Christian Poelitz
An Experimental Comparison of Cognitive Forcing Functions for Execution Plans in AI-Assisted Writing: Effects On Trust, Overreliance, and Perceived Critical Thinking
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Generative AI (GenAI) tools improve productivity in knowledge workflows such as writing, but also risk overreliance and reduced critical thinking. Cognitive forcing functions (CFFs) mitigate these risks by requiring active engagement with AI output. As GenAI workflows grow more complex, systems increasingly present execution plans for user review. However, these plans are themselves AI-generated and prone to overreliance, and the effectiveness of applying CFFs to AI plans remains underexplored. We conduct a controlled experiment in which participants completed AI-assisted writing tasks while reviewing AI-generated plans under four CFF conditions: Assumption (argument analysis), WhatIf (hypothesis testing), Both, and a no-CFF control. A follow-up think-aloud and interview study qualitatively compared these conditions. Results show that the Assumption CFF most effectively reduced overreliance without increasing cognitive load, while participants perceived the WhatIf CFF as most helpful. These findings highlight the value of plan-focused CFFs for supporting critical reflection in GenAI-assisted knowledge work.
Synthetic Function Demonstrations Improve Generation in Low-Resource Programming Languages
Mar 24, 2025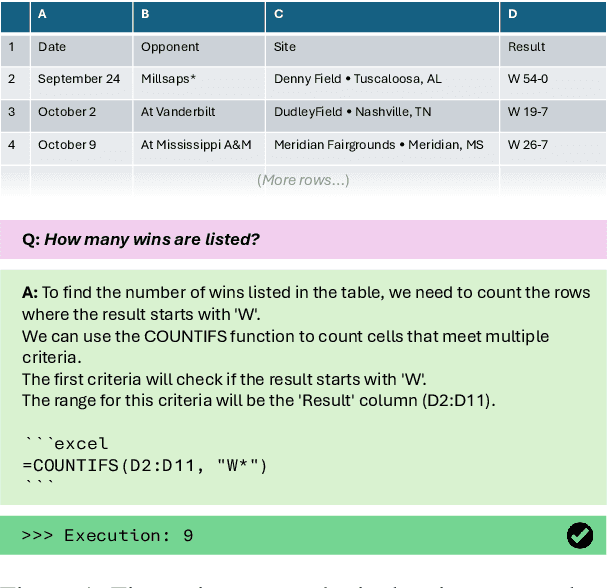
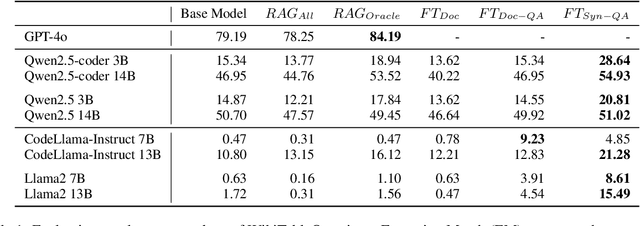
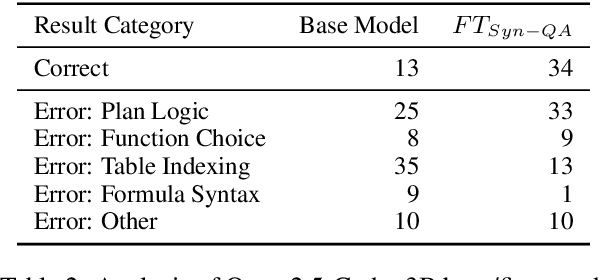

Abstract:A key consideration when training an LLM is whether the target language is more or less resourced, whether this is English compared to Welsh, or Python compared to Excel. Typical training data for programming languages consist of real program demonstrations coupled with human-written comments. Here we present novel approaches to the creation of such data for low resource programming languages. We generate fully-synthetic, textbook-quality demonstrations of common library functions in an example domain of Excel formulas, using a teacher model. We then finetune an underperforming student model, and show improvement on 2 question-answering datasets recast into the Excel domain. We show advantages of finetuning over standard, off-the-shelf RAG approaches, which can offer only modest improvement due to the unfamiliar target domain.
Synthetic Clarification and Correction Dialogues about Data-Centric Tasks -- A Teacher-Student Approach
Mar 18, 2025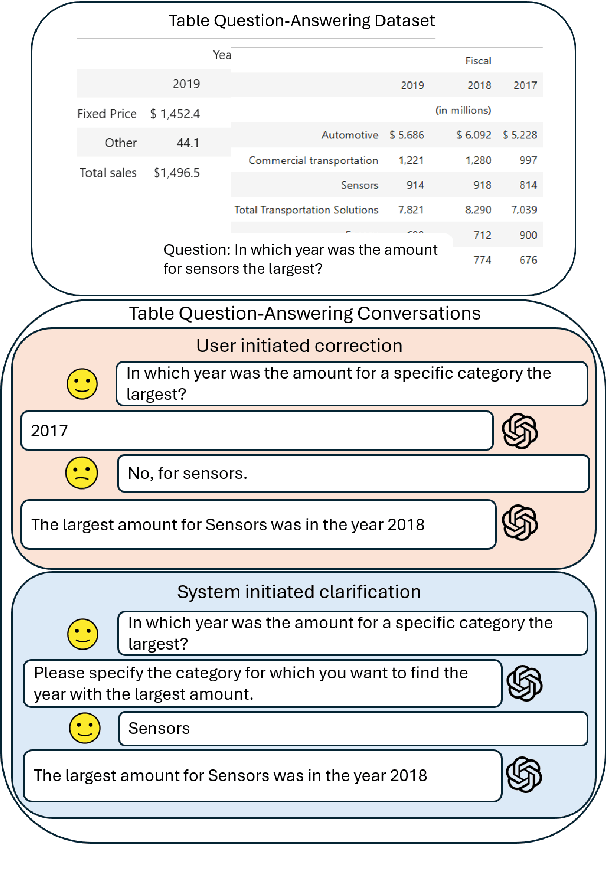
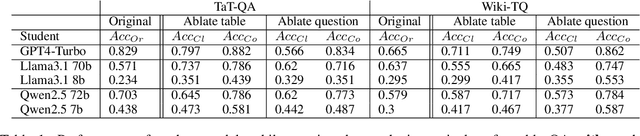
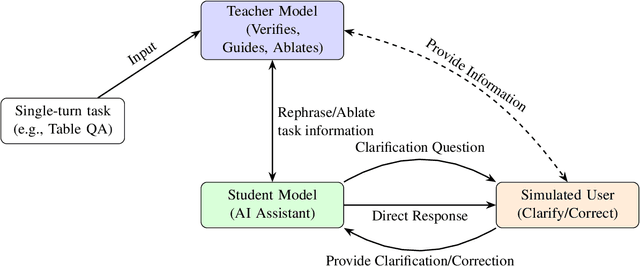
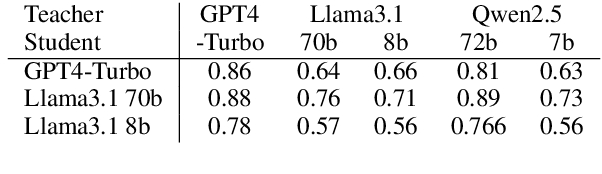
Abstract:Real dialogues with AI assistants for solving data-centric tasks often follow dynamic, unpredictable paths due to imperfect information provided by the user or in the data, which must be caught and handled. Developing datasets which capture such user-AI interactions is difficult and time-consuming. In this work, we develop a novel framework for synthetically generating controlled, multi-turn conversations between a user and AI assistant for the task of table-based question answering, which can be generated from an existing dataset with fully specified table QA examples for any target domain. Each conversation aims to solve a table-based reasoning question through collaborative effort, modeling one of two real-world scenarios: (1) an AI-initiated clarification, or (2) a user-initiated correction. Critically, we employ a strong teacher LLM to verify the correctness of our synthetic conversations, ensuring high quality. We demonstrate synthetic datasets generated from TAT-QA and WikiTableQuestions as benchmarks of frontier LLMs. We find that even larger models struggle to effectively issuing clarification questions and accurately integrate user feedback for corrections.
Evaluating the Evaluator: Measuring LLMs' Adherence to Task Evaluation Instructions
Aug 16, 2024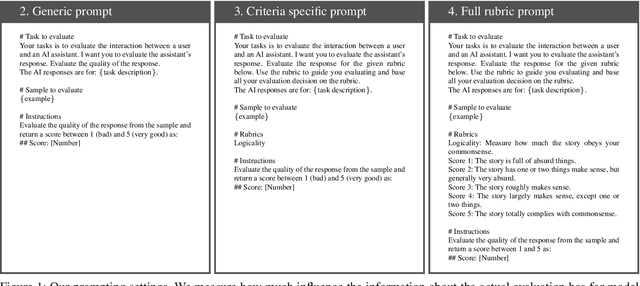
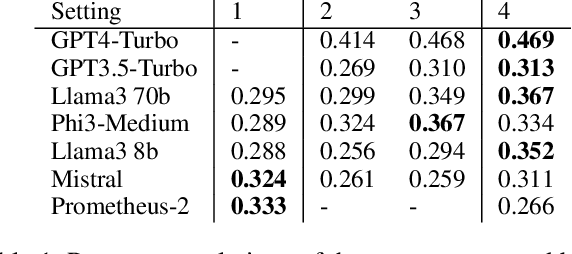
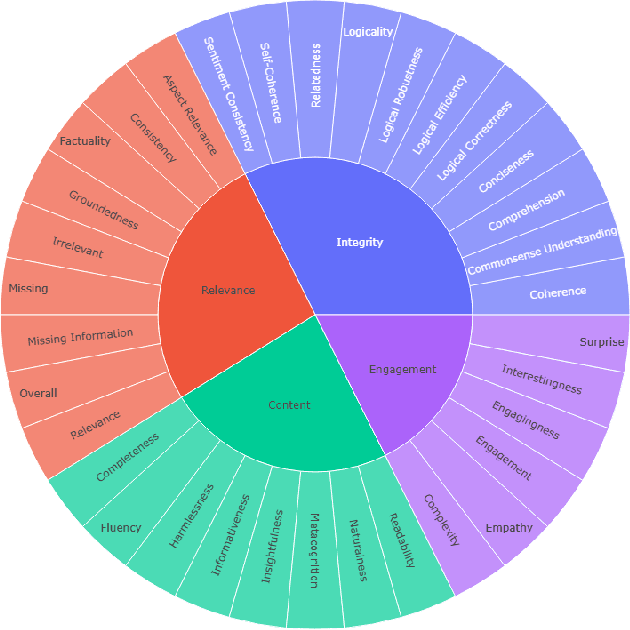
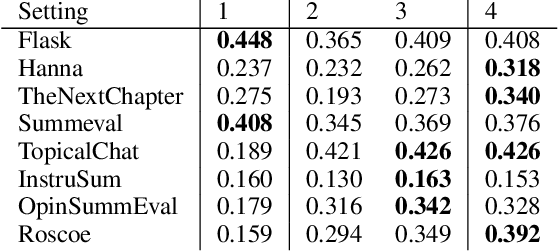
Abstract:LLMs-as-a-judge is a recently popularized method which replaces human judgements in task evaluation (Zheng et al. 2024) with automatic evaluation using LLMs. Due to widespread use of RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback), state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT4 and Llama3 are expected to have strong alignment with human preferences when prompted for a quality judgement, such as the coherence of a text. While this seems beneficial, it is not clear whether the assessments by an LLM-as-a-judge constitute only an evaluation based on the instructions in the prompts, or reflect its preference for high-quality data similar to its fine-tune data. To investigate how much influence prompting the LLMs-as-a-judge has on the alignment of AI judgements to human judgements, we analyze prompts with increasing levels of instructions about the target quality of an evaluation, for several LLMs-as-a-judge. Further, we compare to a prompt-free method using model perplexity as a quality measure instead. We aggregate a taxonomy of quality criteria commonly used across state-of-the-art evaluations with LLMs and provide this as a rigorous benchmark of models as judges. Overall, we show that the LLMs-as-a-judge benefit only little from highly detailed instructions in prompts and that perplexity can sometimes align better with human judgements than prompting, especially on textual quality.
MAGIC: Generating Self-Correction Guideline for In-Context Text-to-SQL
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Self-correction in text-to-SQL is the process of prompting large language model (LLM) to revise its previously incorrectly generated SQL, and commonly relies on manually crafted self-correction guidelines by human experts that are not only labor-intensive to produce but also limited by the human ability in identifying all potential error patterns in LLM responses. We introduce MAGIC, a novel multi-agent method that automates the creation of the self-correction guideline. MAGIC uses three specialized agents: a manager, a correction, and a feedback agent. These agents collaborate on the failures of an LLM-based method on the training set to iteratively generate and refine a self-correction guideline tailored to LLM mistakes, mirroring human processes but without human involvement. Our extensive experiments show that MAGIC's guideline outperforms expert human's created ones. We empirically find out that the guideline produced by MAGIC enhance the interpretability of the corrections made, providing insights in analyzing the reason behind the failures and successes of LLMs in self-correction. We make all agent interactions publicly available to the research community, to foster further research in this area, offering a synthetic dataset for future explorations into automatic self-correction guideline generation.
Solving Data-centric Tasks using Large Language Models
Feb 18, 2024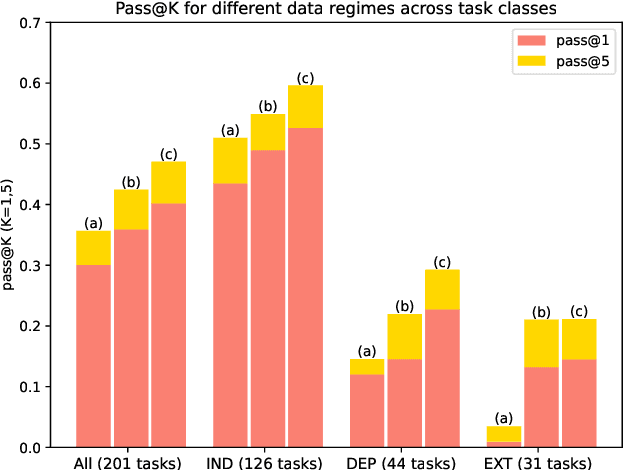
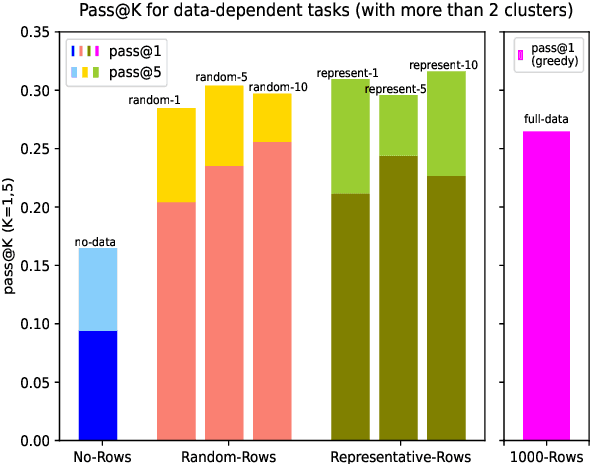
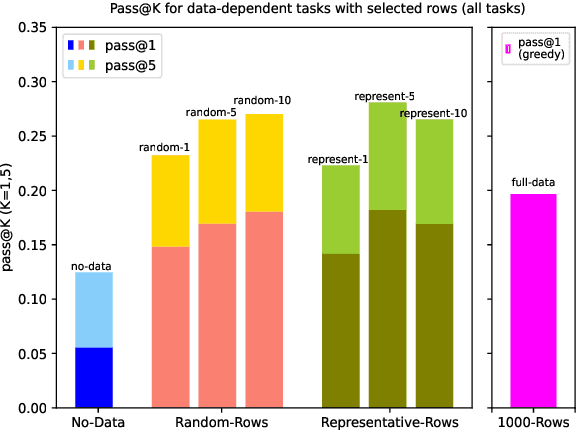
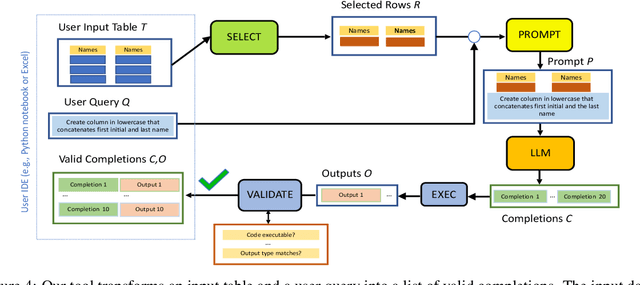
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly replacing help forums like StackOverflow, and are especially helpful for non-professional programmers and end users. These users are often interested in data-centric tasks, such as spreadsheet manipulation and data wrangling, which are hard to solve if the intent is only communicated using a natural-language description, without including the data. But how do we decide how much data and which data to include in the prompt? This paper makes two contributions towards answering this question. First, we create a dataset of real-world NL-to-code tasks manipulating tabular data, mined from StackOverflow posts. Second, we introduce a cluster-then-select prompting technique, which adds the most representative rows from the input data to the LLM prompt. Our experiments show that LLM performance is indeed sensitive to the amount of data passed in the prompt, and that for tasks with a lot of syntactic variation in the input table, our cluster-then-select technique outperforms a random selection baseline.
InstructExcel: A Benchmark for Natural Language Instruction in Excel
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:With the evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) we can solve increasingly more complex NLP tasks across various domains, including spreadsheets. This work investigates whether LLMs can generate code (Excel OfficeScripts, a TypeScript API for executing many tasks in Excel) that solves Excel specific tasks provided via natural language user instructions. To do so we introduce a new large-scale benchmark, InstructExcel, created by leveraging the 'Automate' feature in Excel to automatically generate OfficeScripts from users' actions. Our benchmark includes over 10k samples covering 170+ Excel operations across 2,000 publicly available Excel spreadsheets. Experiments across various zero-shot and few-shot settings show that InstructExcel is a hard benchmark for state of the art models like GPT-4. We observe that (1) using GPT-4 over GPT-3.5, (2) providing more in-context examples, and (3) dynamic prompting can help improve performance on this benchmark.
What is it like to program with artificial intelligence?
Aug 12, 2022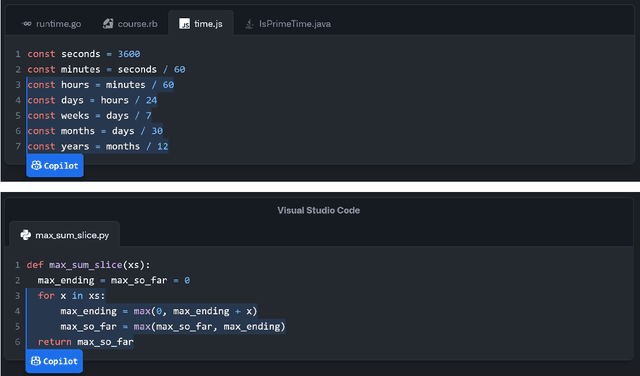
Abstract:Large language models, such as OpenAI's codex and Deepmind's AlphaCode, can generate code to solve a variety of problems expressed in natural language. This technology has already been commercialised in at least one widely-used programming editor extension: GitHub Copilot. In this paper, we explore how programming with large language models (LLM-assisted programming) is similar to, and differs from, prior conceptualisations of programmer assistance. We draw upon publicly available experience reports of LLM-assisted programming, as well as prior usability and design studies. We find that while LLM-assisted programming shares some properties of compilation, pair programming, and programming via search and reuse, there are fundamental differences both in the technical possibilities as well as the practical experience. Thus, LLM-assisted programming ought to be viewed as a new way of programming with its own distinct properties and challenges. Finally, we draw upon observations from a user study in which non-expert end user programmers use LLM-assisted tools for solving data tasks in spreadsheets. We discuss the issues that might arise, and open research challenges, in applying large language models to end-user programming, particularly with users who have little or no programming expertise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge