Aliasghar Mortazi
Selecting the Best Optimizers for Deep Learning based Medical Image Segmentation
Feb 05, 2023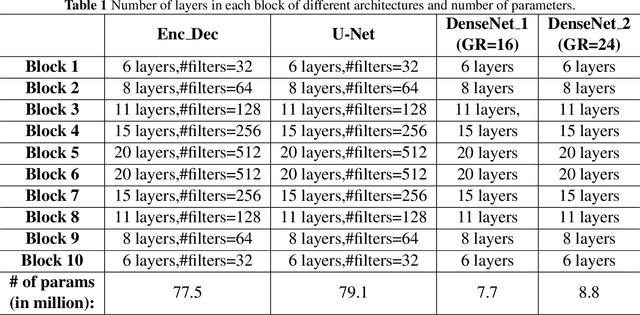
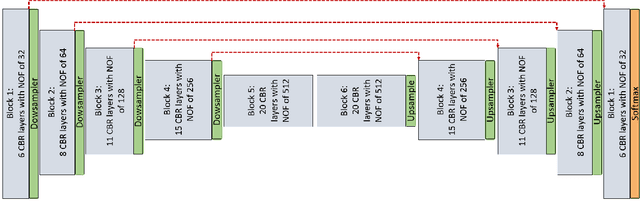
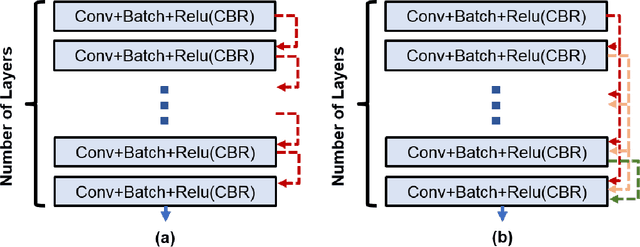
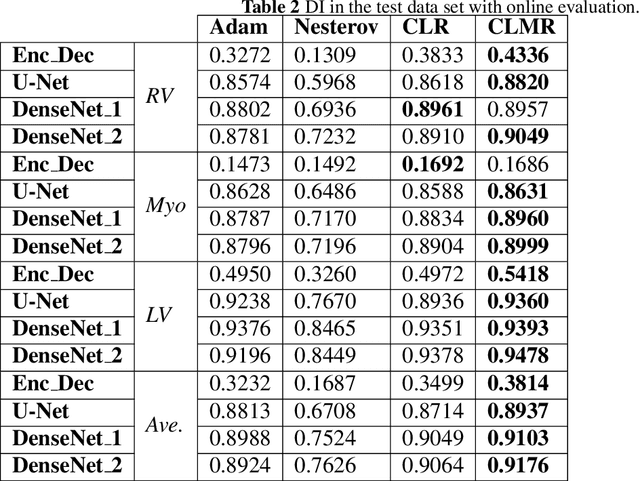
Abstract:The goal of this work is to identify the best optimizers for deep learning in the context of cardiac image segmentation and to provide guidance on how to design segmentation networks with effective optimization strategies. Adaptive learning helps with fast convergence by starting with a larger learning rate (LR) and gradually decreasing it. Momentum optimizers are particularly effective at quickly optimizing neural networks within the accelerated schemes category. By revealing the potential interplay between these two types of algorithms (LR and momentum optimizers or momentum rate (MR) in short), in this article, we explore the two variants of SGD algorithms in a single setting. We suggest using cyclic learning as the base optimizer and integrating optimal values of learning rate and momentum rate. We investigated the relationship of LR and MR under an important problem of medical image segmentation of cardiac structures from MRI and CT scans. We conducted experiments using the cardiac imaging dataset from the ACDC challenge of MICCAI 2017, and four different architectures shown to be successful for cardiac image segmentation problems. Our comprehensive evaluations demonstrated that the proposed optimizer achieved better results (over a 2\% improvement in the dice metric) than other optimizers in deep learning literature with similar or lower computational cost in both single and multi-object segmentation settings. We hypothesized that combination of accelerated and adaptive optimization methods can have a drastic effect in medical image segmentation performances. To this end, we proposed a new cyclic optimization method (\textit{CLMR}) to address the efficiency and accuracy problems in deep learning based medical image segmentation. The proposed strategy yielded better generalization in comparison to adaptive optimizers.
The International Workshop on Osteoarthritis Imaging Knee MRI Segmentation Challenge: A Multi-Institute Evaluation and Analysis Framework on a Standardized Dataset
May 26, 2020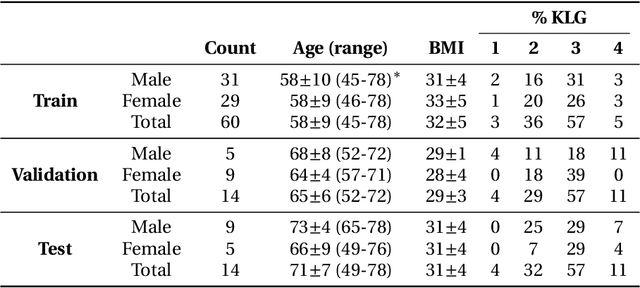
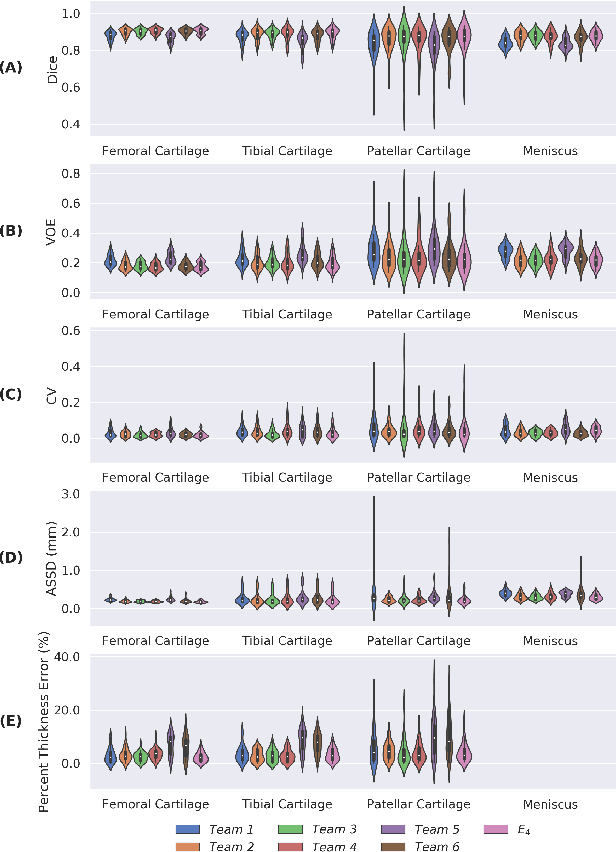
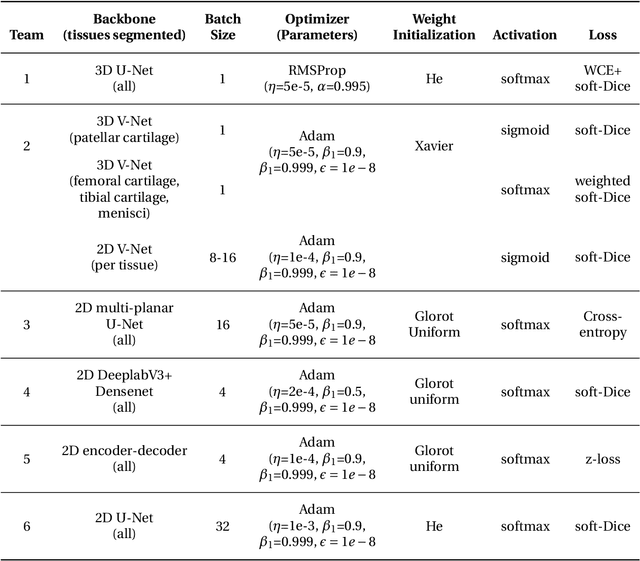
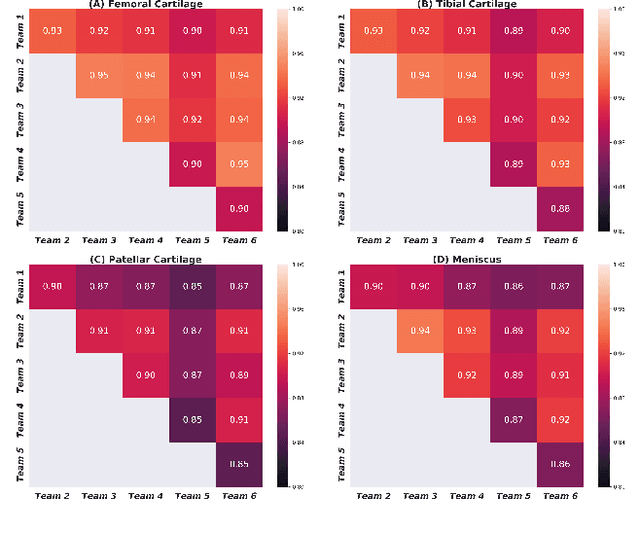
Abstract:Purpose: To organize a knee MRI segmentation challenge for characterizing the semantic and clinical efficacy of automatic segmentation methods relevant for monitoring osteoarthritis progression. Methods: A dataset partition consisting of 3D knee MRI from 88 subjects at two timepoints with ground-truth articular (femoral, tibial, patellar) cartilage and meniscus segmentations was standardized. Challenge submissions and a majority-vote ensemble were evaluated using Dice score, average symmetric surface distance, volumetric overlap error, and coefficient of variation on a hold-out test set. Similarities in network segmentations were evaluated using pairwise Dice correlations. Articular cartilage thickness was computed per-scan and longitudinally. Correlation between thickness error and segmentation metrics was measured using Pearson's coefficient. Two empirical upper bounds for ensemble performance were computed using combinations of model outputs that consolidated true positives and true negatives. Results: Six teams (T1-T6) submitted entries for the challenge. No significant differences were observed across all segmentation metrics for all tissues (p=1.0) among the four top-performing networks (T2, T3, T4, T6). Dice correlations between network pairs were high (>0.85). Per-scan thickness errors were negligible among T1-T4 (p=0.99) and longitudinal changes showed minimal bias (<0.03mm). Low correlations (<0.41) were observed between segmentation metrics and thickness error. The majority-vote ensemble was comparable to top performing networks (p=1.0). Empirical upper bound performances were similar for both combinations (p=1.0). Conclusion: Diverse networks learned to segment the knee similarly where high segmentation accuracy did not correlate to cartilage thickness accuracy. Voting ensembles did not outperform individual networks but may help regularize individual models.
Weakly Supervised Segmentation by A Deep Geodesic Prior
Aug 18, 2019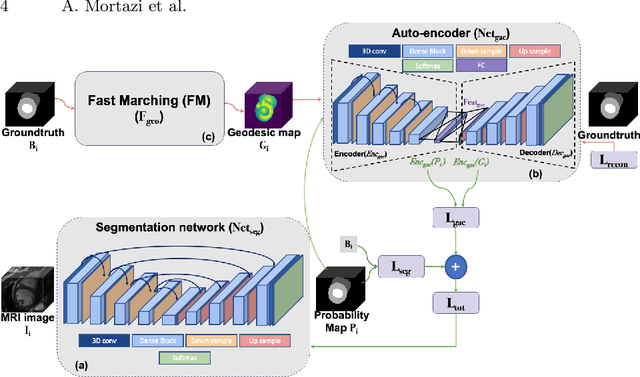
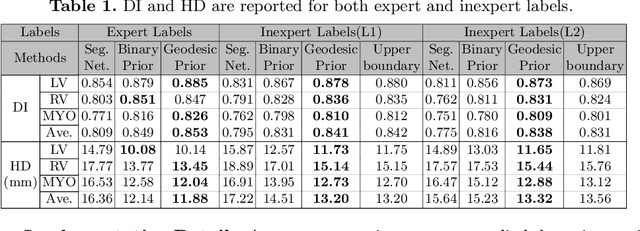
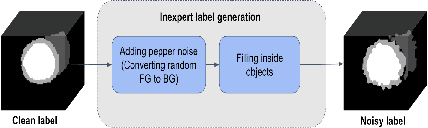
Abstract:The performance of the state-of-the-art image segmentation methods heavily relies on the high-quality annotations, which are not easily affordable, particularly for medical data. To alleviate this limitation, in this study, we propose a weakly supervised image segmentation method based on a deep geodesic prior. We hypothesize that integration of this prior information can reduce the adverse effects of weak labels in segmentation accuracy. Our proposed algorithm is based on a prior information, extracted from an auto-encoder, trained to map objects geodesic maps to their corresponding binary maps. The obtained information is then used as an extra term in the loss function of the segmentor. In order to show efficacy of the proposed strategy, we have experimented segmentation of cardiac substructures with clean and two levels of noisy labels (L1, L2). Our experiments showed that the proposed algorithm boosted the performance of baseline deep learning-based segmentation for both clean and noisy labels by 4.4%, 4.6%(L1), and 6.3%(L2) in dice score, respectively. We also showed that the proposed method was more robust in the presence of high-level noise due to the existence of shape priors.
PAN: Projective Adversarial Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Jun 11, 2019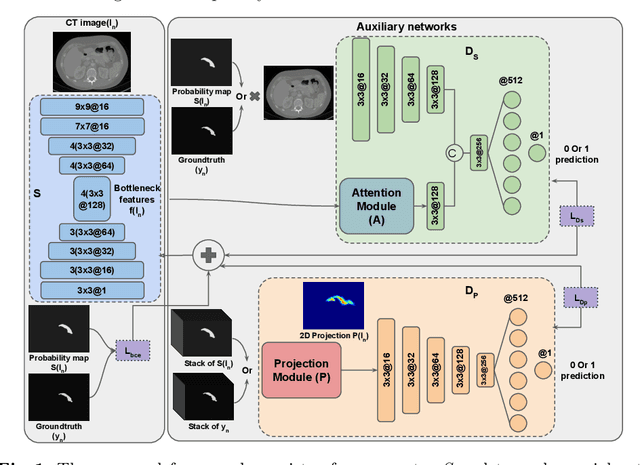
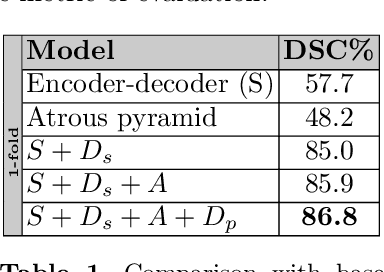
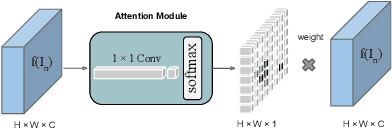
Abstract:Adversarial learning has been proven to be effective for capturing long-range and high-level label consistencies in semantic segmentation. Unique to medical imaging, capturing 3D semantics in an effective yet computationally efficient way remains an open problem. In this study, we address this computational burden by proposing a novel projective adversarial network, called PAN, which incorporates high-level 3D information through 2D projections. Furthermore, we introduce an attention module into our framework that helps for a selective integration of global information directly from our segmentor to our adversarial network. For the clinical application we chose pancreas segmentation from CT scans. Our proposed framework achieved state-of-the-art performance without adding to the complexity of the segmentor.
Evaluation of Algorithms for Multi-Modality Whole Heart Segmentation: An Open-Access Grand Challenge
Feb 21, 2019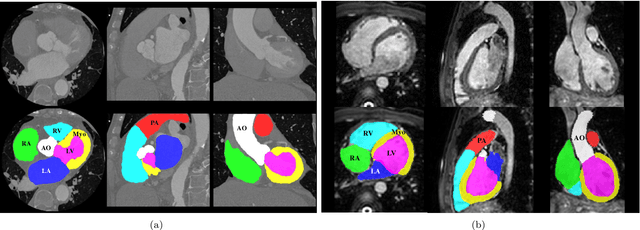
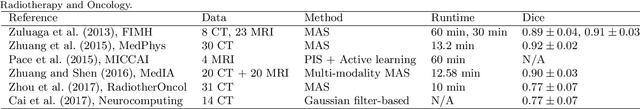
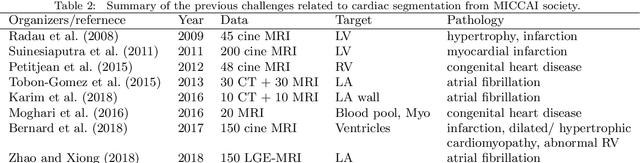
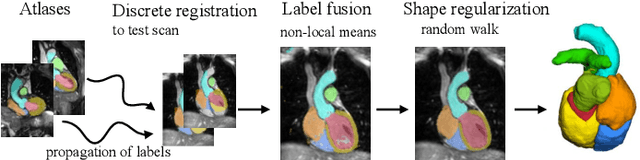
Abstract:Knowledge of whole heart anatomy is a prerequisite for many clinical applications. Whole heart segmentation (WHS), which delineates substructures of the heart, can be very valuable for modeling and analysis of the anatomy and functions of the heart. However, automating this segmentation can be arduous due to the large variation of the heart shape, and different image qualities of the clinical data. To achieve this goal, a set of training data is generally needed for constructing priors or for training. In addition, it is difficult to perform comparisons between different methods, largely due to differences in the datasets and evaluation metrics used. This manuscript presents the methodologies and evaluation results for the WHS algorithms selected from the submissions to the Multi-Modality Whole Heart Segmentation (MM-WHS) challenge, in conjunction with MICCAI 2017. The challenge provides 120 three-dimensional cardiac images covering the whole heart, including 60 CT and 60 MRI volumes, all acquired in clinical environments with manual delineation. Ten algorithms for CT data and eleven algorithms for MRI data, submitted from twelve groups, have been evaluated. The results show that many of the deep learning (DL) based methods achieved high accuracy, even though the number of training datasets was limited. A number of them also reported poor results in the blinded evaluation, probably due to overfitting in their training. The conventional algorithms, mainly based on multi-atlas segmentation, demonstrated robust and stable performance, even though the accuracy is not as good as the best DL method in CT segmentation. The challenge, including the provision of the annotated training data and the blinded evaluation for submitted algorithms on the test data, continues as an ongoing benchmarking resource via its homepage (\url{www.sdspeople.fudan.edu.cn/zhuangxiahai/0/mmwhs/}).
Automatically Designing CNN Architectures for Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 19, 2018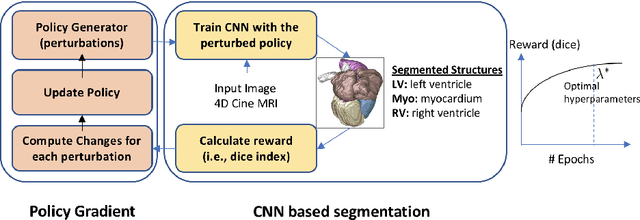
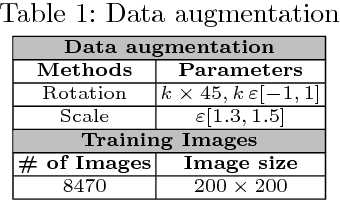

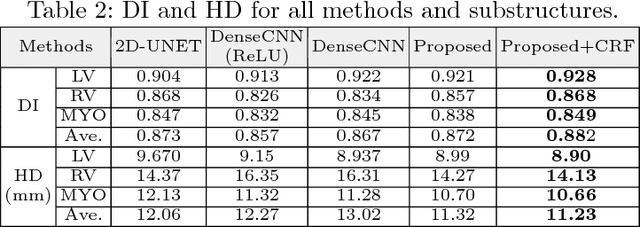
Abstract:Deep neural network architectures have traditionally been designed and explored with human expertise in a long-lasting trial-and-error process. This process requires huge amount of time, expertise, and resources. To address this tedious problem, we propose a novel algorithm to optimally find hyperparameters of a deep network architecture automatically. We specifically focus on designing neural architectures for medical image segmentation task. Our proposed method is based on a policy gradient reinforcement learning for which the reward function is assigned a segmentation evaluation utility (i.e., dice index). We show the efficacy of the proposed method with its low computational cost in comparison with the state-of-the-art medical image segmentation networks. We also present a new architecture design, a densely connected encoder-decoder CNN, as a strong baseline architecture to apply the proposed hyperparameter search algorithm. We apply the proposed algorithm to each layer of the baseline architectures. As an application, we train the proposed system on cine cardiac MR images from Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) MICCAI 2017. Starting from a baseline segmentation architecture, the resulting network architecture obtains the state-of-the-art results in accuracy without performing any trial-and-error based architecture design approaches or close supervision of the hyperparameters changes.
Multi-Planar Deep Segmentation Networks for Cardiac Substructures from MRI and CT
Aug 03, 2017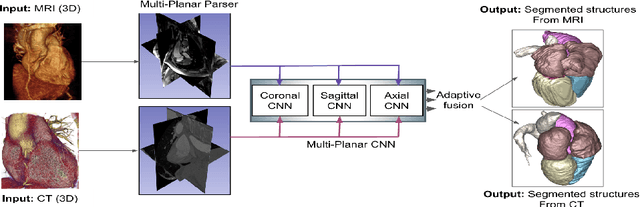
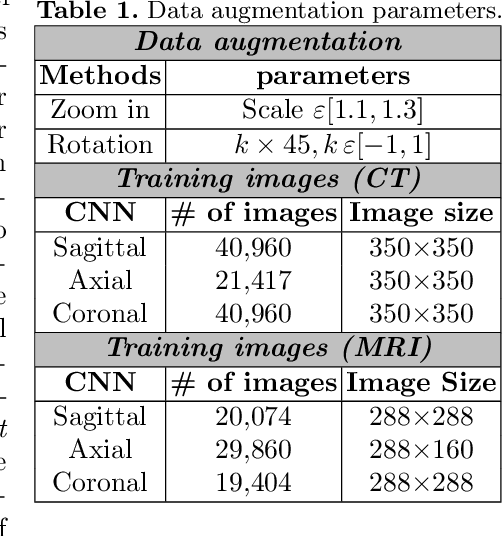
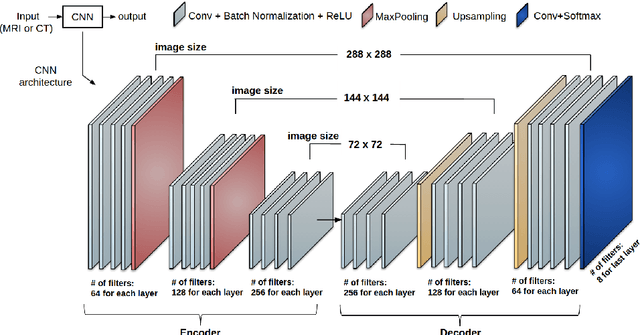
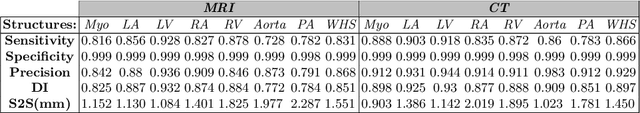
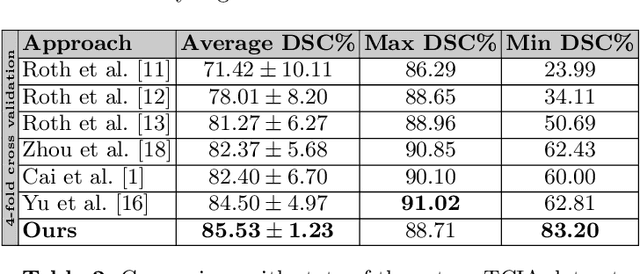
Abstract:Non-invasive detection of cardiovascular disorders from radiology scans requires quantitative image analysis of the heart and its substructures. There are well-established measurements that radiologists use for diseases assessment such as ejection fraction, volume of four chambers, and myocardium mass. These measurements are derived as outcomes of precise segmentation of the heart and its substructures. The aim of this paper is to provide such measurements through an accurate image segmentation algorithm that automatically delineates seven substructures of the heart from MRI and/or CT scans. Our proposed method is based on multi-planar deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) with an adaptive fusion strategy where we automatically utilize complementary information from different planes of the 3D scans for improved delineations. For CT and MRI, we have separately designed three CNNs (the same architectural configuration) for three planes, and have trained the networks from scratch for voxel-wise labeling for the following cardiac structures: myocardium of left ventricle (Myo), left atrium (LA), left ventricle (LV), right atrium (RA), right ventricle (RV), ascending aorta (Ao), and main pulmonary artery (PA). We have evaluated the proposed method with 4-fold-cross validation on the multi-modality whole heart segmentation challenge (MM-WHS 2017) dataset. The precision and dice index of 0.93 and 0.90, and 0.87 and 0.85 were achieved for CT and MR images, respectively. While a CT volume was segmented about 50 seconds, an MRI scan was segmented around 17 seconds with the GPUs/CUDA implementation.
CardiacNET: Segmentation of Left Atrium and Proximal Pulmonary Veins from MRI Using Multi-View CNN
May 19, 2017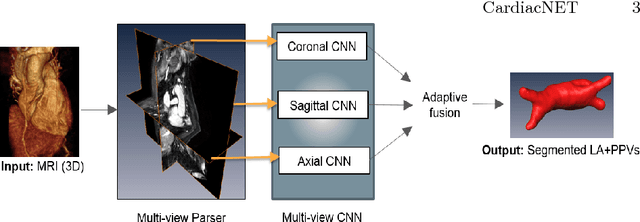
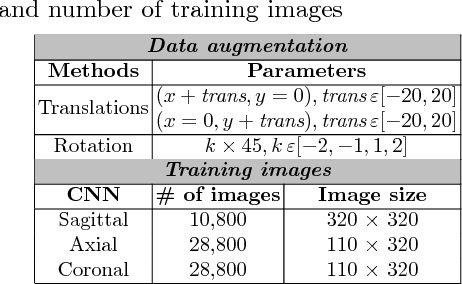
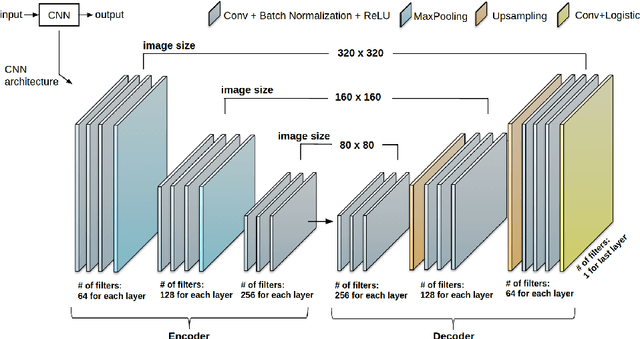
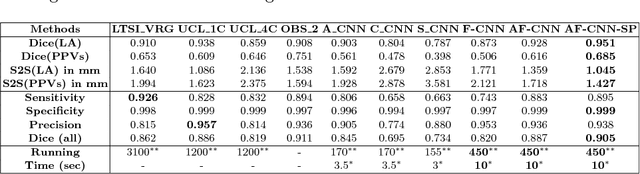
Abstract:Anatomical and biophysical modeling of left atrium (LA) and proximal pulmonary veins (PPVs) is important for clinical management of several cardiac diseases. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows qualitative assessment of LA and PPVs through visualization. However, there is a strong need for an advanced image segmentation method to be applied to cardiac MRI for quantitative analysis of LA and PPVs. In this study, we address this unmet clinical need by exploring a new deep learning-based segmentation strategy for quantification of LA and PPVs with high accuracy and heightened efficiency. Our approach is based on a multi-view convolutional neural network (CNN) with an adaptive fusion strategy and a new loss function that allows fast and more accurate convergence of the backpropagation based optimization. After training our network from scratch by using more than 60K 2D MRI images (slices), we have evaluated our segmentation strategy to the STACOM 2013 cardiac segmentation challenge benchmark. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations, obtained from the segmentation challenge, indicate that the proposed method achieved the state-of-the-art sensitivity (90%), specificity (99%), precision (94%), and efficiency levels (10 seconds in GPU, and 7.5 minutes in CPU).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge