Charlie Zhang
Standards and Mobility Innovation Laboratory - Samsung Research America
On the Interplay of Pre-Training, Mid-Training, and RL on Reasoning Language Models
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Recent reinforcement learning (RL) techniques have yielded impressive reasoning improvements in language models, yet it remains unclear whether post-training truly extends a model's reasoning ability beyond what it acquires during pre-training. A central challenge is the lack of control in modern training pipelines: large-scale pre-training corpora are opaque, mid-training is often underexamined, and RL objectives interact with unknown prior knowledge in complex ways. To resolve this ambiguity, we develop a fully controlled experimental framework that isolates the causal contributions of pre-training, mid-training, and RL-based post-training. Our approach employs synthetic reasoning tasks with explicit atomic operations, parseable step-by-step reasoning traces, and systematic manipulation of training distributions. We evaluate models along two axes: extrapolative generalization to more complex compositions and contextual generalization across surface contexts. Using this framework, we reconcile competing views on RL's effectiveness. We show that: 1) RL produces true capability gains (pass@128) only when pre-training leaves sufficient headroom and when RL data target the model's edge of competence, tasks at the boundary that are difficult but not yet out of reach. 2) Contextual generalization requires minimal yet sufficient pre-training exposure, after which RL can reliably transfer. 3) Mid-training significantly enhances performance under fixed compute compared with RL only, demonstrating its central but underexplored role in training pipelines. 4) Process-level rewards reduce reward hacking and improve reasoning fidelity. Together, these results clarify the interplay between pre-training, mid-training, and RL, offering a foundation for understanding and improving reasoning LM training strategies.
An Ultra-Wideband Study of Vegetation Impact on Upper Midband / FR3 Communication
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Growing demand for high data rates is driving interest in the upper mid-band (FR 3) spectrum (6-24 GHz). While some propagation measurements exist in literature, the impact of vegetation on link performance remains under-explored. This study examines vegetation-induced losses in an urban scenario across 6-18 GHz. A simple method for calculating vegetation depth is introduced, along with a model that quantifies additional attenuation based on vegetation depth and frequency, divided into 1 GHz sub-bands. We see that excess vegetation loss increases with vegetation depth and higher frequencies. These findings provide insights for designing reliable, foliage-aware communication networks in FR 3.
Large Language Model (LLM) for Telecommunications: A Comprehensive Survey on Principles, Key Techniques, and Opportunities
May 17, 2024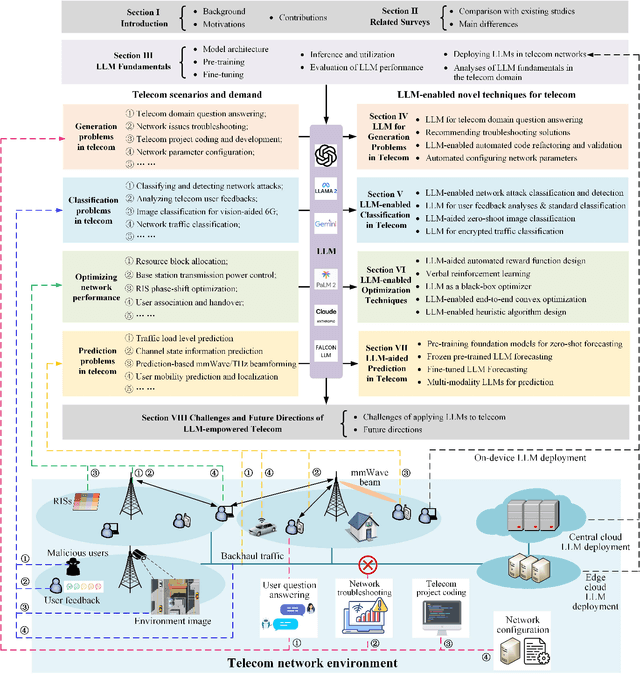
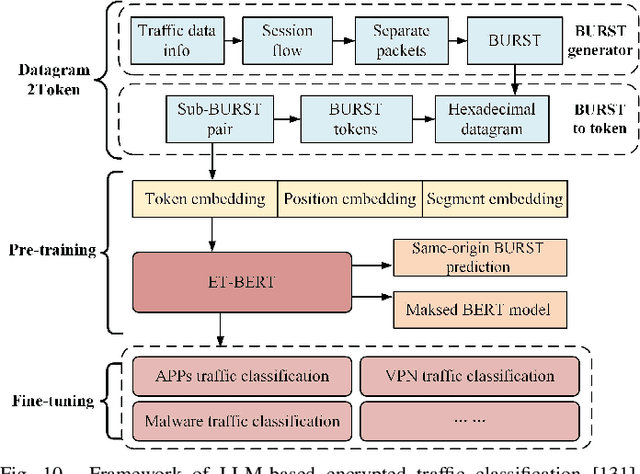
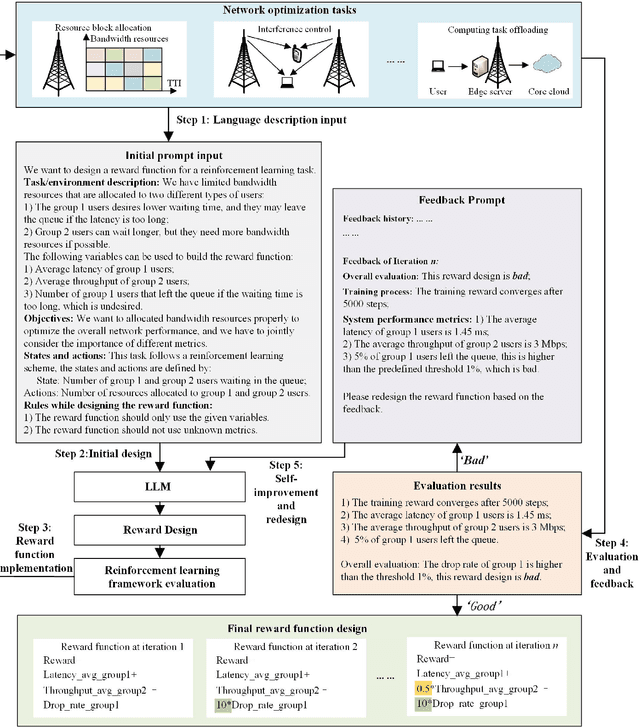
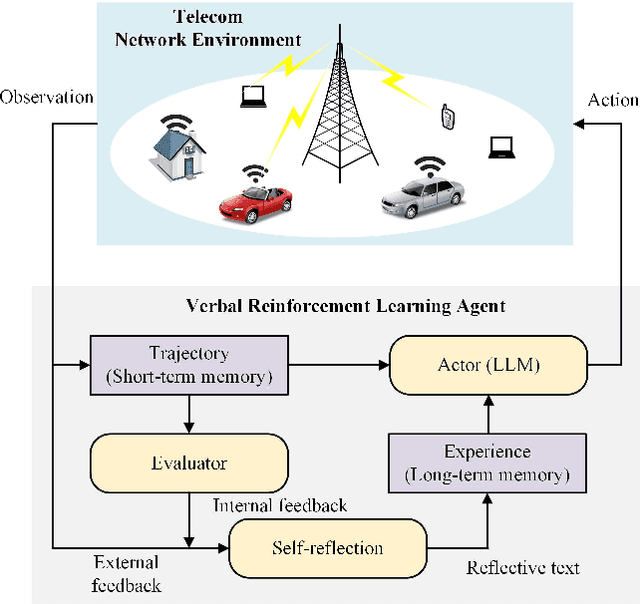
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have received considerable attention recently due to their outstanding comprehension and reasoning capabilities, leading to great progress in many fields. The advancement of LLM techniques also offers promising opportunities to automate many tasks in the telecommunication (telecom) field. After pre-training and fine-tuning, LLMs can perform diverse downstream tasks based on human instructions, paving the way to artificial general intelligence (AGI)-enabled 6G. Given the great potential of LLM technologies, this work aims to provide a comprehensive overview of LLM-enabled telecom networks. In particular, we first present LLM fundamentals, including model architecture, pre-training, fine-tuning, inference and utilization, model evaluation, and telecom deployment. Then, we introduce LLM-enabled key techniques and telecom applications in terms of generation, classification, optimization, and prediction problems. Specifically, the LLM-enabled generation applications include telecom domain knowledge, code, and network configuration generation. After that, the LLM-based classification applications involve network security, text, image, and traffic classification problems. Moreover, multiple LLM-enabled optimization techniques are introduced, such as automated reward function design for reinforcement learning and verbal reinforcement learning. Furthermore, for LLM-aided prediction problems, we discussed time-series prediction models and multi-modality prediction problems for telecom. Finally, we highlight the challenges and identify the future directions of LLM-enabled telecom networks.
Deep Learning and Transfer Learning Architectures for English Premier League Player Performance Forecasting
May 03, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a groundbreaking model for forecasting English Premier League (EPL) player performance using convolutional neural networks (CNNs). We evaluate Ridge regression, LightGBM and CNNs on the task of predicting upcoming player FPL score based on historical FPL data over the previous weeks. Our baseline models, Ridge regression and LightGBM, achieve solid performance and emphasize the importance of recent FPL points, influence, creativity, threat, and playtime in predicting EPL player performances. Our optimal CNN architecture achieves better performance with fewer input features and even outperforms the best previous EPL player performance forecasting models in the literature. The optimal CNN architecture also achieves very strong Spearman correlation with player rankings, indicating its strong implications for supporting the development of FPL artificial intelligence (AI) Agents and providing analysis for FPL managers. We additionally perform transfer learning experiments on soccer news data collected from The Guardian, for the same task of predicting upcoming player score, but do not identify a strong predictive signal in natural language news texts, achieving worse performance compared to both the CNN and baseline models. Overall, our CNN-based approach marks a significant advancement in EPL player performance forecasting and lays the foundation for transfer learning to other EPL prediction tasks such as win-loss odds for sports betting and the development of cutting-edge FPL AI Agents.
Nested Construction of Polar Codes via Transformers
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:Tailoring polar code construction for decoding algorithms beyond successive cancellation has remained a topic of significant interest in the field. However, despite the inherent nested structure of polar codes, the use of sequence models in polar code construction is understudied. In this work, we propose using a sequence modeling framework to iteratively construct a polar code for any given length and rate under various channel conditions. Simulations show that polar codes designed via sequential modeling using transformers outperform both 5G-NR sequence and Density Evolution based approaches for both AWGN and Rayleigh fading channels.
Towards Intelligent Network Management: Leveraging AI for Network Service Detection
Oct 14, 2023Abstract:As the complexity and scale of modern computer networks continue to increase, there has emerged an urgent need for precise traffic analysis, which plays a pivotal role in cutting-edge wireless connectivity technologies. This study focuses on leveraging Machine Learning methodologies to create an advanced network traffic classification system. We introduce a novel data-driven approach that excels in identifying various network service types in real-time, by analyzing patterns within the network traffic. Our method organizes similar kinds of network traffic into distinct categories, referred to as network services, based on latency requirement. Furthermore, it decomposes the network traffic stream into multiple, smaller traffic flows, with each flow uniquely carrying a specific service. Our ML models are trained on a dataset comprised of labeled examples representing different network service types collected on various Wi-Fi network conditions. Upon evaluation, our system demonstrates a remarkable accuracy in distinguishing the network services. These results emphasize the substantial promise of integrating Artificial Intelligence in wireless technologies. Such an approach encourages more efficient energy consumption, enhances Quality of Service assurance, and optimizes the allocation of network resources, thus laying a solid groundwork for the development of advanced intelligent networks.
Predicting Future CSI Feedback For Highly-Mobile Massive MIMO Systems
Feb 05, 2022Abstract:Massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system is promising in providing unprecedentedly high data rate. To achieve its full potential, the transceiver needs complete channel state information (CSI) to perform transmit/receive precoding/combining. This requirement, however, is challenging in the practical systems due to the unavoidable processing and feedback delays, which oftentimes degrades the performance to a great extent, especially in the high mobility scenarios. In this paper, we develop a deep learning based channel prediction framework that proactively predicts the downlink channel state information based on the past observed channel sequence. In its core, the model adopts a 3-D convolutional neural network (CNN) based architecture to efficiently learn the temporal, spatial and frequency correlations of downlink channel samples, based on which accurate channel prediction can be performed. Simulation results highlight the potential of the developed learning model in extracting information and predicting future downlink channels directly from the observed past channel sequence, which significantly improves the performance compared to the sample-and-hold approach, and mitigates the impact of the dynamic communication environment.
THz Band Channel Measurements and Statistical Modeling for Urban Microcellular Environments
Dec 03, 2021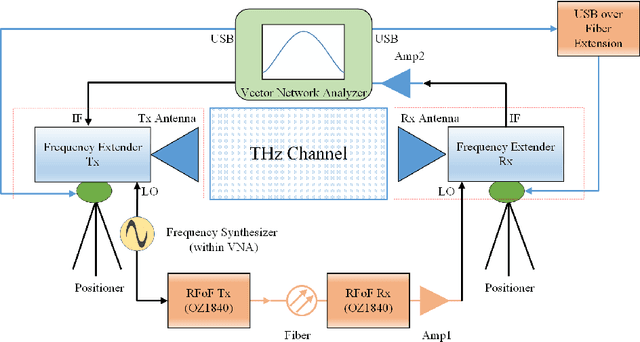
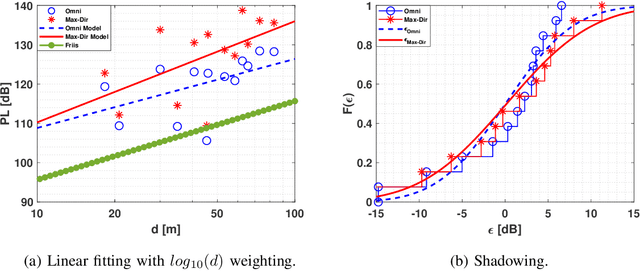
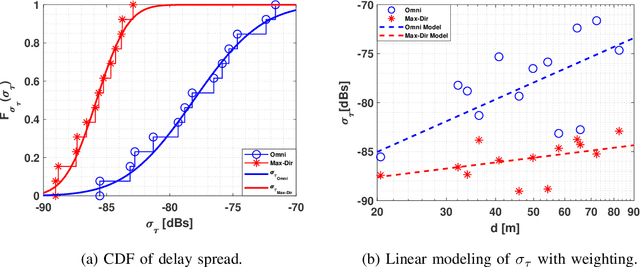
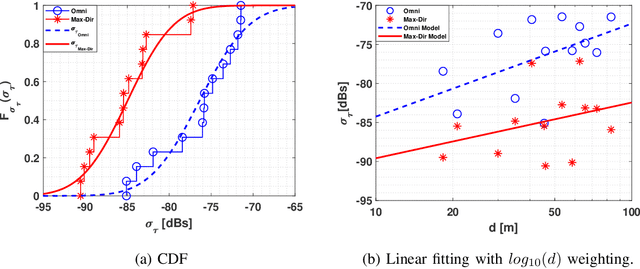
Abstract:The THz band (0.1-10 THz) has attracted considerable attention for next-generation wireless communications, due to the large amount of available bandwidth that may be key to meet the rapidly increasing data rate requirements. Before deploying a system in this band, a detailed wireless channel analysis is required as the basis for proper design and testing of system implementations. One of the most important deployment scenarios of this band is the outdoor microcellular environment, where the Transmitter (Tx) and the Receiver (Rx) have a significant height difference (typically $ \ge 10$ m). In this paper, we present double-directional (i.e., directionally resolved at both link ends) channel measurements in such a microcellular scenario encompassing street canyons and an open square. Measurements are done for a 1 GHz bandwidth between 145-146 GHz and an antenna beamwidth of 13 degree; distances between Tx and Rx are up to 85 m and the Tx is at a height of 11.5 m from the ground. The measurements are analyzed to estimate path loss, shadowing, delay spread, angular spread, and multipath component (MPC) power distribution. These results allow the development of more realistic and detailed THz channel models and system performance assessment.
THz Band Channel Measurements and Statistical Modeling for Urban D2D Environments
Sep 28, 2021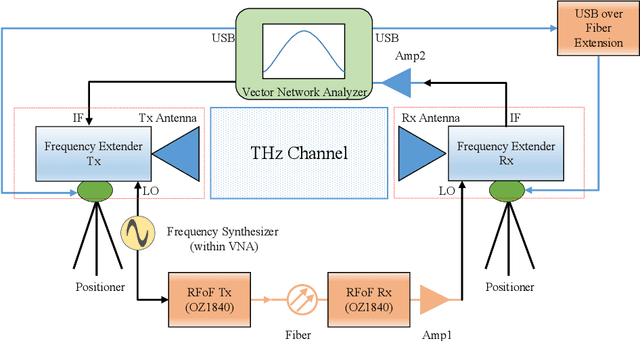
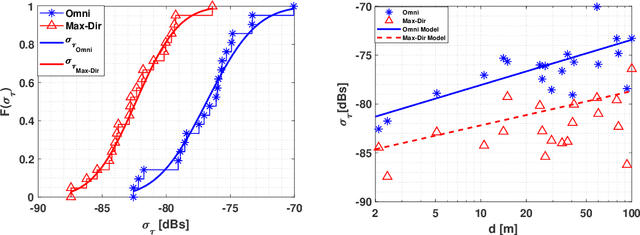
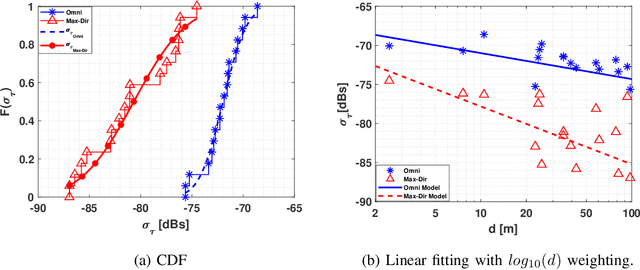
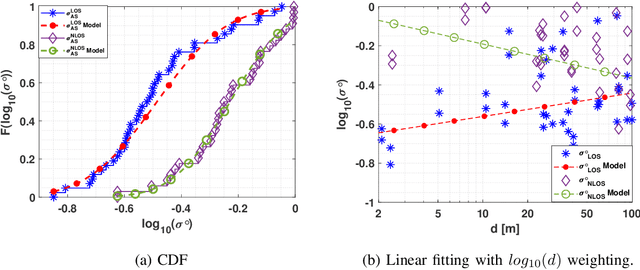
Abstract:THz band is envisioned to be used in 6G systems to meet the ever-increasing demand for data rate. However, before an eventual system design and deployment can proceed, detailed channel sounding measurements are required to understand key channel characteristics. In this paper, we present a first extensive set of channel measurements for urban outdoor environments that are ultra-wideband (1 GHz 3dB bandwidth), and double-directional where both the transmitter and receiver are at the same height. In all, we present measurements at 38 Tx/Rx location pairs, consisting of a total of nearly 50,000 impulse responses, at both line-of-sight (LoS) and non-line-of-sight (NLoS) cases in the 1-100 m range. We provide modeling for path loss, shadowing, delay spread, angular spread and multipath component (MPC) power distribution. We find, among other things, that outdoor communication over tens of meters is feasible in this frequency range even in NLoS scenarios, that omni-directional delay spreads of up to 100 ns, and directional delay spreads of up to 10 ns are observed, while angular spreads are also quite significant, and a surprisingly large number of MPCs are observed for 1 GHz bandwidth and 13 degree beamwidth. These results constitute an important first step towards better understanding the wireless channel in the THz band.
Pareto Deterministic Policy Gradients and Its Application in 5G Massive MIMO Networks
Dec 02, 2020

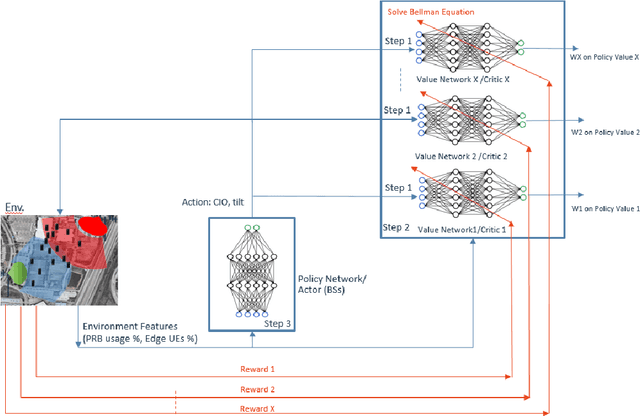
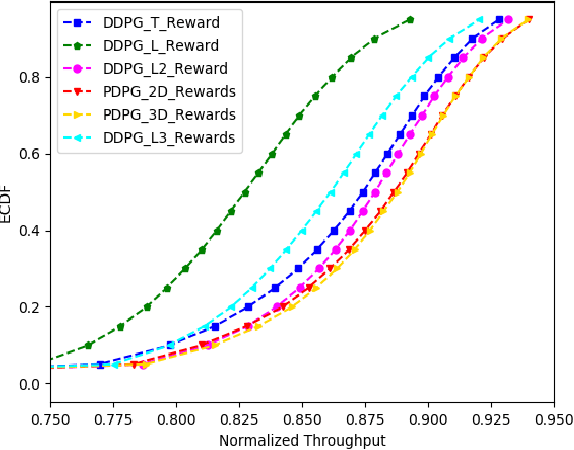
Abstract:In this paper, we consider jointly optimizing cell load balance and network throughput via a reinforcement learning (RL) approach, where inter-cell handover (i.e., user association assignment) and massive MIMO antenna tilting are configured as the RL policy to learn. Our rationale behind using RL is to circumvent the challenges of analytically modeling user mobility and network dynamics. To accomplish this joint optimization, we integrate vector rewards into the RL value network and conduct RL action via a separate policy network. We name this method as Pareto deterministic policy gradients (PDPG). It is an actor-critic, model-free and deterministic policy algorithm which can handle the coupling objectives with the following two merits: 1) It solves the optimization via leveraging the degree of freedom of vector reward as opposed to choosing handcrafted scalar-reward; 2) Cross-validation over multiple policies can be significantly reduced. Accordingly, the RL enabled network behaves in a self-organized way: It learns out the underlying user mobility through measurement history to proactively operate handover and antenna tilt without environment assumptions. Our numerical evaluation demonstrates that the introduced RL method outperforms scalar-reward based approaches. Meanwhile, to be self-contained, an ideal static optimization based brute-force search solver is included as a benchmark. The comparison shows that the RL approach performs as well as this ideal strategy, though the former one is constrained with limited environment observations and lower action frequency, whereas the latter ones have full access to the user mobility. The convergence of our introduced approach is also tested under different user mobility environment based on our measurement data from a real scenario.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge