Hu Gao
From Physical Degradation Models to Task-Aware All-in-One Image Restoration
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:All-in-one image restoration aims to adaptively handle multiple restoration tasks with a single trained model. Although existing methods achieve promising results by introducing prompt information or leveraging large models, the added learning modules increase system complexity and hinder real-time applicability. In this paper, we adopt a physical degradation modeling perspective and predict a task-aware inverse degradation operator for efficient all-in-one image restoration. The framework consists of two stages. In the first stage, the predicted inverse operator produces an initial restored image together with an uncertainty perception map that highlights regions difficult to reconstruct, ensuring restoration reliability. In the second stage, the restoration is further refined under the guidance of this uncertainty map. The same inverse operator prediction network is used in both stages, with task-aware parameters introduced after operator prediction to adapt to different degradation tasks. Moreover, by accelerating the convolution of the inverse operator, the proposed method achieves efficient all-in-one image restoration. The resulting tightly integrated architecture, termed OPIR, is extensively validated through experiments, demonstrating superior all-in-one restoration performance while remaining highly competitive on task-aligned restoration.
Establishing Stochastic Object Models from Noisy Data via Ambient Measurement-Integrated Diffusion
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Task-based measures of image quality (IQ) are critical for evaluating medical imaging systems, which must account for randomness including anatomical variability. Stochastic object models (SOMs) provide a statistical description of such variability, but conventional mathematical SOMs fail to capture realistic anatomy, while data-driven approaches typically require clean data rarely available in clinical tasks. To address this challenge, we propose AMID, an unsupervised Ambient Measurement-Integrated Diffusion with noise decoupling, which establishes clean SOMs directly from noisy measurements. AMID introduces a measurement-integrated strategy aligning measurement noise with the diffusion trajectory, and explicitly models coupling between measurement and diffusion noise across steps, an ambient loss is thus designed base on it to learn clean SOMs. Experiments on real CT and mammography datasets show that AMID outperforms existing methods in generation fidelity and yields more reliable task-based IQ evaluation, demonstrating its potential for unsupervised medical imaging analysis.
Physically Interpretable Multi-Degradation Image Restoration via Deep Unfolding and Explainable Convolution
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Although image restoration has advanced significantly, most existing methods target only a single type of degradation. In real-world scenarios, images often contain multiple degradations simultaneously, such as rain, noise, and haze, requiring models capable of handling diverse degradation types. Moreover, methods that improve performance through module stacking often suffer from limited interpretability. In this paper, we propose a novel interpretability-driven approach for multi-degradation image restoration, built upon a deep unfolding network that maps the iterative process of a mathematical optimization algorithm into a learnable network structure. Specifically, we employ an improved second-order semi-smooth Newton algorithm to ensure that each module maintains clear physical interpretability. To further enhance interpretability and adaptability, we design an explainable convolution module inspired by the human brain's flexible information processing and the intrinsic characteristics of images, allowing the network to flexibly leverage learned knowledge and autonomously adjust parameters for different input. The resulting tightly integrated architecture, named InterIR, demonstrates excellent performance in multi-degradation restoration while remaining highly competitive on single-degradation tasks.
Learning to Restore Multi-Degraded Images via Ingredient Decoupling and Task-Aware Path Adaptation
Nov 07, 2025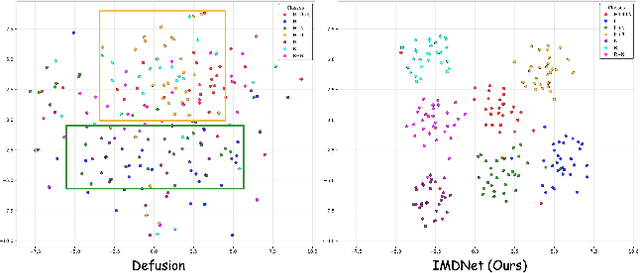
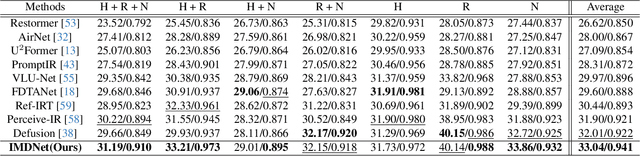
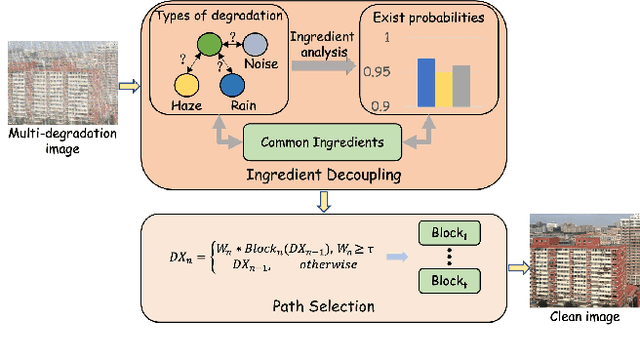
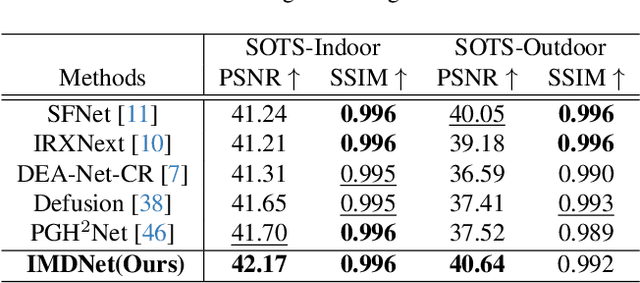
Abstract:Image restoration (IR) aims to recover clean images from degraded observations. Despite remarkable progress, most existing methods focus on a single degradation type, whereas real-world images often suffer from multiple coexisting degradations, such as rain, noise, and haze coexisting in a single image, which limits their practical effectiveness. In this paper, we propose an adaptive multi-degradation image restoration network that reconstructs images by leveraging decoupled representations of degradation ingredients to guide path selection. Specifically, we design a degradation ingredient decoupling block (DIDBlock) in the encoder to separate degradation ingredients statistically by integrating spatial and frequency domain information, enhancing the recognition of multiple degradation types and making their feature representations independent. In addition, we present fusion block (FBlock) to integrate degradation information across all levels using learnable matrices. In the decoder, we further introduce a task adaptation block (TABlock) that dynamically activates or fuses functional branches based on the multi-degradation representation, flexibly selecting optimal restoration paths under diverse degradation conditions. The resulting tightly integrated architecture, termed IMDNet, is extensively validated through experiments, showing superior performance on multi-degradation restoration while maintaining strong competitiveness on single-degradation tasks.
MBMamba: When Memory Buffer Meets Mamba for Structure-Aware Image Deblurring
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:The Mamba architecture has emerged as a promising alternative to CNNs and Transformers for image deblurring. However, its flatten-and-scan strategy often results in local pixel forgetting and channel redundancy, limiting its ability to effectively aggregate 2D spatial information. Although existing methods mitigate this by modifying the scan strategy or incorporating local feature modules, it increase computational complexity and hinder real-time performance. In this paper, we propose a structure-aware image deblurring network without changing the original Mamba architecture. Specifically, we design a memory buffer mechanism to preserve historical information for later fusion, enabling reliable modeling of relevance between adjacent features. Additionally, we introduce an Ising-inspired regularization loss that simulates the energy minimization of the physical system's "mutual attraction" between pixels, helping to maintain image structure and coherence. Building on this, we develop MBMamba. Experimental results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on widely used benchmarks.
Salient Region-Guided Spacecraft Image Arbitrary-Scale Super-Resolution Network
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Spacecraft image super-resolution seeks to enhance low-resolution spacecraft images into high-resolution ones. Although existing arbitrary-scale super-resolution methods perform well on general images, they tend to overlook the difference in features between the spacecraft core region and the large black space background, introducing irrelevant noise. In this paper, we propose a salient region-guided spacecraft image arbitrary-scale super-resolution network (SGSASR), which uses features from the spacecraft core salient regions to guide latent modulation and achieve arbitrary-scale super-resolution. Specifically, we design a spacecraft core region recognition block (SCRRB) that identifies the core salient regions in spacecraft images using a pre-trained saliency detection model. Furthermore, we present an adaptive-weighted feature fusion enhancement mechanism (AFFEM) to selectively aggregate the spacecraft core region features with general image features by dynamic weight parameter to enhance the response of the core salient regions. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SGSASR outperforms state-of-the-art approaches.
Enhancing Image Restoration through Learning Context-Rich and Detail-Accurate Features
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Image restoration involves recovering high-quality images from their corrupted versions, requiring a nuanced balance between spatial details and contextual information. While certain methods address this balance, they predominantly emphasize spatial aspects, neglecting frequency variation comprehension. In this paper, we present a multi-scale design that optimally balances these competing objectives, seamlessly integrating spatial and frequency domain knowledge to selectively recover the most informative information. Specifically, we develop a hybrid scale frequency selection block (HSFSBlock), which not only captures multi-scale information from the spatial domain, but also selects the most informative components for image restoration in the frequency domain. Furthermore, to mitigate the inherent noise introduced by skip connections employing only addition or concatenation, we introduce a skip connection attention mechanism (SCAM) to selectively determines the information that should propagate through skip connections. The resulting tightly interlinked architecture, named as LCDNet. Extensive experiments conducted across diverse image restoration tasks showcase that our model attains performance levels that are either superior or comparable to those of state-of-the-art algorithms.
Adaptive Identification of Blurred Regions for Accurate Image Deblurring
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:Image deblurring aims to restore high-quality images from blurred ones. While existing deblurring methods have made significant progress, most overlook the fact that the degradation degree varies across different regions. In this paper, we propose AIBNet, a network that adaptively identifies the blurred regions, enabling differential restoration of these regions. Specifically, we design a spatial feature differential handling block (SFDHBlock), with the core being the spatial domain feature enhancement module (SFEM). Through the feature difference operation, SFEM not only helps the model focus on the key information in the blurred regions but also eliminates the interference of implicit noise. Additionally, based on the fact that the difference between sharp and blurred images primarily lies in the high-frequency components, we propose a high-frequency feature selection block (HFSBlock). The HFSBlock first uses learnable filters to extract high-frequency features and then selectively retains the most important ones. To fully leverage the decoder's potential, we use a pre-trained model as the encoder and incorporate the above modules only in the decoder. Finally, to alleviate the resource burden during training, we introduce a progressive training strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our AIBNet achieves superior performance in image deblurring.
Towards Differential Handling of Various Blur Regions for Accurate Image Deblurring
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Image deblurring aims to restore high-quality images by removing undesired degradation. Although existing methods have yielded promising results, they either overlook the varying degrees of degradation across different regions of the blurred image, or they approximate nonlinear function properties by stacking numerous nonlinear activation functions. In this paper, we propose a differential handling network (DHNet) to perform differential processing for different blur regions. Specifically, we design a Volterra block (VBlock) to integrate the nonlinear characteristics into the deblurring network, avoiding the previous operation of stacking the number of nonlinear activation functions to map complex input-output relationships. To enable the model to adaptively address varying degradation degrees in blurred regions, we devise the degradation degree recognition expert module (DDRE). This module initially incorporates prior knowledge from a well-trained model to estimate spatially variable blur information. Consequently, the router can map the learned degradation representation and allocate weights to experts according to both the degree of degradation and the size of the regions. Comprehensive experimental results show that DHNet effectively surpasses state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Spatial and Frequency Domain Adaptive Fusion Network for Image Deblurring
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Image deblurring aims to reconstruct a latent sharp image from its corresponding blurred one. Although existing methods have achieved good performance, most of them operate exclusively in either the spatial domain or the frequency domain, rarely exploring solutions that fuse both domains. In this paper, we propose a spatial-frequency domain adaptive fusion network (SFAFNet) to address this limitation. Specifically, we design a gated spatial-frequency domain feature fusion block (GSFFBlock), which consists of three key components: a spatial domain information module, a frequency domain information dynamic generation module (FDGM), and a gated fusion module (GFM). The spatial domain information module employs the NAFBlock to integrate local information. Meanwhile, in the FDGM, we design a learnable low-pass filter that dynamically decomposes features into separate frequency subbands, capturing the image-wide receptive field and enabling the adaptive exploration of global contextual information. Additionally, to facilitate information flow and the learning of complementary representations. In the GFM, we present a gating mechanism (GATE) to re-weight spatial and frequency domain features, which are then fused through the cross-attention mechanism (CAM). Experimental results demonstrate that our SFAFNet performs favorably compared to state-of-the-art approaches on commonly used benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge