The International Workshop on Osteoarthritis Imaging Knee MRI Segmentation Challenge: A Multi-Institute Evaluation and Analysis Framework on a Standardized Dataset
Paper and Code
May 26, 2020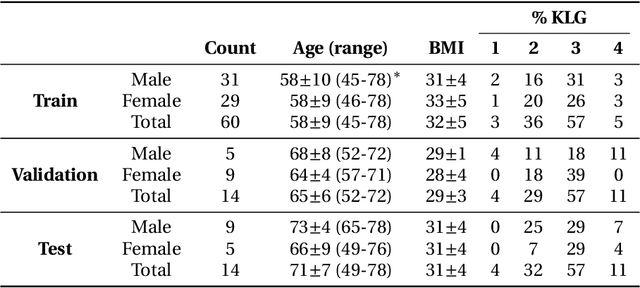
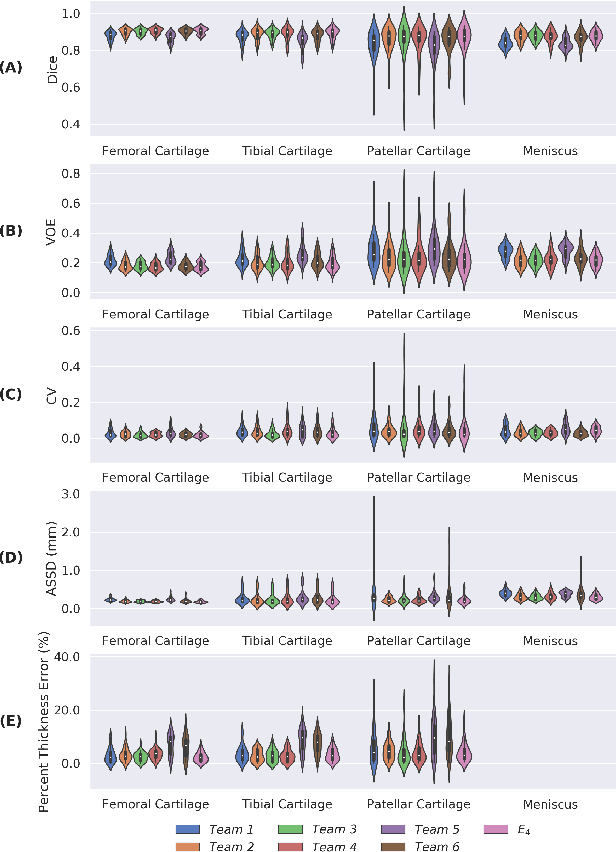
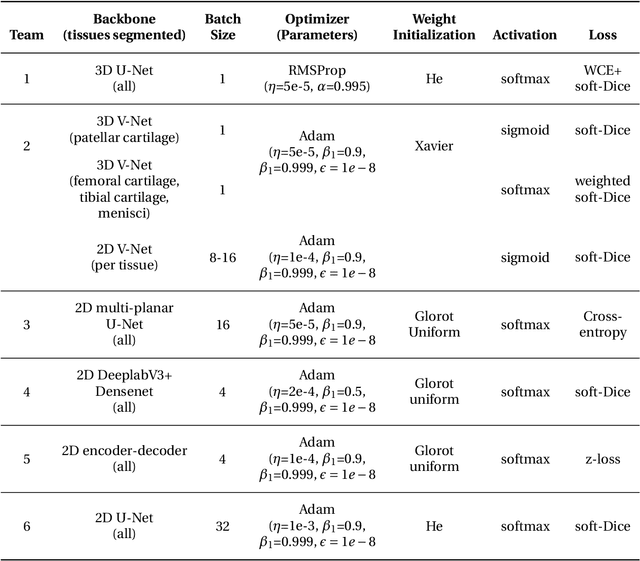
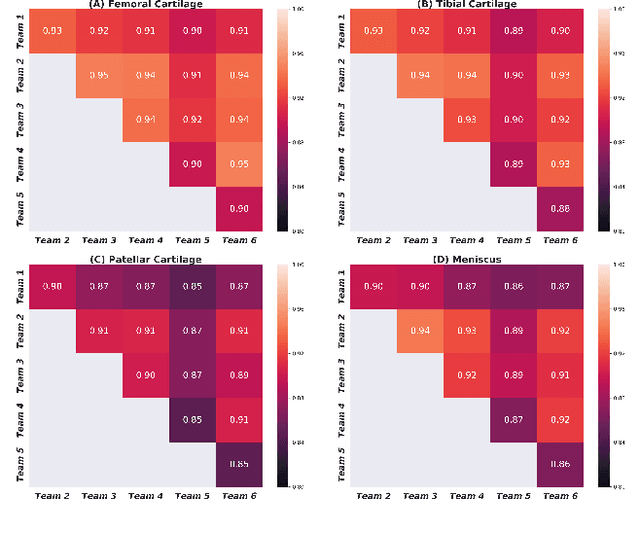
Purpose: To organize a knee MRI segmentation challenge for characterizing the semantic and clinical efficacy of automatic segmentation methods relevant for monitoring osteoarthritis progression. Methods: A dataset partition consisting of 3D knee MRI from 88 subjects at two timepoints with ground-truth articular (femoral, tibial, patellar) cartilage and meniscus segmentations was standardized. Challenge submissions and a majority-vote ensemble were evaluated using Dice score, average symmetric surface distance, volumetric overlap error, and coefficient of variation on a hold-out test set. Similarities in network segmentations were evaluated using pairwise Dice correlations. Articular cartilage thickness was computed per-scan and longitudinally. Correlation between thickness error and segmentation metrics was measured using Pearson's coefficient. Two empirical upper bounds for ensemble performance were computed using combinations of model outputs that consolidated true positives and true negatives. Results: Six teams (T1-T6) submitted entries for the challenge. No significant differences were observed across all segmentation metrics for all tissues (p=1.0) among the four top-performing networks (T2, T3, T4, T6). Dice correlations between network pairs were high (>0.85). Per-scan thickness errors were negligible among T1-T4 (p=0.99) and longitudinal changes showed minimal bias (<0.03mm). Low correlations (<0.41) were observed between segmentation metrics and thickness error. The majority-vote ensemble was comparable to top performing networks (p=1.0). Empirical upper bound performances were similar for both combinations (p=1.0). Conclusion: Diverse networks learned to segment the knee similarly where high segmentation accuracy did not correlate to cartilage thickness accuracy. Voting ensembles did not outperform individual networks but may help regularize individual models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge