Somayeh Bakhtiari Ramezani
Generating Synthetic Time Series Data for Cyber-Physical Systems
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:Data augmentation is an important facilitator of deep learning applications in the time series domain. A gap is identified in the literature, demonstrating sparse exploration of the transformer, the dominant sequence model, for data augmentation in time series. A architecture hybridizing several successful priors is put forth and tested using a powerful time domain similarity metric. Results suggest the challenge of this domain, and several valuable directions for future work.
Explainable Predictive Maintenance: A Survey of Current Methods, Challenges and Opportunities
Jan 15, 2024



Abstract:Predictive maintenance is a well studied collection of techniques that aims to prolong the life of a mechanical system by using artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict the optimal time to perform maintenance. The methods allow maintainers of systems and hardware to reduce financial and time costs of upkeep. As these methods are adopted for more serious and potentially life-threatening applications, the human operators need trust the predictive system. This attracts the field of Explainable AI (XAI) to introduce explainability and interpretability into the predictive system. XAI brings methods to the field of predictive maintenance that can amplify trust in the users while maintaining well-performing systems. This survey on explainable predictive maintenance (XPM) discusses and presents the current methods of XAI as applied to predictive maintenance while following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. We categorize the different XPM methods into groups that follow the XAI literature. Additionally, we include current challenges and a discussion on future research directions in XPM.
Deep representation learning: Fundamentals, Perspectives, Applications, and Open Challenges
Nov 27, 2022
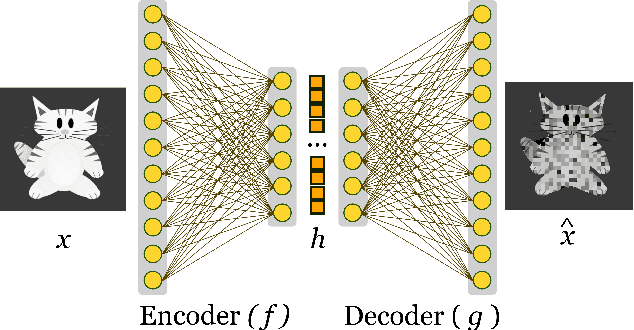
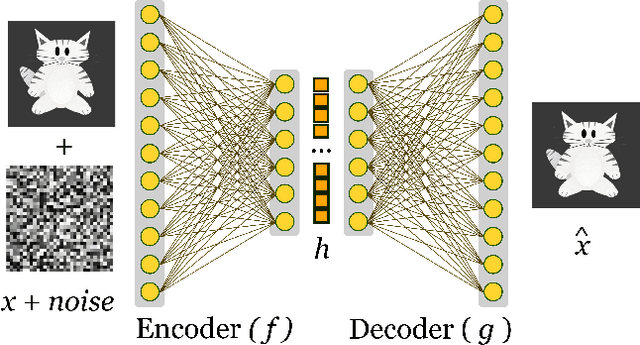
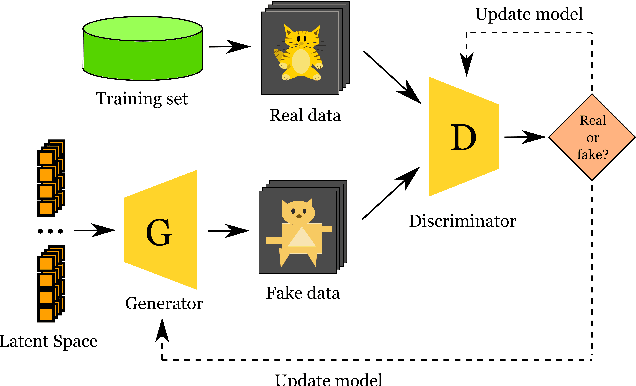
Abstract:Machine Learning algorithms have had a profound impact on the field of computer science over the past few decades. These algorithms performance is greatly influenced by the representations that are derived from the data in the learning process. The representations learned in a successful learning process should be concise, discrete, meaningful, and able to be applied across a variety of tasks. A recent effort has been directed toward developing Deep Learning models, which have proven to be particularly effective at capturing high-dimensional, non-linear, and multi-modal characteristics. In this work, we discuss the principles and developments that have been made in the process of learning representations, and converting them into desirable applications. In addition, for each framework or model, the key issues and open challenges, as well as the advantages, are examined.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge