Bowen Ma
FOAM: A General Frequency-Optimized Anti-Overlapping Framework for Overlapping Object Perception
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Overlapping object perception aims to decouple the randomly overlapping foreground-background features, extracting foreground features while suppressing background features, which holds significant application value in fields such as security screening and medical auxiliary diagnosis. Despite some research efforts to tackle the challenge of overlapping object perception, most solutions are confined to the spatial domain. Through frequency domain analysis, we observe that the degradation of contours and textures due to the overlapping phenomenon can be intuitively reflected in the magnitude spectrum. Based on this observation, we propose a general Frequency-Optimized Anti-Overlapping Framework (FOAM) to assist the model in extracting more texture and contour information, thereby enhancing the ability for anti-overlapping object perception. Specifically, we design the Frequency Spatial Transformer Block (FSTB), which can simultaneously extract features from both the frequency and spatial domains, helping the network capture more texture features from the foreground. In addition, we introduce the Hierarchical De-Corrupting (HDC) mechanism, which aligns adjacent features in the separately constructed base branch and corruption branch using a specially designed consistent loss during the training phase. This mechanism suppresses the response to irrelevant background features of FSTBs, thereby improving the perception of foreground contour. We conduct extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness and generalization of the proposed FOAM, which further improves the accuracy of state-of-the-art models on four datasets, specifically for the three overlapping object perception tasks: Prohibited Item Detection, Prohibited Item Segmentation, and Pneumonia Detection. The code will be open source once the paper is accepted.
CSPCL: Category Semantic Prior Contrastive Learning for Deformable DETR-Based Prohibited Item Detectors
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Prohibited item detection based on X-ray images is one of the most effective security inspection methods. However, the foreground-background feature coupling caused by the overlapping phenomenon specific to X-ray images makes general detectors designed for natural images perform poorly. To address this issue, we propose a Category Semantic Prior Contrastive Learning (CSPCL) mechanism, which aligns the class prototypes perceived by the classifier with the content queries to correct and supplement the missing semantic information responsible for classification, thereby enhancing the model sensitivity to foreground features.To achieve this alignment, we design a specific contrastive loss, CSP loss, which includes Intra-Class Truncated Attraction (ITA) loss and Inter-Class Adaptive Repulsion (IAR) loss, and outperforms classic N-pair loss and InfoNCE loss. Specifically, ITA loss leverages class prototypes to attract intra-class category-specific content queries while preserving necessary distinctiveness. IAR loss utilizes class prototypes to adaptively repel inter-class category-specific content queries based on the similarity between class prototypes, helping disentangle features of similar categories.CSPCL is general and can be easily integrated into Deformable DETR-based models. Extensive experiments on the PIXray and OPIXray datasets demonstrate that CSPCL significantly enhances the performance of various state-of-the-art models without increasing complexity.The code will be open source once the paper is accepted.
Edge Modeling Activation Free Fourier Network for Spacecraft Image Denoising
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Spacecraft image denoising is a crucial basic technology closely related to aerospace research. However, the existing deep learning-based image denoising methods lack deep consideration of the characteristics of spacecraft image. To address the aforementioned shortcomings, we analyses spacecraft noise image and identifies two main characteristics. One is that there are a large number of low-light images in the obtained spacecraft noise image dataset. Another is there are a lot of repetitive periodic features in spacecraft image. According to the above mentioned characteristics, we propose a Edge modeling Activation Free Fourier Network (EAFFN), which is an efficient spacecraft image denoising method including Edge Modeling Block (EMB) and Activation Free Fourier Block (AFFB). We present EMB to effectively model edge and extract structural information and better identify the spacecraft components from dark regions in spacecraft noise image. We present AFFB and utilize an improved fast fourier block to extract repetitive periodic features and long-range information in noisy spacecraft image. In addition, Simple Gate is designed in our AFFB to reduce the computational complexity. Extensive experimental results demonstrate our EAFFN performs competitively to the state-of-the-art on spacecraft noise image datasets.
Norface: Improving Facial Expression Analysis by Identity Normalization
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:Facial Expression Analysis remains a challenging task due to unexpected task-irrelevant noise, such as identity, head pose, and background. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel framework, called Norface, that is unified for both Action Unit (AU) analysis and Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) tasks. Norface consists of a normalization network and a classification network. First, the carefully designed normalization network struggles to directly remove the above task-irrelevant noise, by maintaining facial expression consistency but normalizing all original images to a common identity with consistent pose, and background. Then, these additional normalized images are fed into the classification network. Due to consistent identity and other factors (e.g. head pose, background, etc.), the normalized images enable the classification network to extract useful expression information more effectively. Additionally, the classification network incorporates a Mixture of Experts to refine the latent representation, including handling the input of facial representations and the output of multiple (AU or emotion) labels. Extensive experiments validate the carefully designed framework with the insight of identity normalization. The proposed method outperforms existing SOTA methods in multiple facial expression analysis tasks, including AU detection, AU intensity estimation, and FER tasks, as well as their cross-dataset tasks. For the normalized datasets and code please visit {https://norface-fea.github.io/}.
Open-Vocabulary X-ray Prohibited Item Detection via Fine-tuning CLIP
Jun 16, 2024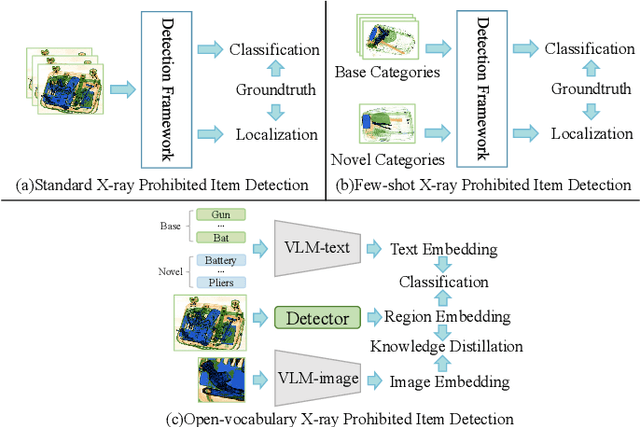
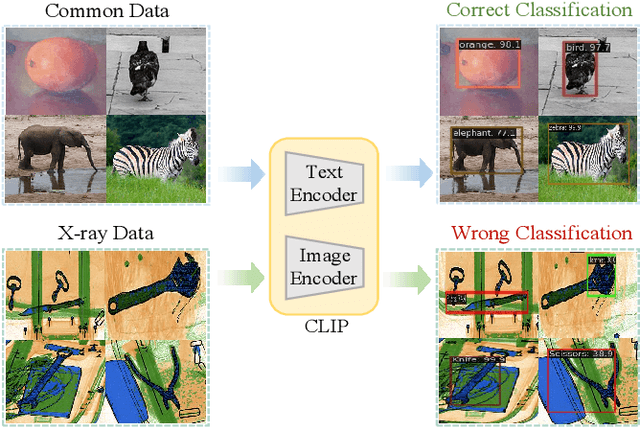
Abstract:X-ray prohibited item detection is an essential component of security check and categories of prohibited item are continuously increasing in accordance with the latest laws. Previous works all focus on close-set scenarios, which can only recognize known categories used for training and often require time-consuming as well as labor-intensive annotations when learning novel categories, resulting in limited real-world applications. Although the success of vision-language models (e.g. CLIP) provides a new perspectives for open-set X-ray prohibited item detection, directly applying CLIP to X-ray domain leads to a sharp performance drop due to domain shift between X-ray data and general data used for pre-training CLIP. To address aforementioned challenges, in this paper, we introduce distillation-based open-vocabulary object detection (OVOD) task into X-ray security inspection domain by extending CLIP to learn visual representations in our specific X-ray domain, aiming to detect novel prohibited item categories beyond base categories on which the detector is trained. Specifically, we propose X-ray feature adapter and apply it to CLIP within OVOD framework to develop OVXD model. X-ray feature adapter containing three adapter submodules of bottleneck architecture, which is simple but can efficiently integrate new knowledge of X-ray domain with original knowledge, further bridge domain gap and promote alignment between X-ray images and textual concepts. Extensive experiments conducted on PIXray and PIDray datasets demonstrate that proposed method performs favorably against other baseline OVOD methods in detecting novel categories in X-ray scenario. It outperforms previous best result by 15.2 AP50 and 1.5 AP50 on PIXray and PIDray with achieving 21.0 AP50 and 27.8 AP50 respectively.
MMCL: Boosting Deformable DETR-Based Detectors with Multi-Class Min-Margin Contrastive Learning for Superior Prohibited Item Detection
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Prohibited Item detection in X-ray images is one of the most effective security inspection methods.However, differing from natural light images, the unique overlapping phenomena in X-ray images lead to the coupling of foreground and background features, thereby lowering the accuracy of general object detectors.Therefore, we propose a Multi-Class Min-Margin Contrastive Learning (MMCL) method that, by clarifying the category semantic information of content queries under the deformable DETR architecture, aids the model in extracting specific category foreground information from coupled features.Specifically, after grouping content queries by the number of categories, we employ the Multi-Class Inter-Class Exclusion (MIE) loss to push apart content queries from different groups. Concurrently, the Intra-Class Min-Margin Clustering (IMC) loss is utilized to attract content queries within the same group, while ensuring the preservation of necessary disparity. As training, the inherent Hungarian matching of the model progressively strengthens the alignment between each group of queries and the semantic features of their corresponding category of objects. This evolving coherence ensures a deep-seated grasp of category characteristics, consequently bolstering the anti-overlapping detection capabilities of models.MMCL is versatile and can be easily plugged into any deformable DETR-based model with dozens of lines of code. Extensive experiments on the PIXray and OPIXray datasets demonstrate that MMCL significantly enhances the performance of various state-of-the-art models without increasing complexity. The code has been released at https://github.com/anonymity0403/MMCL.
Emphasizing Crucial Features for Efficient Image Restoration
May 19, 2024



Abstract:Image restoration is a challenging ill-posed problem which estimates latent sharp image from its degraded counterpart. Although the existing methods have achieved promising performance by designing novelty architecture of module, they ignore the fact that different regions in a corrupted image undergo varying degrees of degradation. In this paper, we propose an efficient and effective framework to adapt to varying degrees of degradation across different regions for image restoration. Specifically, we design a spatial and frequency attention mechanism (SFAM) to emphasize crucial features for restoration. SFAM consists of two modules: the spatial domain attention module (SDAM) and the frequency domain attention module (FDAM). The SFAM discerns the degradation location through spatial selective attention and channel selective attention in the spatial domain, while the FDAM enhances high-frequency signals to amplify the disparities between sharp and degraded image pairs in the spectral domain. Additionally, to capture global range information, we introduce a multi-scale block (MSBlock) that consists of three scale branches, each containing multiple simplified channel attention blocks (SCABlocks) and a multi-scale feed-forward block (MSFBlock). Finally, we propose our ECFNet, which integrates the aforementioned components into a U-shaped backbone for recovering high-quality images. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of ECFNet, outperforming state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
AO-DETR: Anti-Overlapping DETR for X-Ray Prohibited Items Detection
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:Prohibited item detection in X-ray images is one of the most essential and highly effective methods widely employed in various security inspection scenarios. Considering the significant overlapping phenomenon in X-ray prohibited item images, we propose an Anti-Overlapping DETR (AO-DETR) based on one of the state-of-the-art general object detectors, DINO. Specifically, to address the feature coupling issue caused by overlapping phenomena, we introduce the Category-Specific One-to-One Assignment (CSA) strategy to constrain category-specific object queries in predicting prohibited items of fixed categories, which can enhance their ability to extract features specific to prohibited items of a particular category from the overlapping foreground-background features. To address the edge blurring problem caused by overlapping phenomena, we propose the Look Forward Densely (LFD) scheme, which improves the localization accuracy of reference boxes in mid-to-high-level decoder layers and enhances the ability to locate blurry edges of the final layer. Similar to DINO, our AO-DETR provides two different versions with distinct backbones, tailored to meet diverse application requirements. Extensive experiments on the PIXray and OPIXray datasets demonstrate that the proposed method surpasses the state-of-the-art object detectors, indicating its potential applications in the field of prohibited item detection. The source code will be released at https://github.com/Limingyuan001/AO-DETR-test.
Towards a Simultaneous and Granular Identity-Expression Control in Personalized Face Generation
Jan 02, 2024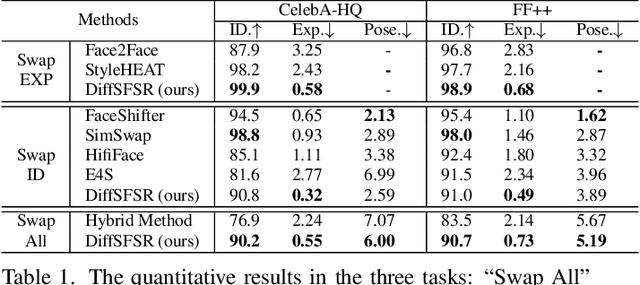
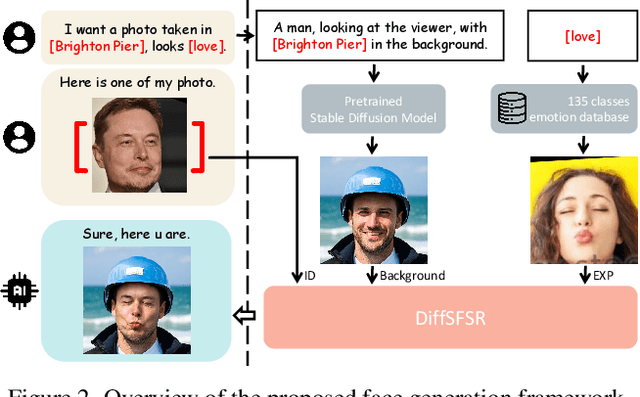

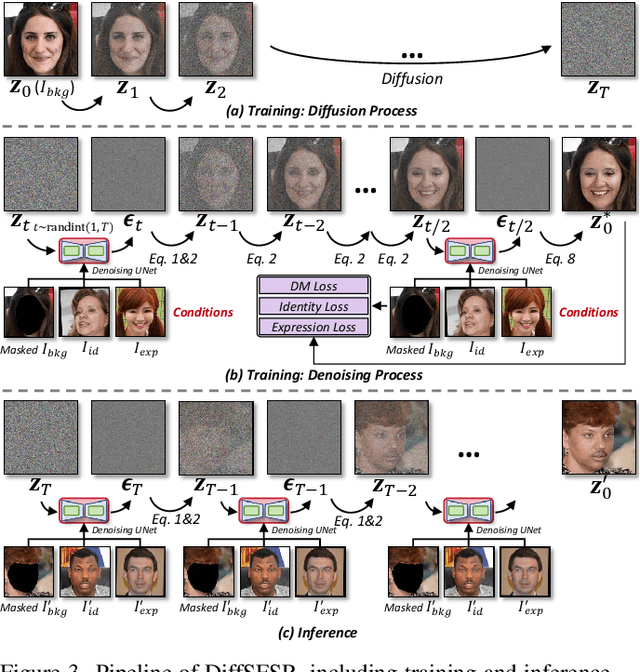
Abstract:In human-centric content generation, the pre-trained text-to-image models struggle to produce user-wanted portrait images, which retain the identity of individuals while exhibiting diverse expressions. This paper introduces our efforts towards personalized face generation. To this end, we propose a novel multi-modal face generation framework, capable of simultaneous identity-expression control and more fine-grained expression synthesis. Our expression control is so sophisticated that it can be specialized by the fine-grained emotional vocabulary. We devise a novel diffusion model that can undertake the task of simultaneously face swapping and reenactment. Due to the entanglement of identity and expression, it's nontrivial to separately and precisely control them in one framework, thus has not been explored yet. To overcome this, we propose several innovative designs in the conditional diffusion model, including balancing identity and expression encoder, improved midpoint sampling, and explicitly background conditioning. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the controllability and scalability of the proposed framework, in comparison with state-of-the-art text-to-image, face swapping, and face reenactment methods.
FlowFace++: Explicit Semantic Flow-supervised End-to-End Face Swapping
Jun 26, 2023



Abstract:This work proposes a novel face-swapping framework FlowFace++, utilizing explicit semantic flow supervision and end-to-end architecture to facilitate shape-aware face-swapping. Specifically, our work pretrains a facial shape discriminator to supervise the face swapping network. The discriminator is shape-aware and relies on a semantic flow-guided operation to explicitly calculate the shape discrepancies between the target and source faces, thus optimizing the face swapping network to generate highly realistic results. The face swapping network is a stack of a pre-trained face-masked autoencoder (MAE), a cross-attention fusion module, and a convolutional decoder. The MAE provides a fine-grained facial image representation space, which is unified for the target and source faces and thus facilitates final realistic results. The cross-attention fusion module carries out the source-to-target face swapping in a fine-grained latent space while preserving other attributes of the target image (e.g. expression, head pose, hair, background, illumination, etc). Lastly, the convolutional decoder further synthesizes the swapping results according to the face-swapping latent embedding from the cross-attention fusion module. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments on in-the-wild faces demonstrate that our FlowFace++ outperforms the state-of-the-art significantly, particularly while the source face is obstructed by uneven lighting or angle offset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge