Amirreza Payandeh
Narrate2Nav: Real-Time Visual Navigation with Implicit Language Reasoning in Human-Centric Environments
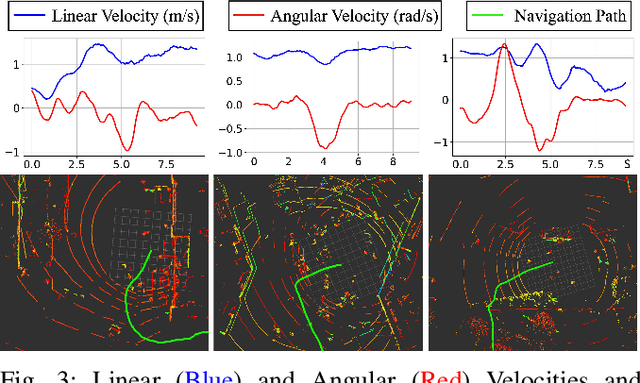
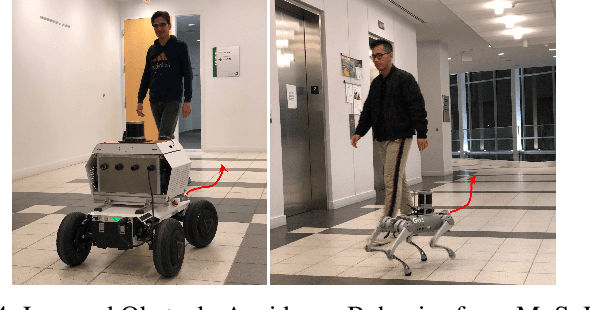
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated potential in enhancing mobile robot navigation in human-centric environments by understanding contextual cues, human intentions, and social dynamics while exhibiting reasoning capabilities. However, their computational complexity and limited sensitivity to continuous numerical data impede real-time performance and precise motion control. To this end, we propose Narrate2Nav, a novel real-time vision-action model that leverages a novel self-supervised learning framework based on the Barlow Twins redundancy reduction loss to embed implicit natural language reasoning, social cues, and human intentions within a visual encoder-enabling reasoning in the model's latent space rather than token space. The model combines RGB inputs, motion commands, and textual signals of scene context during training to bridge from robot observations to low-level motion commands for short-horizon point-goal navigation during deployment. Extensive evaluation of Narrate2Nav across various challenging scenarios in both offline unseen dataset and real-world experiments demonstrates an overall improvement of 52.94 percent and 41.67 percent, respectively, over the next best baseline. Additionally, qualitative comparative analysis of Narrate2Nav's visual encoder attention map against four other baselines demonstrates enhanced attention to navigation-critical scene elements, underscoring its effectiveness in human-centric navigation tasks.
Socially Aware Robot Navigation through Scoring Using Vision-Language Models
Mar 30, 2024Abstract:We propose VLM-Social-Nav, a novel Vision-Language Model (VLM) based navigation approach to compute a robot's trajectory in human-centered environments. Our goal is to make real-time decisions on robot actions that are socially compliant with human expectations. We utilize a perception model to detect important social entities and prompt a VLM to generate guidance for socially compliant robot behavior. VLM-Social-Nav uses a VLM-based scoring module that computes a cost term that ensures socially appropriate and effective robot actions generated by the underlying planner. Our overall approach reduces reliance on large datasets (for training) and enhances adaptability in decision-making. In practice, it results in improved socially compliant navigation in human-shared environments. We demonstrate and evaluate our system in four different real-world social navigation scenarios with a Turtlebot robot. We observe at least 36.37% improvement in average success rate and 20.00% improvement in average collision rate in the four social navigation scenarios. The user study score shows that VLM-Social-Nav generates the most socially compliant navigation behavior.
DTG : Diffusion-based Trajectory Generation for Mapless Global Navigation
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:We present a novel end-to-end diffusion-based trajectory generation method, DTG, for mapless global navigation in challenging outdoor scenarios with occlusions and unstructured off-road features like grass, buildings, bushes, etc. Given a distant goal, our approach computes a trajectory that satisfies the following goals: (1) minimize the travel distance to the goal; (2) maximize the traversability by choosing paths that do not lie in undesirable areas. Specifically, we present a novel Conditional RNN(CRNN) for diffusion models to efficiently generate trajectories. Furthermore, we propose an adaptive training method that ensures that the diffusion model generates more traversable trajectories. We evaluate our methods in various outdoor scenes and compare the performance with other global navigation algorithms on a Husky robot. In practice, we observe at least a 15% improvement in traveling distance and around a 7% improvement in traversability.
VANP: Learning Where to See for Navigation with Self-Supervised Vision-Action Pre-Training
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:Humans excel at efficiently navigating through crowds without collision by focusing on specific visual regions relevant to navigation. However, most robotic visual navigation methods rely on deep learning models pre-trained on vision tasks, which prioritize salient objects -- not necessarily relevant to navigation and potentially misleading. Alternative approaches train specialized navigation models from scratch, requiring significant computation. On the other hand, self-supervised learning has revolutionized computer vision and natural language processing, but its application to robotic navigation remains underexplored due to the difficulty of defining effective self-supervision signals. Motivated by these observations, in this work, we propose a Self-Supervised Vision-Action Model for Visual Navigation Pre-Training (VANP). Instead of detecting salient objects that are beneficial for tasks such as classification or detection, VANP learns to focus only on specific visual regions that are relevant to the navigation task. To achieve this, VANP uses a history of visual observations, future actions, and a goal image for self-supervision, and embeds them using two small Transformer Encoders. Then, VANP maximizes the information between the embeddings by using a mutual information maximization objective function. We demonstrate that most VANP-extracted features match with human navigation intuition. VANP achieves comparable performance as models learned end-to-end with half the training time and models trained on a large-scale, fully supervised dataset, i.e., ImageNet, with only 0.08% data.
Targeted Learning: A Hybrid Approach to Social Robot Navigation
Sep 23, 2023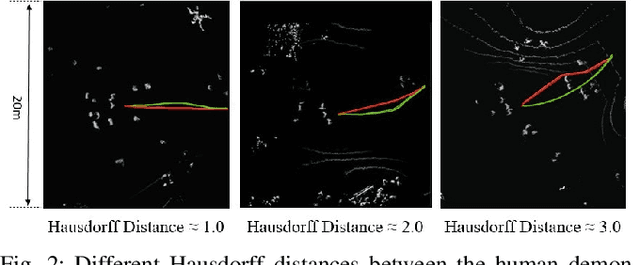



Abstract:Empowering robots to navigate in a socially compliant manner is essential for the acceptance of robots moving in human-inhabited environments. Previously, roboticists have developed classical navigation systems with decades of empirical validation to achieve safety and efficiency. However, the many complex factors of social compliance make classical navigation systems hard to adapt to social situations, where no amount of tuning enables them to be both safe (people are too unpredictable) and efficient (the frozen robot problem). With recent advances in deep learning approaches, the common reaction has been to entirely discard classical navigation systems and start from scratch, building a completely new learning-based social navigation planner. In this work, we find that this reaction is unnecessarily extreme: using a large-scale real-world social navigation dataset, SCAND, we find that classical systems can be used safely and efficiently in a large number of social situations (up to 80%). We therefore ask if we can rethink this problem by leveraging the advantages of both classical and learning-based approaches. We propose a hybrid strategy in which we learn to switch between a classical geometric planner and a data-driven method. Our experiments on both SCAND and two physical robots show that the hybrid planner can achieve better social compliance in terms of a variety of metrics, compared to using either the classical or learning-based approach alone.
How susceptible are LLMs to Logical Fallacies?
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:This paper investigates the rational thinking capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) in multi-round argumentative debates by exploring the impact of fallacious arguments on their logical reasoning performance. More specifically, we present Logic Competence Measurement Benchmark (LOGICOM), a diagnostic benchmark to assess the robustness of LLMs against logical fallacies. LOGICOM involves two agents: a persuader and a debater engaging in a multi-round debate on a controversial topic, where the persuader tries to convince the debater of the correctness of its claim. First, LOGICOM assesses the potential of LLMs to change their opinions through reasoning. Then, it evaluates the debater's performance in logical reasoning by contrasting the scenario where the persuader employs logical fallacies against one where logical reasoning is used. We use this benchmark to evaluate the performance of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 using a dataset containing controversial topics, claims, and reasons supporting them. Our findings indicate that both GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 can adjust their opinion through reasoning. However, when presented with logical fallacies, GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 are erroneously convinced 41% and 69% more often, respectively, compared to when logical reasoning is used. Finally, we introduce a new dataset containing over 5k pairs of logical vs. fallacious arguments. The source code and dataset of this work are made publicly available.
Toward Human-Like Social Robot Navigation: A Large-Scale, Multi-Modal, Social Human Navigation Dataset
Mar 27, 2023
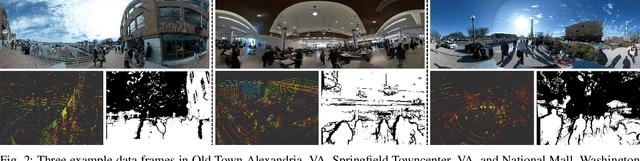
Abstract:Humans are well-adept at navigating public spaces shared with others, where current autonomous mobile robots still struggle: while safely and efficiently reaching their goals, humans communicate their intentions and conform to unwritten social norms on a daily basis; conversely, robots become clumsy in those daily social scenarios, getting stuck in dense crowds, surprising nearby pedestrians, or even causing collisions. While recent research on robot learning has shown promises in data-driven social robot navigation, good-quality training data is still difficult to acquire through either trial and error or expert demonstrations. In this work, we propose to utilize the body of rich, widely available, social human navigation data in many natural human-inhabited public spaces for robots to learn similar, human-like, socially compliant navigation behaviors. To be specific, we design an open-source egocentric data collection sensor suite wearable by walking humans to provide multi-modal robot perception data; we collect a large-scale (~50 km, 10 hours, 150 trials, 7 humans) dataset in a variety of public spaces which contain numerous natural social navigation interactions; we analyze our dataset, demonstrate its usability, and point out future research directions and use cases.
Deep representation learning: Fundamentals, Perspectives, Applications, and Open Challenges
Nov 27, 2022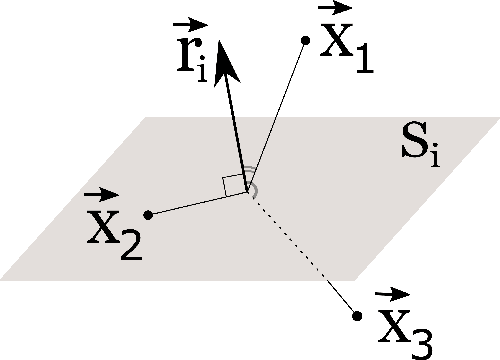
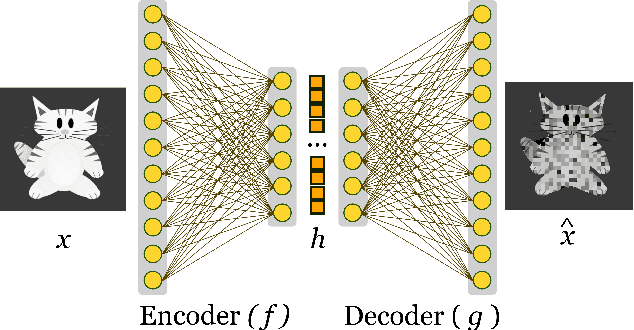
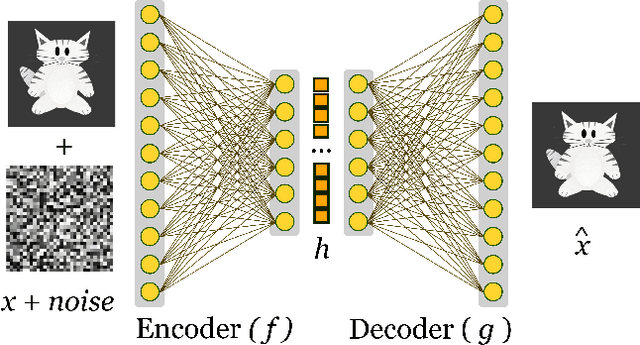
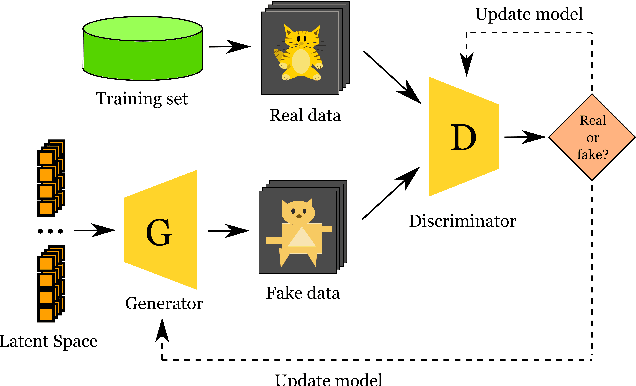
Abstract:Machine Learning algorithms have had a profound impact on the field of computer science over the past few decades. These algorithms performance is greatly influenced by the representations that are derived from the data in the learning process. The representations learned in a successful learning process should be concise, discrete, meaningful, and able to be applied across a variety of tasks. A recent effort has been directed toward developing Deep Learning models, which have proven to be particularly effective at capturing high-dimensional, non-linear, and multi-modal characteristics. In this work, we discuss the principles and developments that have been made in the process of learning representations, and converting them into desirable applications. In addition, for each framework or model, the key issues and open challenges, as well as the advantages, are examined.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge