Gary Xu
THz Band Channel Measurements and Statistical Modeling for Urban Microcellular Environments
Dec 03, 2021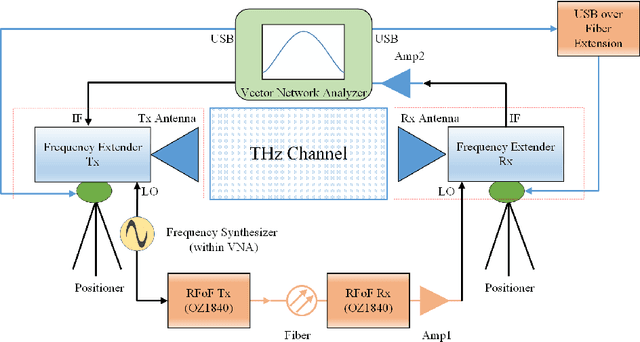
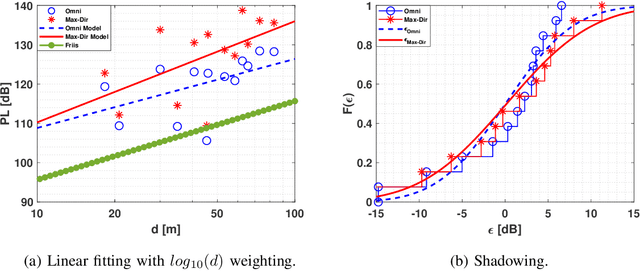
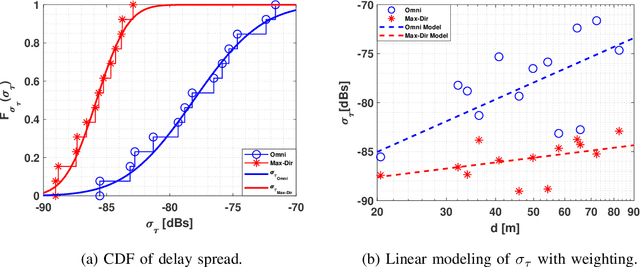
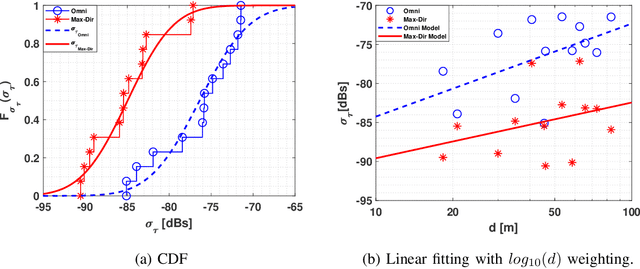
Abstract:The THz band (0.1-10 THz) has attracted considerable attention for next-generation wireless communications, due to the large amount of available bandwidth that may be key to meet the rapidly increasing data rate requirements. Before deploying a system in this band, a detailed wireless channel analysis is required as the basis for proper design and testing of system implementations. One of the most important deployment scenarios of this band is the outdoor microcellular environment, where the Transmitter (Tx) and the Receiver (Rx) have a significant height difference (typically $ \ge 10$ m). In this paper, we present double-directional (i.e., directionally resolved at both link ends) channel measurements in such a microcellular scenario encompassing street canyons and an open square. Measurements are done for a 1 GHz bandwidth between 145-146 GHz and an antenna beamwidth of 13 degree; distances between Tx and Rx are up to 85 m and the Tx is at a height of 11.5 m from the ground. The measurements are analyzed to estimate path loss, shadowing, delay spread, angular spread, and multipath component (MPC) power distribution. These results allow the development of more realistic and detailed THz channel models and system performance assessment.
THz Band Channel Measurements and Statistical Modeling for Urban D2D Environments
Sep 28, 2021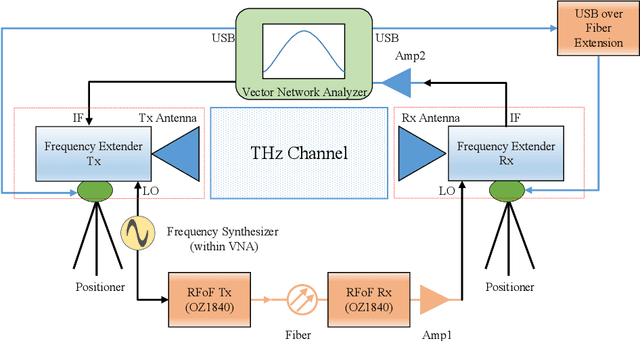
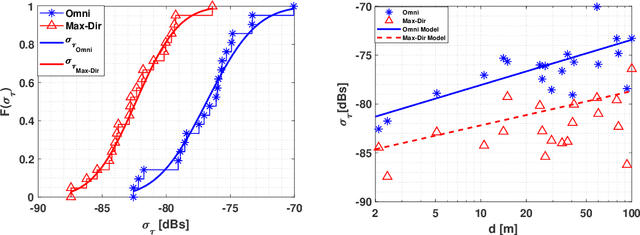
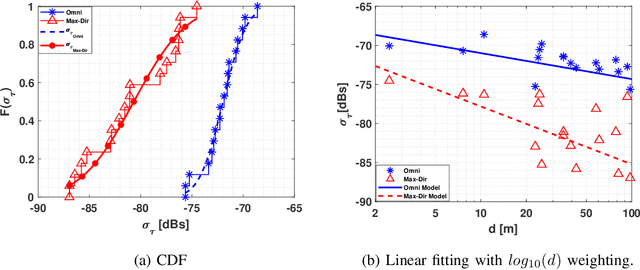
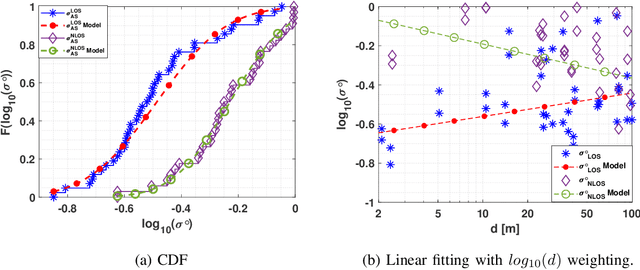
Abstract:THz band is envisioned to be used in 6G systems to meet the ever-increasing demand for data rate. However, before an eventual system design and deployment can proceed, detailed channel sounding measurements are required to understand key channel characteristics. In this paper, we present a first extensive set of channel measurements for urban outdoor environments that are ultra-wideband (1 GHz 3dB bandwidth), and double-directional where both the transmitter and receiver are at the same height. In all, we present measurements at 38 Tx/Rx location pairs, consisting of a total of nearly 50,000 impulse responses, at both line-of-sight (LoS) and non-line-of-sight (NLoS) cases in the 1-100 m range. We provide modeling for path loss, shadowing, delay spread, angular spread and multipath component (MPC) power distribution. We find, among other things, that outdoor communication over tens of meters is feasible in this frequency range even in NLoS scenarios, that omni-directional delay spreads of up to 100 ns, and directional delay spreads of up to 10 ns are observed, while angular spreads are also quite significant, and a surprisingly large number of MPCs are observed for 1 GHz bandwidth and 13 degree beamwidth. These results constitute an important first step towards better understanding the wireless channel in the THz band.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge