Bozhao Nan
MolX: Enhancing Large Language Models for Molecular Learning with A Multi-Modal Extension
Jun 10, 2024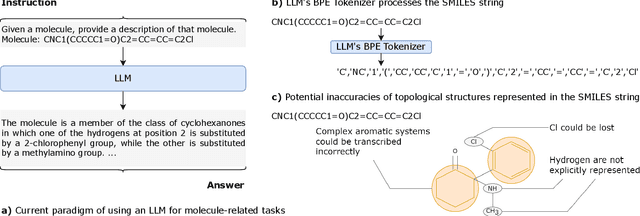
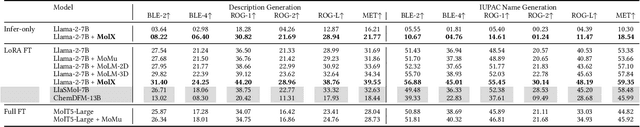
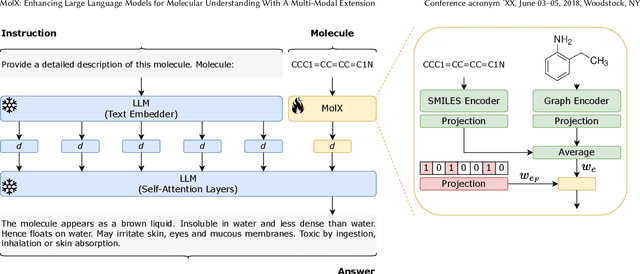
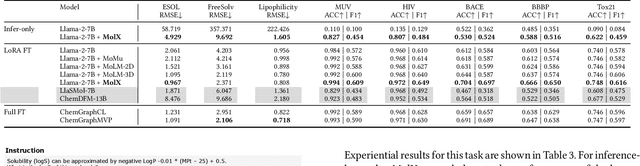
Abstract:Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) with their strong task-handling capabilities have shown remarkable advancements across a spectrum of fields, moving beyond natural language understanding. However, their proficiency within the chemistry domain remains restricted, especially in solving professional molecule-related tasks. This challenge is attributed to their inherent limitations in comprehending molecules using only common textual representations, i.e., SMILES strings. In this study, we seek to enhance the ability of LLMs to comprehend molecules by designing and equipping them with a multi-modal external module, namely MolX. In particular, instead of directly using a SMILES string to represent a molecule, we utilize specific encoders to extract fine-grained features from both SMILES string and 2D molecular graph representations for feeding into an LLM. Moreover, a human-defined molecular fingerprint is incorporated to leverage its embedded domain knowledge. Then, to establish an alignment between MolX and the LLM's textual input space, the whole model in which the LLM is frozen, is pre-trained with a versatile strategy including a diverse set of tasks. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that our proposed method only introduces a small number of trainable parameters while outperforming baselines on various downstream molecule-related tasks ranging from molecule-to-text translation to retrosynthesis, with and without fine-tuning the LLM.
Are we making much progress? Revisiting chemical reaction yield prediction from an imbalanced regression perspective
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:The yield of a chemical reaction quantifies the percentage of the target product formed in relation to the reactants consumed during the chemical reaction. Accurate yield prediction can guide chemists toward selecting high-yield reactions during synthesis planning, offering valuable insights before dedicating time and resources to wet lab experiments. While recent advancements in yield prediction have led to overall performance improvement across the entire yield range, an open challenge remains in enhancing predictions for high-yield reactions, which are of greater concern to chemists. In this paper, we argue that the performance gap in high-yield predictions results from the imbalanced distribution of real-world data skewed towards low-yield reactions, often due to unreacted starting materials and inherent ambiguities in the reaction processes. Despite this data imbalance, existing yield prediction methods continue to treat different yield ranges equally, assuming a balanced training distribution. Through extensive experiments on three real-world yield prediction datasets, we emphasize the urgent need to reframe reaction yield prediction as an imbalanced regression problem. Finally, we demonstrate that incorporating simple cost-sensitive re-weighting methods can significantly enhance the performance of yield prediction models on underrepresented high-yield regions.
Modeling non-uniform uncertainty in Reaction Prediction via Boosting and Dropout
Oct 07, 2023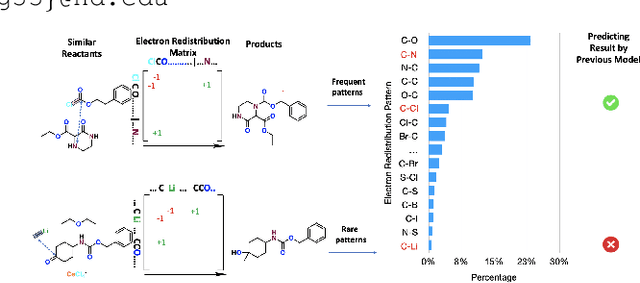
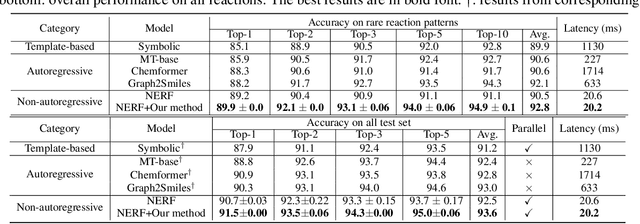
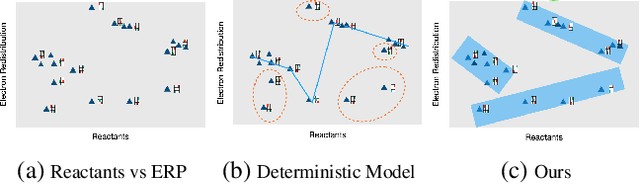
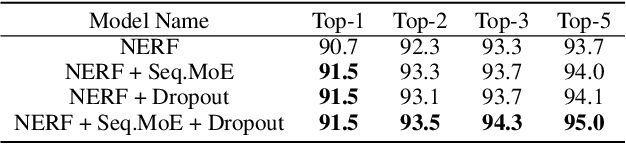
Abstract:Reaction prediction has been recognized as a critical task in synthetic chemistry, where the goal is to predict the outcome of a reaction based on the given reactants. With the widespread adoption of generative models, the Variational Autoencoder(VAE) framework has typically been employed to tackle challenges in reaction prediction, where the reactants are encoded as a condition for the decoder, which then generates the product. Despite effectiveness, these conditional VAE (CVAE) models still fail to adequately account for the inherent uncertainty in reaction prediction, which primarily stems from the stochastic reaction process. The principal limitations are twofold. Firstly, in these CVAE models, the prior is independent of the reactants, leading to a default wide and assumed uniform distribution variance of the generated product. Secondly, reactants with analogous molecular representations are presumed to undergo similar electronic transition processes, thereby producing similar products. This hinders the ability to model diverse reaction mechanisms effectively. Since the variance in outcomes is inherently non-uniform, we are thus motivated to develop a framework that generates reaction products with non-uniform uncertainty. Firstly, we eliminate the latent variable in previous CVAE models to mitigate uncontrol-label noise. Instead, we introduce randomness into product generation via boosting to ensemble diverse models and cover the range of potential outcomes, and through dropout to secure models with minor variations. Additionally, we design a ranking method to union the predictions from boosting and dropout, prioritizing the most plausible products. Experimental results on the largest reaction prediction benchmark USPTO-MIT show the superior performance of our proposed method in modeling the non-uniform uncertainty compared to baselines.
Learning Over Molecular Conformer Ensembles: Datasets and Benchmarks
Sep 29, 2023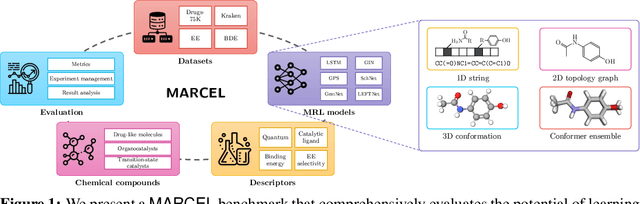
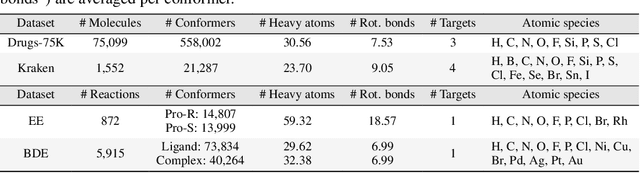
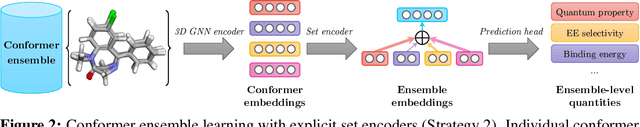
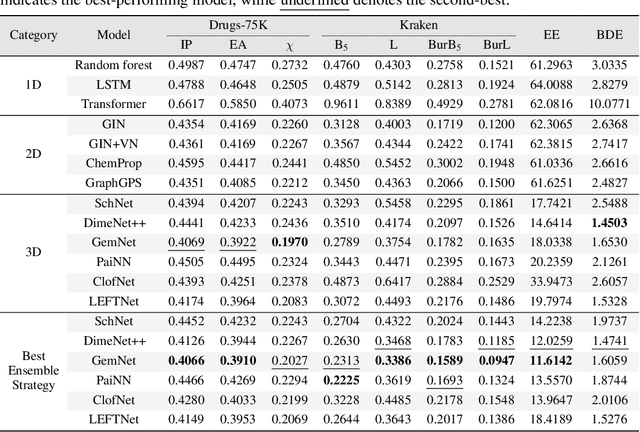
Abstract:Molecular Representation Learning (MRL) has proven impactful in numerous biochemical applications such as drug discovery and enzyme design. While Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are effective at learning molecular representations from a 2D molecular graph or a single 3D structure, existing works often overlook the flexible nature of molecules, which continuously interconvert across conformations via chemical bond rotations and minor vibrational perturbations. To better account for molecular flexibility, some recent works formulate MRL as an ensemble learning problem, focusing on explicitly learning from a set of conformer structures. However, most of these studies have limited datasets, tasks, and models. In this work, we introduce the first MoleculAR Conformer Ensemble Learning (MARCEL) benchmark to thoroughly evaluate the potential of learning on conformer ensembles and suggest promising research directions. MARCEL includes four datasets covering diverse molecule- and reaction-level properties of chemically diverse molecules including organocatalysts and transition-metal catalysts, extending beyond the scope of common GNN benchmarks that are confined to drug-like molecules. In addition, we conduct a comprehensive empirical study, which benchmarks representative 1D, 2D, and 3D molecular representation learning models, along with two strategies that explicitly incorporate conformer ensembles into 3D MRL models. Our findings reveal that direct learning from an accessible conformer space can improve performance on a variety of tasks and models.
What indeed can GPT models do in chemistry? A comprehensive benchmark on eight tasks
May 27, 2023
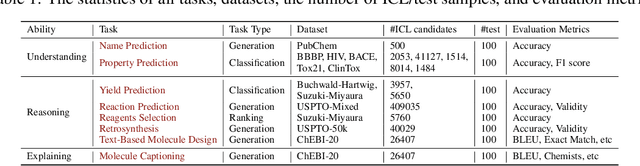
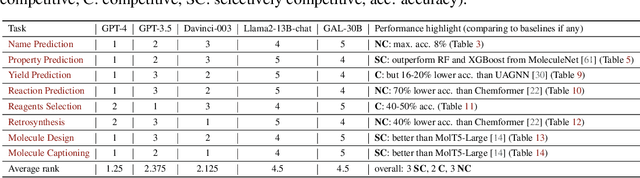

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) with strong abilities in natural language processing tasks have emerged and have been rapidly applied in various kinds of areas such as science, finance and software engineering. However, the capability of LLMs to advance the field of chemistry remains unclear. In this paper,we establish a comprehensive benchmark containing 8 practical chemistry tasks, including 1) name prediction, 2) property prediction, 3) yield prediction, 4) reaction prediction, 5) retrosynthesis (prediction of reactants from products), 6)text-based molecule design, 7) molecule captioning, and 8) reagent selection. Our analysis draws on widely recognized datasets including BBBP, Tox21, PubChem, USPTO, and ChEBI, facilitating a broad exploration of the capacities of LLMs within the context of practical chemistry. Three GPT models (GPT-4, GPT-3.5,and Davinci-003) are evaluated for each chemistry task in zero-shot and few-shot in-context learning settings with carefully selected demonstration examples and specially crafted prompts. The key results of our investigation are 1) GPT-4 outperforms the other two models among the three evaluated; 2) GPT models exhibit less competitive performance in tasks demanding precise understanding of molecular SMILES representation, such as reaction prediction and retrosynthesis;3) GPT models demonstrate strong capabilities in text-related explanation tasks such as molecule captioning; and 4) GPT models exhibit comparable or better performance to classical machine learning models when applied to chemical problems that can be transformed into classification or ranking tasks, such as property prediction, and yield prediction.
Graph-based Molecular Representation Learning
Jul 08, 2022



Abstract:Molecular representation learning (MRL) is a key step to build the connection between machine learning and chemical science. In particular, it encodes molecules as numerical vectors preserving the molecular structures and features, on top of which the downstream tasks (e.g., property prediction) can be performed. Recently, MRL has achieved considerable progress, especially in deep molecular graph learning-based methods. In this survey, we systematically review these graph-based molecular representation techniques. Specifically, we first introduce the data and features of the 2D and 3D graph molecular datasets. Then we summarize the methods specially designed for MRL and categorize them into four strategies. Furthermore, we discuss some typical chemical applications supported by MRL. To facilitate studies in this fast-developing area, we also list the benchmarks and commonly used datasets in the paper. Finally, we share our thoughts on future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge