Ian Drosos
Dynamic Prompt Middleware: Contextual Prompt Refinement Controls for Comprehension Tasks
Dec 03, 2024

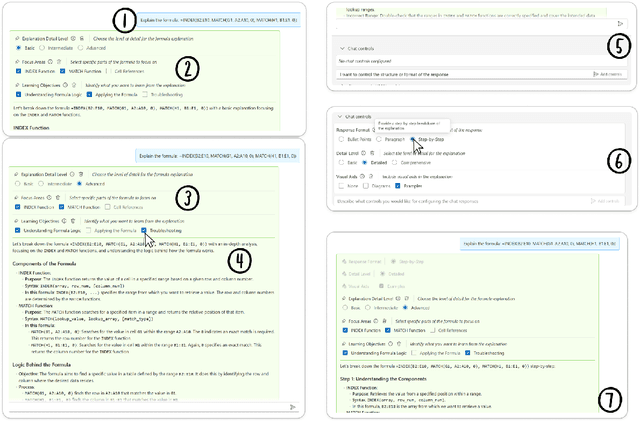

Abstract:Effective prompting of generative AI is challenging for many users, particularly in expressing context for comprehension tasks such as explaining spreadsheet formulas, Python code, and text passages. Prompt middleware aims to address this barrier by assisting in prompt construction, but barriers remain for users in expressing adequate control so that they can receive AI-responses that match their preferences. We conduct a formative survey (n=38) investigating user needs for control over AI-generated explanations in comprehension tasks, which uncovers a trade-off between standardized but predictable support for prompting, and adaptive but unpredictable support tailored to the user and task. To explore this trade-off, we implement two prompt middleware approaches: Dynamic Prompt Refinement Control (Dynamic PRC) and Static Prompt Refinement Control (Static PRC). The Dynamic PRC approach generates context-specific UI elements that provide prompt refinements based on the user's prompt and user needs from the AI, while the Static PRC approach offers a preset list of generally applicable refinements. We evaluate these two approaches with a controlled user study (n=16) to assess the impact of these approaches on user control of AI responses for crafting better explanations. Results show a preference for the Dynamic PRC approach as it afforded more control, lowered barriers to providing context, and encouraged exploration and reflection of the tasks, but that reasoning about the effects of different generated controls on the final output remains challenging. Drawing on participant feedback, we discuss design implications for future Dynamic PRC systems that enhance user control of AI responses. Our findings suggest that dynamic prompt middleware can improve the user experience of generative AI workflows by affording greater control and guide users to a better AI response.
Evaluating the Evaluator: Measuring LLMs' Adherence to Task Evaluation Instructions
Aug 16, 2024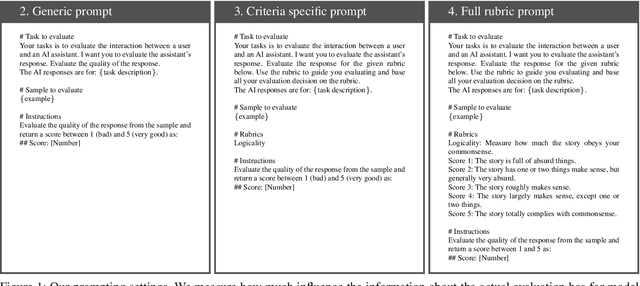
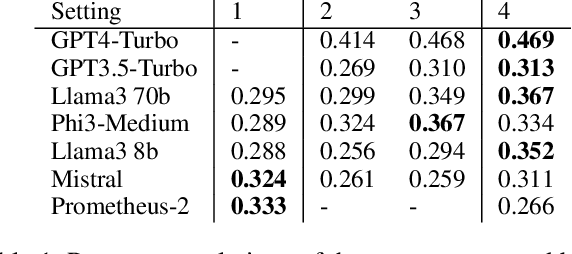
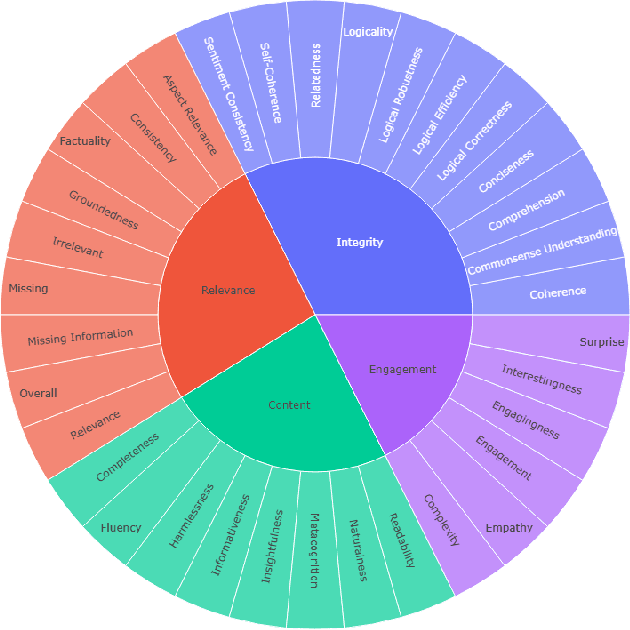
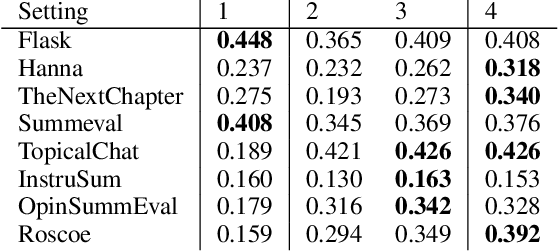
Abstract:LLMs-as-a-judge is a recently popularized method which replaces human judgements in task evaluation (Zheng et al. 2024) with automatic evaluation using LLMs. Due to widespread use of RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback), state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT4 and Llama3 are expected to have strong alignment with human preferences when prompted for a quality judgement, such as the coherence of a text. While this seems beneficial, it is not clear whether the assessments by an LLM-as-a-judge constitute only an evaluation based on the instructions in the prompts, or reflect its preference for high-quality data similar to its fine-tune data. To investigate how much influence prompting the LLMs-as-a-judge has on the alignment of AI judgements to human judgements, we analyze prompts with increasing levels of instructions about the target quality of an evaluation, for several LLMs-as-a-judge. Further, we compare to a prompt-free method using model perplexity as a quality measure instead. We aggregate a taxonomy of quality criteria commonly used across state-of-the-art evaluations with LLMs and provide this as a rigorous benchmark of models as judges. Overall, we show that the LLMs-as-a-judge benefit only little from highly detailed instructions in prompts and that perplexity can sometimes align better with human judgements than prompting, especially on textual quality.
Improving Steering and Verification in AI-Assisted Data Analysis with Interactive Task Decomposition
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:LLM-powered tools like ChatGPT Data Analysis, have the potential to help users tackle the challenging task of data analysis programming, which requires expertise in data processing, programming, and statistics. However, our formative study (n=15) uncovered serious challenges in verifying AI-generated results and steering the AI (i.e., guiding the AI system to produce the desired output). We developed two contrasting approaches to address these challenges. The first (Stepwise) decomposes the problem into step-by-step subgoals with pairs of editable assumptions and code until task completion, while the second (Phasewise) decomposes the entire problem into three editable, logical phases: structured input/output assumptions, execution plan, and code. A controlled, within-subjects experiment (n=18) compared these systems against a conversational baseline. Users reported significantly greater control with the Stepwise and Phasewise systems, and found intervention, correction, and verification easier, compared to the baseline. The results suggest design guidelines and trade-offs for AI-assisted data analysis tools.
Co-audit: tools to help humans double-check AI-generated content
Oct 02, 2023Abstract:Users are increasingly being warned to check AI-generated content for correctness. Still, as LLMs (and other generative models) generate more complex output, such as summaries, tables, or code, it becomes harder for the user to audit or evaluate the output for quality or correctness. Hence, we are seeing the emergence of tool-assisted experiences to help the user double-check a piece of AI-generated content. We refer to these as co-audit tools. Co-audit tools complement prompt engineering techniques: one helps the user construct the input prompt, while the other helps them check the output response. As a specific example, this paper describes recent research on co-audit tools for spreadsheet computations powered by generative models. We explain why co-audit experiences are essential for any application of generative AI where quality is important and errors are consequential (as is common in spreadsheet computations). We propose a preliminary list of principles for co-audit, and outline research challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge