Andre Araujo
Global-to-Local or Local-to-Global? Enhancing Image Retrieval with Efficient Local Search and Effective Global Re-ranking
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:The dominant paradigm in image retrieval systems today is to search large databases using global image features, and re-rank those initial results with local image feature matching techniques. This design, dubbed global-to-local, stems from the computational cost of local matching approaches, which can only be afforded for a small number of retrieved images. However, emerging efficient local feature search approaches have opened up new possibilities, in particular enabling detailed retrieval at large scale, to find partial matches which are often missed by global feature search. In parallel, global feature-based re-ranking has shown promising results with high computational efficiency. In this work, we leverage these building blocks to introduce a local-to-global retrieval paradigm, where efficient local feature search meets effective global feature re-ranking. Critically, we propose a re-ranking method where global features are computed on-the-fly, based on the local feature retrieval similarities. Such re-ranking-only global features leverage multidimensional scaling techniques to create embeddings which respect the local similarities obtained during search, enabling a significant re-ranking boost. Experimentally, we demonstrate solid retrieval performance, setting new state-of-the-art results on the Revisited Oxford and Paris datasets.
AlignDiff: Learning Physically-Grounded Camera Alignment via Diffusion
Mar 27, 2025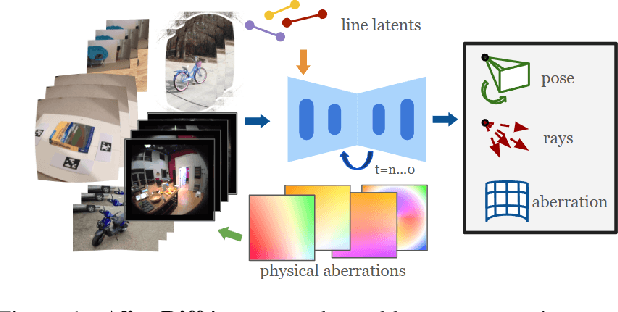
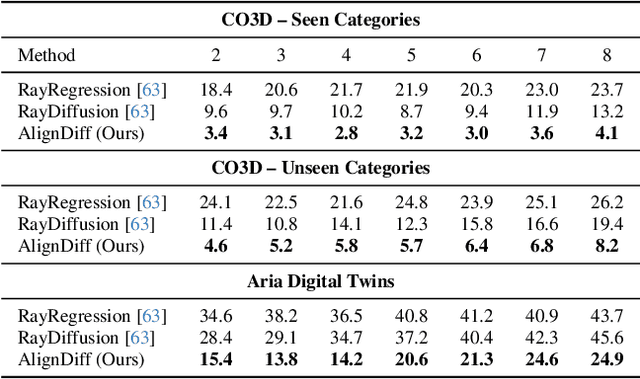
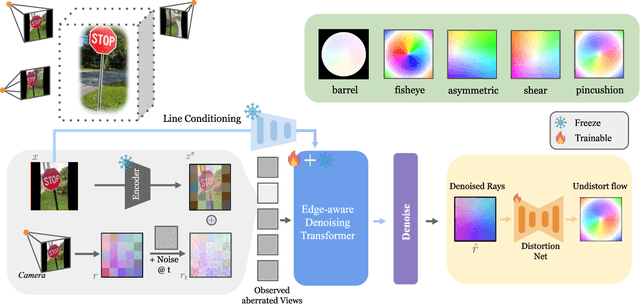
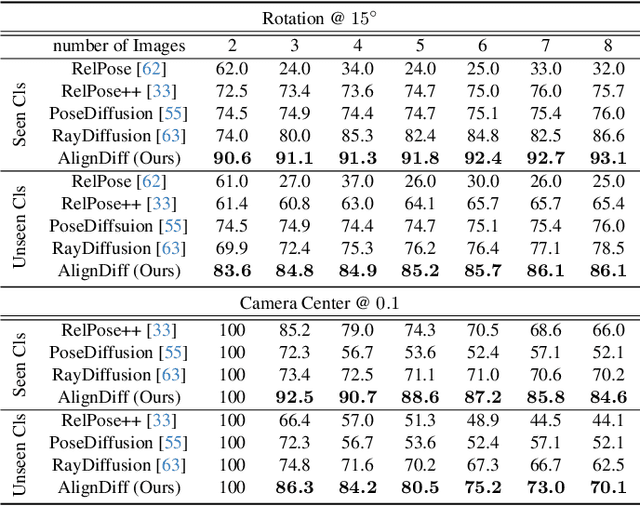
Abstract:Accurate camera calibration is a fundamental task for 3D perception, especially when dealing with real-world, in-the-wild environments where complex optical distortions are common. Existing methods often rely on pre-rectified images or calibration patterns, which limits their applicability and flexibility. In this work, we introduce a novel framework that addresses these challenges by jointly modeling camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters using a generic ray camera model. Unlike previous approaches, AlignDiff shifts focus from semantic to geometric features, enabling more accurate modeling of local distortions. We propose AlignDiff, a diffusion model conditioned on geometric priors, enabling the simultaneous estimation of camera distortions and scene geometry. To enhance distortion prediction, we incorporate edge-aware attention, focusing the model on geometric features around image edges, rather than semantic content. Furthermore, to enhance generalizability to real-world captures, we incorporate a large database of ray-traced lenses containing over three thousand samples. This database characterizes the distortion inherent in a diverse variety of lens forms. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed method significantly reduces the angular error of estimated ray bundles by ~8.2 degrees and overall calibration accuracy, outperforming existing approaches on challenging, real-world datasets.
TIPS: Text-Image Pretraining with Spatial Awareness
Oct 21, 2024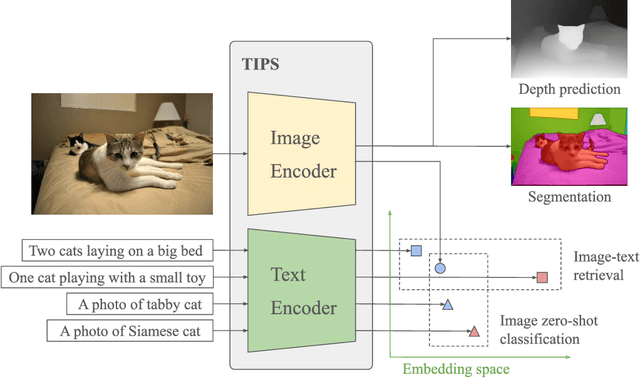
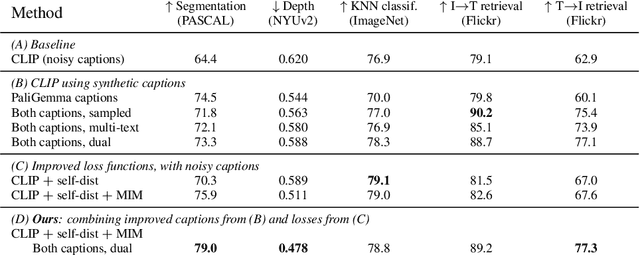
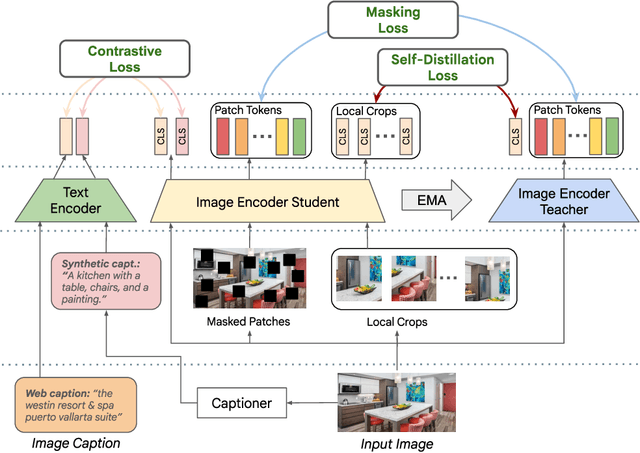
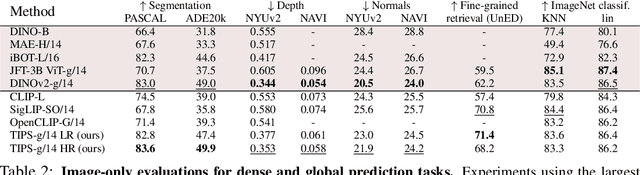
Abstract:While image-text representation learning has become very popular in recent years, existing models tend to lack spatial awareness and have limited direct applicability for dense understanding tasks. For this reason, self-supervised image-only pretraining is still the go-to method for many dense vision applications (e.g. depth estimation, semantic segmentation), despite the lack of explicit supervisory signals. In this paper, we close this gap between image-text and self-supervised learning, by proposing a novel general-purpose image-text model, which can be effectively used off-the-shelf for dense and global vision tasks. Our method, which we refer to as Text-Image Pretraining with Spatial awareness (TIPS), leverages two simple and effective insights. First, on textual supervision: we reveal that replacing noisy web image captions by synthetically generated textual descriptions boosts dense understanding performance significantly, due to a much richer signal for learning spatially aware representations. We propose an adapted training method that combines noisy and synthetic captions, resulting in improvements across both dense and global understanding tasks. Second, on the learning technique: we propose to combine contrastive image-text learning with self-supervised masked image modeling, to encourage spatial coherence, unlocking substantial enhancements for downstream applications. Building on these two ideas, we scale our model using the transformer architecture, trained on a curated set of public images. Our experiments are conducted on 8 tasks involving 16 datasets in total, demonstrating strong off-the-shelf performance on both dense and global understanding, for several image-only and image-text tasks.
OmniGlue: Generalizable Feature Matching with Foundation Model Guidance
May 21, 2024Abstract:The image matching field has been witnessing a continuous emergence of novel learnable feature matching techniques, with ever-improving performance on conventional benchmarks. However, our investigation shows that despite these gains, their potential for real-world applications is restricted by their limited generalization capabilities to novel image domains. In this paper, we introduce OmniGlue, the first learnable image matcher that is designed with generalization as a core principle. OmniGlue leverages broad knowledge from a vision foundation model to guide the feature matching process, boosting generalization to domains not seen at training time. Additionally, we propose a novel keypoint position-guided attention mechanism which disentangles spatial and appearance information, leading to enhanced matching descriptors. We perform comprehensive experiments on a suite of $7$ datasets with varied image domains, including scene-level, object-centric and aerial images. OmniGlue's novel components lead to relative gains on unseen domains of $20.9\%$ with respect to a directly comparable reference model, while also outperforming the recent LightGlue method by $9.5\%$ relatively.Code and model can be found at https://hwjiang1510.github.io/OmniGlue
XFeat: Accelerated Features for Lightweight Image Matching
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a lightweight and accurate architecture for resource-efficient visual correspondence. Our method, dubbed XFeat (Accelerated Features), revisits fundamental design choices in convolutional neural networks for detecting, extracting, and matching local features. Our new model satisfies a critical need for fast and robust algorithms suitable to resource-limited devices. In particular, accurate image matching requires sufficiently large image resolutions - for this reason, we keep the resolution as large as possible while limiting the number of channels in the network. Besides, our model is designed to offer the choice of matching at the sparse or semi-dense levels, each of which may be more suitable for different downstream applications, such as visual navigation and augmented reality. Our model is the first to offer semi-dense matching efficiently, leveraging a novel match refinement module that relies on coarse local descriptors. XFeat is versatile and hardware-independent, surpassing current deep learning-based local features in speed (up to 5x faster) with comparable or better accuracy, proven in pose estimation and visual localization. We showcase it running in real-time on an inexpensive laptop CPU without specialized hardware optimizations. Code and weights are available at www.verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/descriptors/xfeat_cvpr24.
HAMMR: HierArchical MultiModal React agents for generic VQA
Apr 08, 2024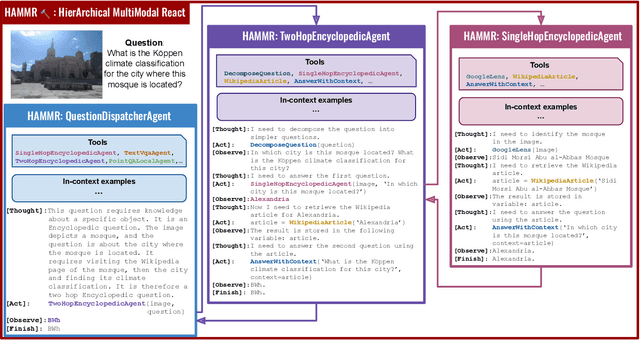
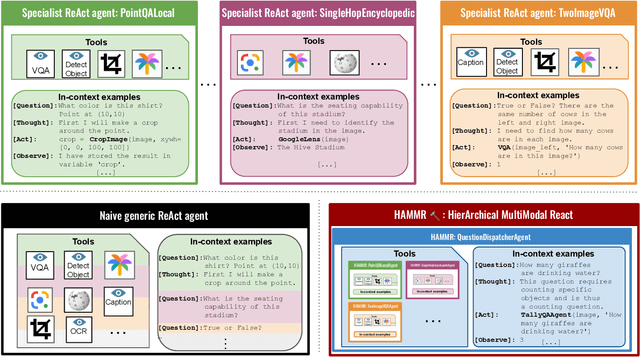

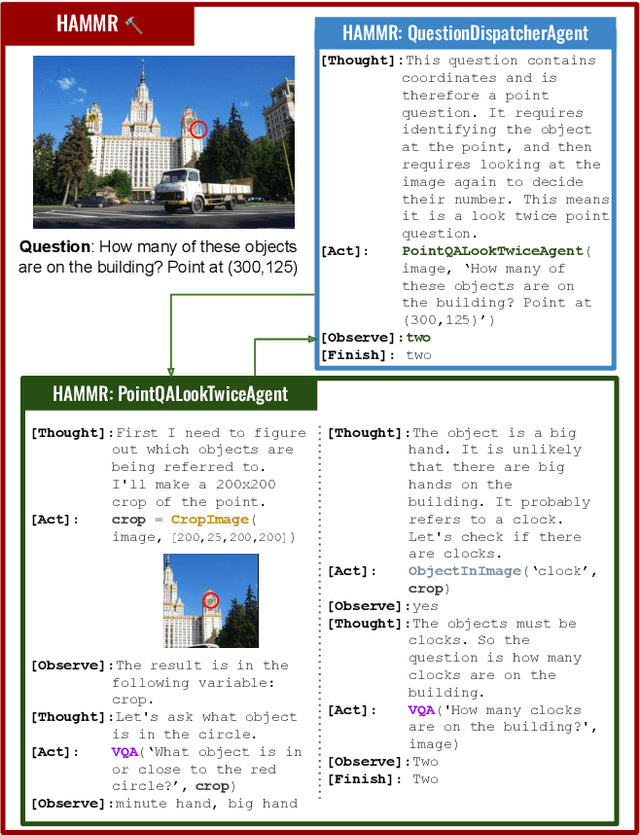
Abstract:Combining Large Language Models (LLMs) with external specialized tools (LLMs+tools) is a recent paradigm to solve multimodal tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA). While this approach was demonstrated to work well when optimized and evaluated for each individual benchmark, in practice it is crucial for the next generation of real-world AI systems to handle a broad range of multimodal problems. Therefore we pose the VQA problem from a unified perspective and evaluate a single system on a varied suite of VQA tasks including counting, spatial reasoning, OCR-based reasoning, visual pointing, external knowledge, and more. In this setting, we demonstrate that naively applying the LLM+tools approach using the combined set of all tools leads to poor results. This motivates us to introduce HAMMR: HierArchical MultiModal React. We start from a multimodal ReAct-based system and make it hierarchical by enabling our HAMMR agents to call upon other specialized agents. This enhances the compositionality of the LLM+tools approach, which we show to be critical for obtaining high accuracy on generic VQA. Concretely, on our generic VQA suite, HAMMR outperforms the naive LLM+tools approach by 19.5%. Additionally, HAMMR achieves state-of-the-art results on this task, outperforming the generic standalone PaLI-X VQA model by 5.0%.
Global Features are All You Need for Image Retrieval and Reranking
Aug 19, 2023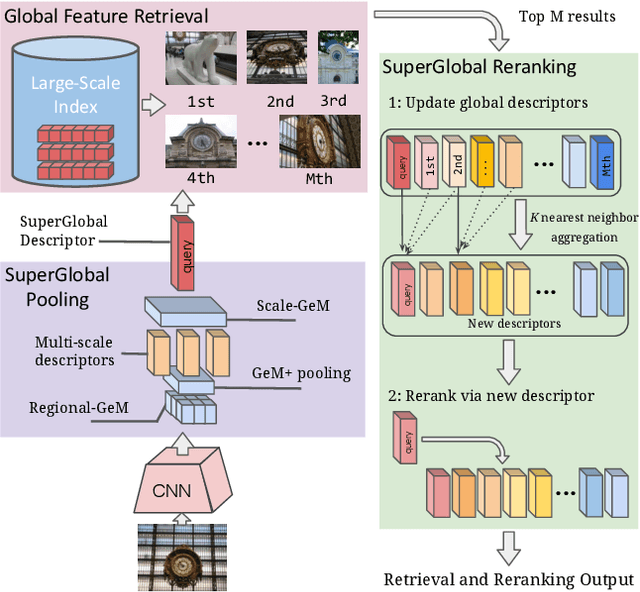
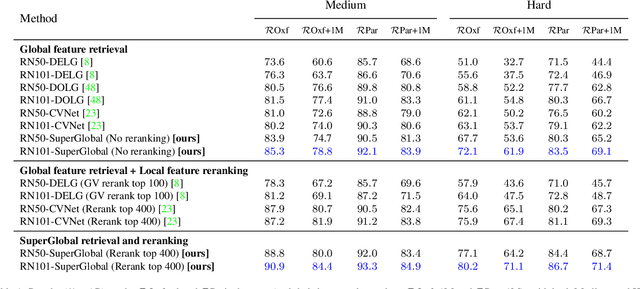
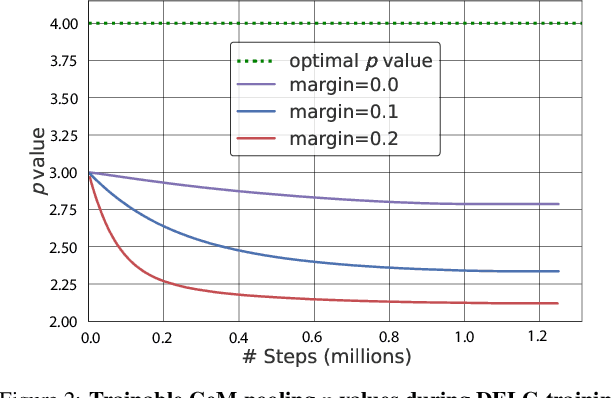
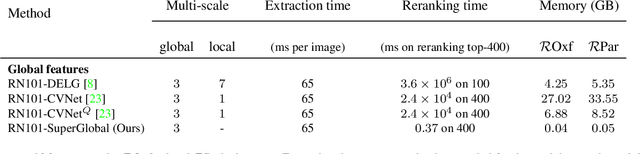
Abstract:Image retrieval systems conventionally use a two-stage paradigm, leveraging global features for initial retrieval and local features for reranking. However, the scalability of this method is often limited due to the significant storage and computation cost incurred by local feature matching in the reranking stage. In this paper, we present SuperGlobal, a novel approach that exclusively employs global features for both stages, improving efficiency without sacrificing accuracy. SuperGlobal introduces key enhancements to the retrieval system, specifically focusing on the global feature extraction and reranking processes. For extraction, we identify sub-optimal performance when the widely-used ArcFace loss and Generalized Mean (GeM) pooling methods are combined and propose several new modules to improve GeM pooling. In the reranking stage, we introduce a novel method to update the global features of the query and top-ranked images by only considering feature refinement with a small set of images, thus being very compute and memory efficient. Our experiments demonstrate substantial improvements compared to the state of the art in standard benchmarks. Notably, on the Revisited Oxford+1M Hard dataset, our single-stage results improve by 7.1%, while our two-stage gain reaches 3.7% with a strong 64,865x speedup. Our two-stage system surpasses the current single-stage state-of-the-art by 16.3%, offering a scalable, accurate alternative for high-performing image retrieval systems with minimal time overhead. Code: https://github.com/ShihaoShao-GH/SuperGlobal.
Enhancing Deformable Local Features by Jointly Learning to Detect and Describe Keypoints
Apr 02, 2023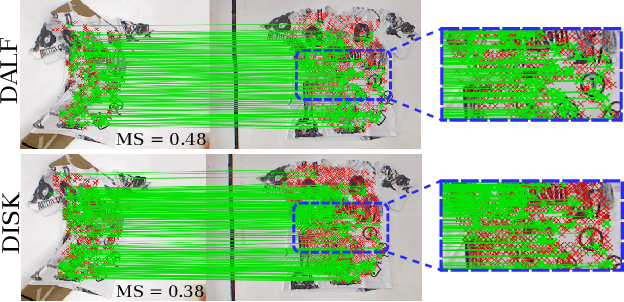

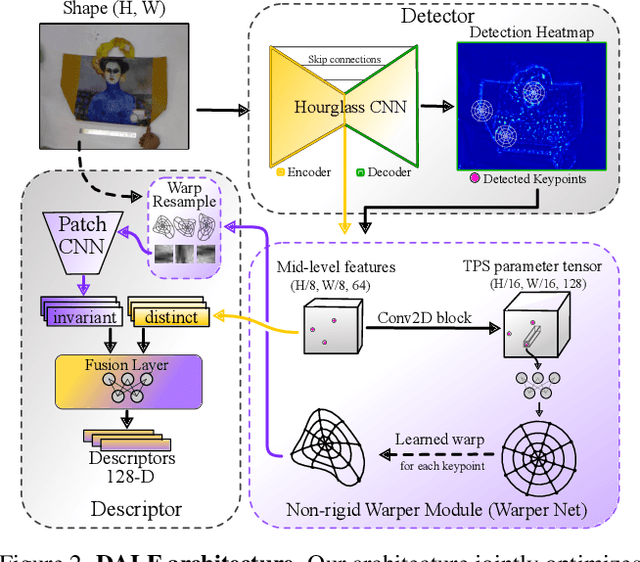

Abstract:Local feature extraction is a standard approach in computer vision for tackling important tasks such as image matching and retrieval. The core assumption of most methods is that images undergo affine transformations, disregarding more complicated effects such as non-rigid deformations. Furthermore, incipient works tailored for non-rigid correspondence still rely on keypoint detectors designed for rigid transformations, hindering performance due to the limitations of the detector. We propose DALF (Deformation-Aware Local Features), a novel deformation-aware network for jointly detecting and describing keypoints, to handle the challenging problem of matching deformable surfaces. All network components work cooperatively through a feature fusion approach that enforces the descriptors' distinctiveness and invariance. Experiments using real deforming objects showcase the superiority of our method, where it delivers 8% improvement in matching scores compared to the previous best results. Our approach also enhances the performance of two real-world applications: deformable object retrieval and non-rigid 3D surface registration. Code for training, inference, and applications are publicly available at https://verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/descriptors/dalf_cvpr23.
LFM-3D: Learnable Feature Matching Across Wide Baselines Using 3D Signals
Mar 22, 2023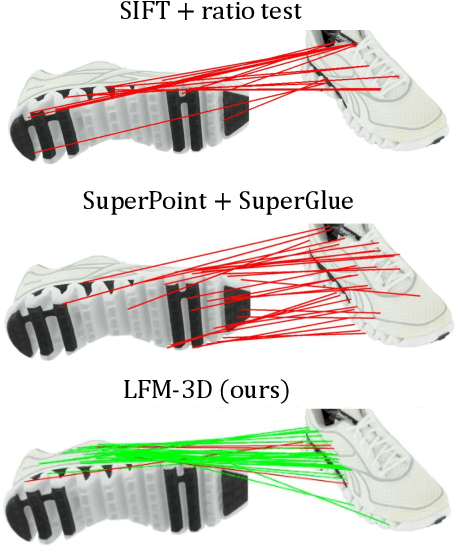
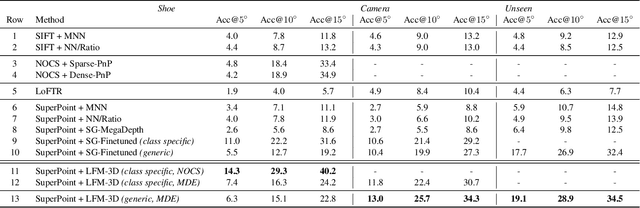
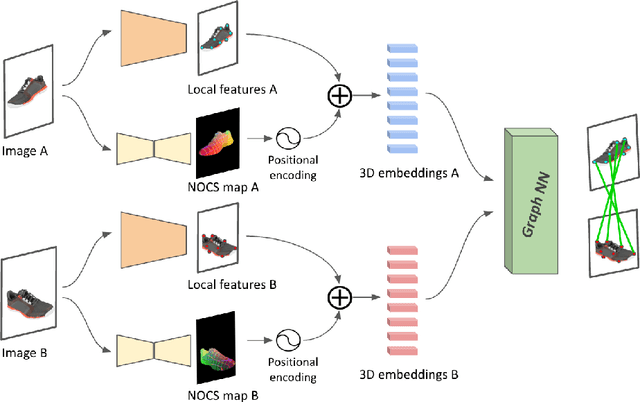
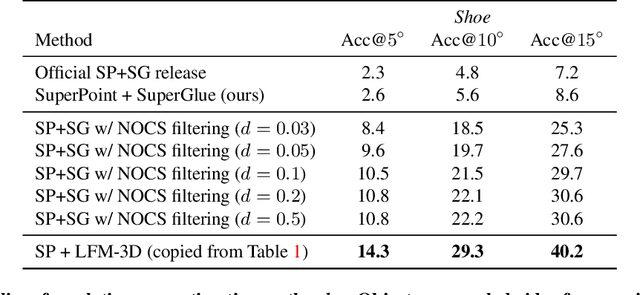
Abstract:Finding localized correspondences across different images of the same object is crucial to understand its geometry. In recent years, this problem has seen remarkable progress with the advent of deep learning based local image features and learnable matchers. Still, learnable matchers often underperform when there exists only small regions of co-visibility between image pairs (i.e. wide camera baselines). To address this problem, we leverage recent progress in coarse single-view geometry estimation methods. We propose LFM-3D, a Learnable Feature Matching framework that uses models based on graph neural networks, and enhances their capabilities by integrating noisy, estimated 3D signals to boost correspondence estimation. When integrating 3D signals into the matcher model, we show that a suitable positional encoding is critical to effectively make use of the low-dimensional 3D information. We experiment with two different 3D signals - normalized object coordinates and monocular depth estimates - and evaluate our method on large-scale (synthetic and real) datasets containing object-centric image pairs across wide baselines. We observe strong feature matching improvements compared to 2D-only methods, with up to +6% total recall and +28% precision at fixed recall. We additionally demonstrate that the resulting improved correspondences lead to much higher relative posing accuracy for in-the-wild image pairs, with a more than 8% boost compared to the 2D-only approach.
Google Landmarks Dataset v2 -- A Large-Scale Benchmark for Instance-Level Recognition and Retrieval
Apr 03, 2020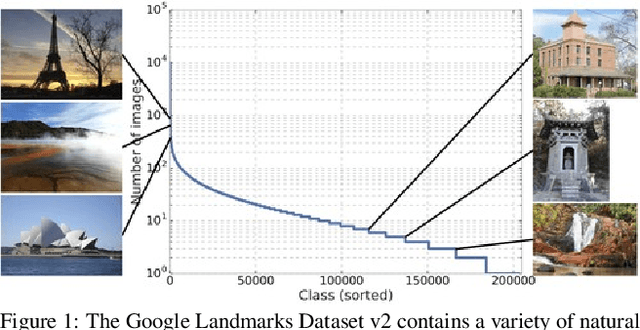
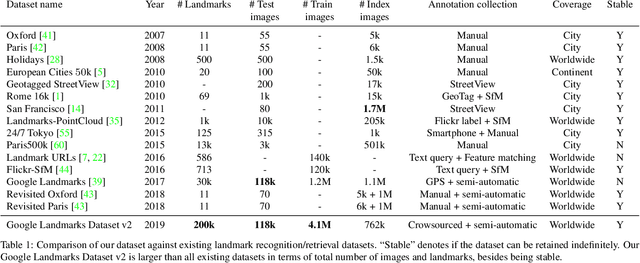
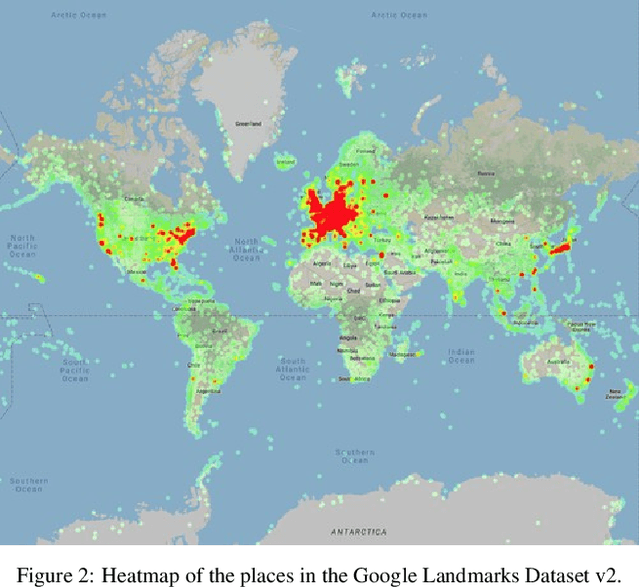

Abstract:While image retrieval and instance recognition techniques are progressing rapidly, there is a need for challenging datasets to accurately measure their performance -- while posing novel challenges that are relevant for practical applications. We introduce the Google Landmarks Dataset v2 (GLDv2), a new benchmark for large-scale, fine-grained instance recognition and image retrieval in the domain of human-made and natural landmarks. GLDv2 is the largest such dataset to date by a large margin, including over 5M images and 200k distinct instance labels. Its test set consists of 118k images with ground truth annotations for both the retrieval and recognition tasks. The ground truth construction involved over 800 hours of human annotator work. Our new dataset has several challenging properties inspired by real world applications that previous datasets did not consider: An extremely long-tailed class distribution, a large fraction of out-of-domain test photos and large intra-class variability. The dataset is sourced from Wikimedia Commons, the world's largest crowdsourced collection of landmark photos. We provide baseline results for both recognition and retrieval tasks based on state-of-the-art methods as well as competitive results from a public challenge. We further demonstrate the suitability of the dataset for transfer learning by showing that image embeddings trained on it achieve competitive retrieval performance on independent datasets. The dataset images, ground-truth and metric scoring code are available at https://github.com/cvdfoundation/google-landmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge