Boaz Carmeli
Investigating the Development of Task-Oriented Communication in Vision-Language Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:We investigate whether \emph{LLM-based agents} can develop task-oriented communication protocols that differ from standard natural language in collaborative reasoning tasks. Our focus is on two core properties such task-oriented protocols may exhibit: Efficiency -- conveying task-relevant information more concisely than natural language, and Covertness -- becoming difficult for external observers to interpret, raising concerns about transparency and control. To investigate these aspects, we use a referential-game framework in which vision-language model (VLM) agents communicate, providing a controlled, measurable setting for evaluating language variants. Experiments show that VLMs can develop effective, task-adapted communication patterns. At the same time, they can develop covert protocols that are difficult for humans and external agents to interpret. We also observe spontaneous coordination between similar models without explicitly shared protocols. These findings highlight both the potential and the risks of task-oriented communication, and position referential games as a valuable testbed for future work in this area.
CtD: Composition through Decomposition in Emergent Communication
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Compositionality is a cognitive mechanism that allows humans to systematically combine known concepts in novel ways. This study demonstrates how artificial neural agents acquire and utilize compositional generalization to describe previously unseen images. Our method, termed "Composition through Decomposition", involves two sequential training steps. In the 'Decompose' step, the agents learn to decompose an image into basic concepts using a codebook acquired during interaction in a multi-target coordination game. Subsequently, in the 'Compose' step, the agents employ this codebook to describe novel images by composing basic concepts into complex phrases. Remarkably, we observe cases where generalization in the `Compose' step is achieved zero-shot, without the need for additional training.
Will it Merge? On The Causes of Model Mergeability
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Model merging has emerged as a promising technique for combining multiple fine-tuned models into a single multitask model without retraining. However, the factors that determine whether merging will succeed or fail remain poorly understood. In this work, we investigate why specific models are merged better than others. To do so, we propose a concrete, measurable definition of mergeability. We investigate several potential causes for high or low mergeability, highlighting the base model knowledge as a dominant factor: Models fine-tuned on instances that the base model knows better are more mergeable than models fine-tuned on instances that the base model struggles with. Based on our mergeability definition, we explore a simple weighted merging technique that better preserves weak knowledge in the base model.
Unsupervised Translation of Emergent Communication
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Emergent Communication (EC) provides a unique window into the language systems that emerge autonomously when agents are trained to jointly achieve shared goals. However, it is difficult to interpret EC and evaluate its relationship with natural languages (NL). This study employs unsupervised neural machine translation (UNMT) techniques to decipher ECs formed during referential games with varying task complexities, influenced by the semantic diversity of the environment. Our findings demonstrate UNMT's potential to translate EC, illustrating that task complexity characterized by semantic diversity enhances EC translatability, while higher task complexity with constrained semantic variability exhibits pragmatic EC, which, although challenging to interpret, remains suitable for translation. This research marks the first attempt, to our knowledge, to translate EC without the aid of parallel data.
Semantics and Spatiality of Emergent Communication
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:When artificial agents are jointly trained to perform collaborative tasks using a communication channel, they develop opaque goal-oriented communication protocols. Good task performance is often considered sufficient evidence that meaningful communication is taking place, but existing empirical results show that communication strategies induced by common objectives can be counterintuitive whilst solving the task nearly perfectly. In this work, we identify a goal-agnostic prerequisite to meaningful communication, which we term semantic consistency, based on the idea that messages should have similar meanings across instances. We provide a formal definition for this idea, and use it to compare the two most common objectives in the field of emergent communication: discrimination and reconstruction. We prove, under mild assumptions, that semantically inconsistent communication protocols can be optimal solutions to the discrimination task, but not to reconstruction. We further show that the reconstruction objective encourages a stricter property, spatial meaningfulness, which also accounts for the distance between messages. Experiments with emergent communication games validate our theoretical results. These findings demonstrate an inherent advantage of distance-based communication goals, and contextualize previous empirical discoveries.
Concept-Best-Matching: Evaluating Compositionality in Emergent Communication
Mar 17, 2024Abstract:Artificial agents that learn to communicate in order to accomplish a given task acquire communication protocols that are typically opaque to a human. A large body of work has attempted to evaluate the emergent communication via various evaluation measures, with \emph{compositionality} featuring as a prominent desired trait. However, current evaluation procedures do not directly expose the compositionality of the emergent communication. We propose a procedure to assess the compositionality of emergent communication by finding the best-match between emerged words and natural language concepts. The best-match algorithm provides both a global score and a translation-map from emergent words to natural language concepts. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time that such direct and interpretable mapping between emergent words and human concepts is provided.
Genie: Achieving Human Parity in Content-Grounded Datasets Generation
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:The lack of high-quality data for content-grounded generation tasks has been identified as a major obstacle to advancing these tasks. To address this gap, we propose Genie, a novel method for automatically generating high-quality content-grounded data. It consists of three stages: (a) Content Preparation, (b) Generation: creating task-specific examples from the content (e.g., question-answer pairs or summaries). (c) Filtering mechanism aiming to ensure the quality and faithfulness of the generated data. We showcase this methodology by generating three large-scale synthetic data, making wishes, for Long-Form Question-Answering (LFQA), summarization, and information extraction. In a human evaluation, our generated data was found to be natural and of high quality. Furthermore, we compare models trained on our data with models trained on human-written data -- ELI5 and ASQA for LFQA and CNN-DailyMail for Summarization. We show that our models are on par with or outperforming models trained on human-generated data and consistently outperforming them in faithfulness. Finally, we applied our method to create LFQA data within the medical domain and compared a model trained on it with models trained on other domains.
QAID: Question Answering Inspired Few-shot Intent Detection
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:Intent detection with semantically similar fine-grained intents is a challenging task. To address it, we reformulate intent detection as a question-answering retrieval task by treating utterances and intent names as questions and answers. To that end, we utilize a question-answering retrieval architecture and adopt a two stages training schema with batch contrastive loss. In the pre-training stage, we improve query representations through self-supervised training. Then, in the fine-tuning stage, we increase contextualized token-level similarity scores between queries and answers from the same intent. Our results on three few-shot intent detection benchmarks achieve state-of-the-art performance.
Measuring the Measuring Tools: An Automatic Evaluation of Semantic Metrics for Text Corpora
Nov 29, 2022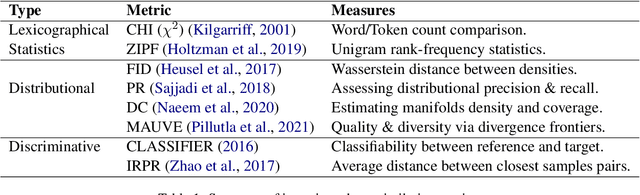
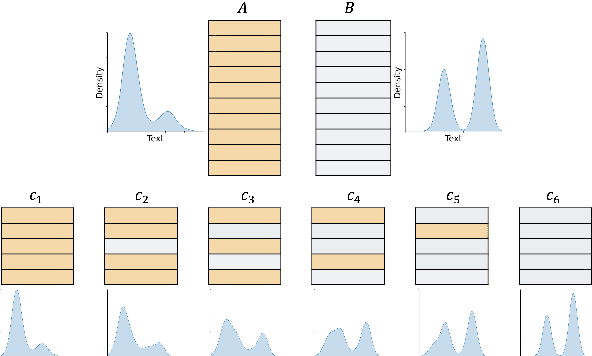
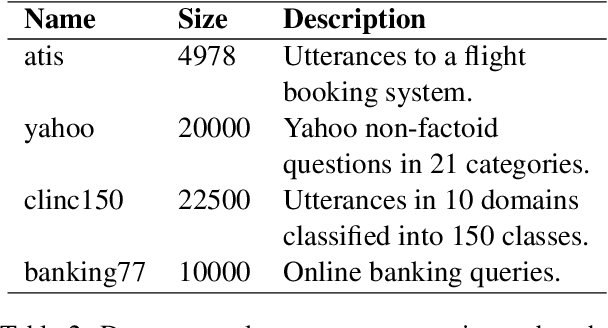
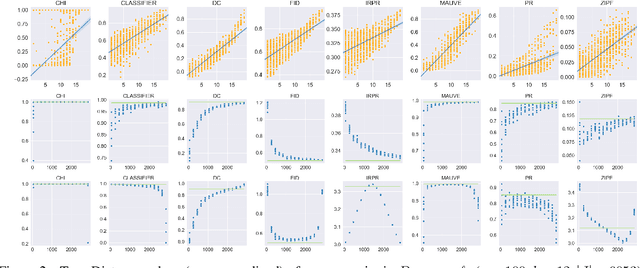
Abstract:The ability to compare the semantic similarity between text corpora is important in a variety of natural language processing applications. However, standard methods for evaluating these metrics have yet to be established. We propose a set of automatic and interpretable measures for assessing the characteristics of corpus-level semantic similarity metrics, allowing sensible comparison of their behavior. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our evaluation measures in capturing fundamental characteristics by evaluating them on a collection of classical and state-of-the-art metrics. Our measures revealed that recently-developed metrics are becoming better in identifying semantic distributional mismatch while classical metrics are more sensitive to perturbations in the surface text levels.
Emergent Quantized Communication
Nov 04, 2022



Abstract:The field of emergent communication aims to understand the characteristics of communication as it emerges from artificial agents solving tasks that require information exchange. Communication with discrete messages is considered a desired characteristic, for both scientific and applied reasons. However, training a multi-agent system with discrete communication is not straightforward, requiring either reinforcement learning algorithms or relaxing the discreteness requirement via a continuous approximation such as the Gumbel-softmax. Both these solutions result in poor performance compared to fully continuous communication. In this work, we propose an alternative approach to achieve discrete communication -- quantization of communicated messages. Using message quantization allows us to train the model end-to-end, achieving superior performance in multiple setups. Moreover, quantization is a natural framework that runs the gamut from continuous to discrete communication. Thus, it sets the ground for a broader view of multi-agent communication in the deep learning era.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge