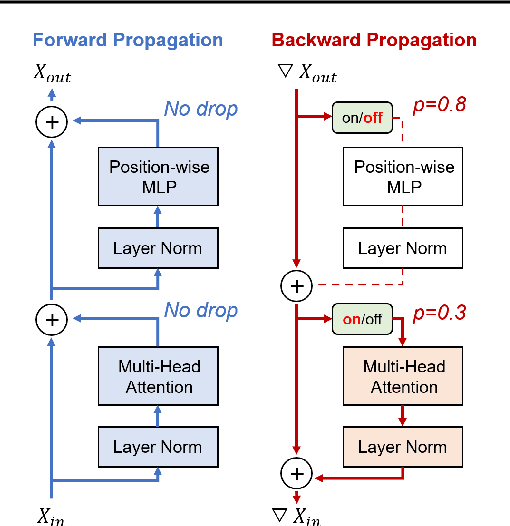

Abstract:Training deep neural networks typically involves substantial computational costs during both forward and backward propagation. The conventional layer dropping techniques drop certain layers during training for reducing the computations burden. However, dropping layers during forward propagation adversely affects the training process by degrading accuracy. In this paper, we propose Dropping Backward Propagation (DropBP), a novel approach designed to reduce computational costs while maintaining accuracy. DropBP randomly drops layers during the backward propagation, which does not deviate forward propagation. Moreover, DropBP calculates the sensitivity of each layer to assign appropriate drop rate, thereby stabilizing the training process. DropBP is designed to enhance the efficiency of the training process with backpropagation, thereby enabling the acceleration of both full fine-tuning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning using backpropagation. Specifically, utilizing DropBP in QLoRA reduces training time by 44%, increases the convergence speed to the identical loss level by 1.5$\times$, and enables training with a 6.2$\times$ larger sequence length on a single NVIDIA-A100 80GiB GPU in LLaMA2-70B. The code is available at https://github.com/WooSunghyeon/dropbp.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge