Agnes B. Fogo
Circle Representation for Medical Instance Object Segmentation
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:Recently, circle representation has been introduced for medical imaging, designed specifically to enhance the detection of instance objects that are spherically shaped (e.g., cells, glomeruli, and nuclei). Given its outstanding effectiveness in instance detection, it is compelling to consider the application of circle representation for segmenting instance medical objects. In this study, we introduce CircleSnake, a simple end-to-end segmentation approach that utilizes circle contour deformation for segmenting ball-shaped medical objects at the instance level. The innovation of CircleSnake lies in these three areas: (1) It substitutes the complex bounding box-to-octagon contour transformation with a more consistent and rotation-invariant bounding circle-to-circle contour adaptation. This adaptation specifically targets ball-shaped medical objects. (2) The circle representation employed in CircleSnake significantly reduces the degrees of freedom to two, compared to eight in the octagon representation. This reduction enhances both the robustness of the segmentation performance and the rotational consistency of the method. (3) CircleSnake is the first end-to-end deep instance segmentation pipeline to incorporate circle representation, encompassing consistent circle detection, circle contour proposal, and circular convolution in a unified framework. This integration is achieved through the novel application of circular graph convolution within the context of circle detection and instance segmentation. In practical applications, such as the detection of glomeruli, nuclei, and eosinophils in pathological images, CircleSnake has demonstrated superior performance and greater rotation invariance when compared to benchmarks. The code has been made publicly available: https://github.com/hrlblab/CircleSnake.
Spatial Pathomics Toolkit for Quantitative Analysis of Podocyte Nuclei with Histology and Spatial Transcriptomics Data in Renal Pathology
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Podocytes, specialized epithelial cells that envelop the glomerular capillaries, play a pivotal role in maintaining renal health. The current description and quantification of features on pathology slides are limited, prompting the need for innovative solutions to comprehensively assess diverse phenotypic attributes within Whole Slide Images (WSIs). In particular, understanding the morphological characteristics of podocytes, terminally differentiated glomerular epithelial cells, is crucial for studying glomerular injury. This paper introduces the Spatial Pathomics Toolkit (SPT) and applies it to podocyte pathomics. The SPT consists of three main components: (1) instance object segmentation, enabling precise identification of podocyte nuclei; (2) pathomics feature generation, extracting a comprehensive array of quantitative features from the identified nuclei; and (3) robust statistical analyses, facilitating a comprehensive exploration of spatial relationships between morphological and spatial transcriptomics features.The SPT successfully extracted and analyzed morphological and textural features from podocyte nuclei, revealing a multitude of podocyte morphomic features through statistical analysis. Additionally, we demonstrated the SPT's ability to unravel spatial information inherent to podocyte distribution, shedding light on spatial patterns associated with glomerular injury. By disseminating the SPT, our goal is to provide the research community with a powerful and user-friendly resource that advances cellular spatial pathomics in renal pathology. The implementation and its complete source code of the toolkit are made openly accessible at https://github.com/hrlblab/spatial_pathomics.
Segment Anything Model (SAM) for Digital Pathology: Assess Zero-shot Segmentation on Whole Slide Imaging
Apr 09, 2023Abstract:The segment anything model (SAM) was released as a foundation model for image segmentation. The promptable segmentation model was trained by over 1 billion masks on 11M licensed and privacy-respecting images. The model supports zero-shot image segmentation with various segmentation prompts (e.g., points, boxes, masks). It makes the SAM attractive for medical image analysis, especially for digital pathology where the training data are rare. In this study, we evaluate the zero-shot segmentation performance of SAM model on representative segmentation tasks on whole slide imaging (WSI), including (1) tumor segmentation, (2) non-tumor tissue segmentation, (3) cell nuclei segmentation. Core Results: The results suggest that the zero-shot SAM model achieves remarkable segmentation performance for large connected objects. However, it does not consistently achieve satisfying performance for dense instance object segmentation, even with 20 prompts (clicks/boxes) on each image. We also summarized the identified limitations for digital pathology: (1) image resolution, (2) multiple scales, (3) prompt selection, and (4) model fine-tuning. In the future, the few-shot fine-tuning with images from downstream pathological segmentation tasks might help the model to achieve better performance in dense object segmentation.
CircleSnake: Instance Segmentation with Circle Representation
Nov 02, 2022Abstract:Circle representation has recently been introduced as a medical imaging optimized representation for more effective instance object detection on ball-shaped medical objects. With its superior performance on instance detection, it is appealing to extend the circle representation to instance medical object segmentation. In this work, we propose CircleSnake, a simple end-to-end circle contour deformation-based segmentation method for ball-shaped medical objects. Compared to the prevalent DeepSnake method, our contribution is three-fold: (1) We replace the complicated bounding box to octagon contour transformation with a computation-free and consistent bounding circle to circle contour adaption for segmenting ball-shaped medical objects; (2) Circle representation has fewer degrees of freedom (DoF=2) as compared with the octagon representation (DoF=8), thus yielding a more robust segmentation performance and better rotation consistency; (3) To the best of our knowledge, the proposed CircleSnake method is the first end-to-end circle representation deep segmentation pipeline method with consistent circle detection, circle contour proposal, and circular convolution. The key innovation is to integrate the circular graph convolution with circle detection into an end-to-end instance segmentation framework, enabled by the proposed simple and consistent circle contour representation. Glomeruli are used to evaluate the performance of the benchmarks. From the results, CircleSnake increases the average precision of glomerular detection from 0.559 to 0.614. The Dice score increased from 0.804 to 0.849. The code has been released: https://github.com/hrlblab/CircleSnake
Compound Figure Separation of Biomedical Images: Mining Large Datasets for Self-supervised Learning
Aug 30, 2022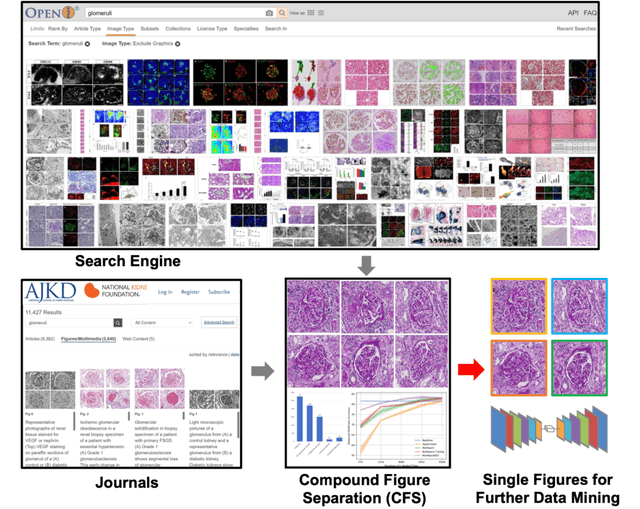
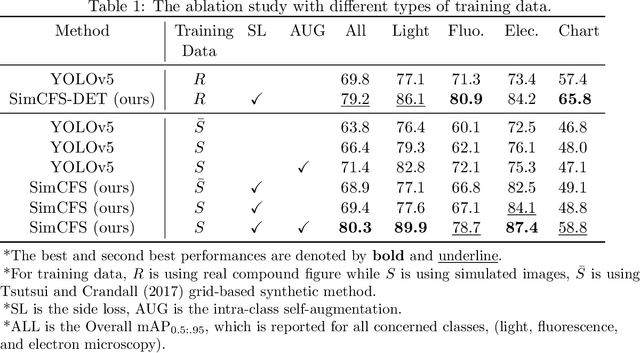
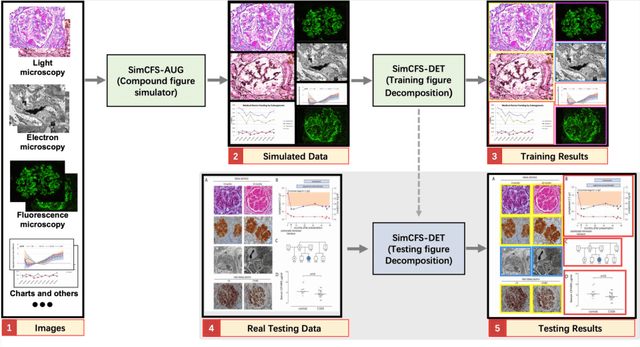
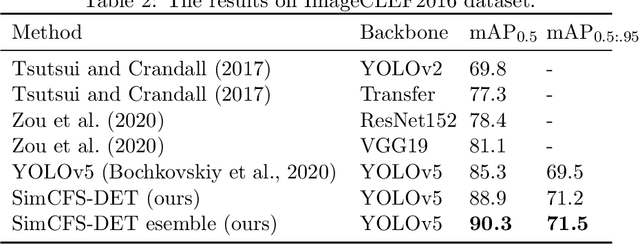
Abstract:With the rapid development of self-supervised learning (e.g., contrastive learning), the importance of having large-scale images (even without annotations) for training a more generalizable AI model has been widely recognized in medical image analysis. However, collecting large-scale task-specific unannotated data at scale can be challenging for individual labs. Existing online resources, such as digital books, publications, and search engines, provide a new resource for obtaining large-scale images. However, published images in healthcare (e.g., radiology and pathology) consist of a considerable amount of compound figures with subplots. In order to extract and separate compound figures into usable individual images for downstream learning, we propose a simple compound figure separation (SimCFS) framework without using the traditionally required detection bounding box annotations, with a new loss function and a hard case simulation. Our technical contribution is four-fold: (1) we introduce a simulation-based training framework that minimizes the need for resource extensive bounding box annotations; (2) we propose a new side loss that is optimized for compound figure separation; (3) we propose an intra-class image augmentation method to simulate hard cases; and (4) to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that evaluates the efficacy of leveraging self-supervised learning with compound image separation. From the results, the proposed SimCFS achieved state-of-the-art performance on the ImageCLEF 2016 Compound Figure Separation Database. The pretrained self-supervised learning model using large-scale mined figures improved the accuracy of downstream image classification tasks with a contrastive learning algorithm. The source code of SimCFS is made publicly available at https://github.com/hrlblab/ImageSeperation.
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://www.melba-journal.org/papers/2022:025.html. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2107.08650
Omni-Seg+: A Scale-aware Dynamic Network for Pathological Image Segmentation
Jun 27, 2022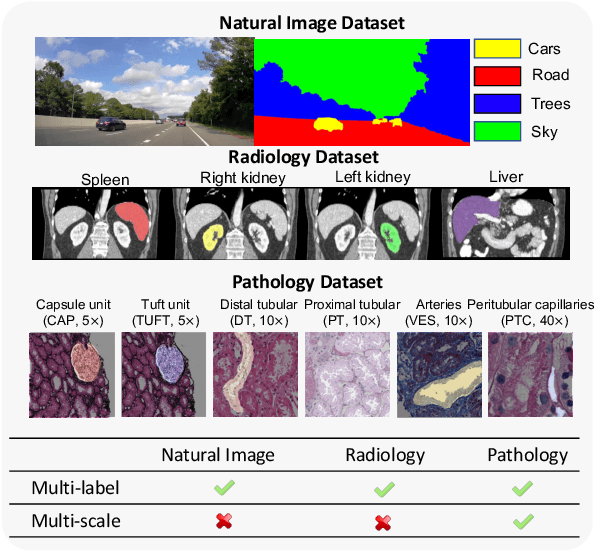
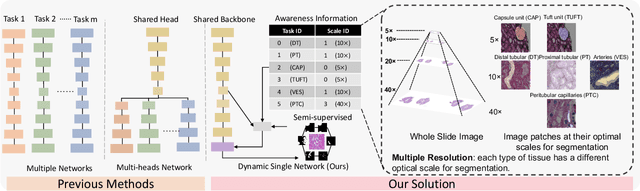
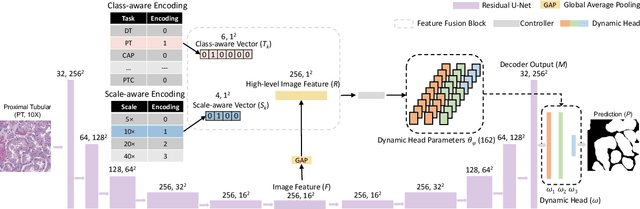
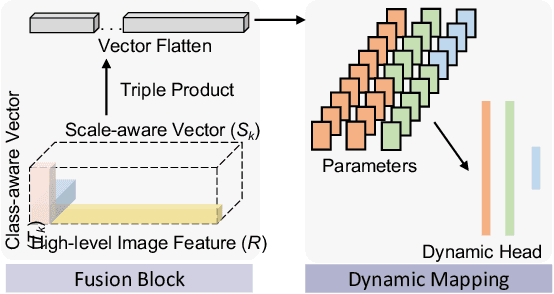
Abstract:Comprehensive semantic segmentation on renal pathological images is challenging due to the heterogeneous scales of the objects. For example, on a whole slide image (WSI), the cross-sectional areas of glomeruli can be 64 times larger than that of the peritubular capillaries, making it impractical to segment both objects on the same patch, at the same scale. To handle this scaling issue, prior studies have typically trained multiple segmentation networks in order to match the optimal pixel resolution of heterogeneous tissue types. This multi-network solution is resource-intensive and fails to model the spatial relationship between tissue types. In this paper, we propose the Omni-Seg+ network, a scale-aware dynamic neural network that achieves multi-object (six tissue types) and multi-scale (5X to 40X scale) pathological image segmentation via a single neural network. The contribution of this paper is three-fold: (1) a novel scale-aware controller is proposed to generalize the dynamic neural network from single-scale to multi-scale; (2) semi-supervised consistency regularization of pseudo-labels is introduced to model the inter-scale correlation of unannotated tissue types into a single end-to-end learning paradigm; and (3) superior scale-aware generalization is evidenced by directly applying a model trained on human kidney images to mouse kidney images, without retraining. By learning from ~150,000 human pathological image patches from six tissue types at three different resolutions, our approach achieved superior segmentation performance according to human visual assessment and evaluation of image-omics (i.e., spatial transcriptomics). The official implementation is available at https://github.com/ddrrnn123/Omni-Seg.
Glo-In-One: Holistic Glomerular Detection, Segmentation, and Lesion Characterization with Large-scale Web Image Mining
May 31, 2022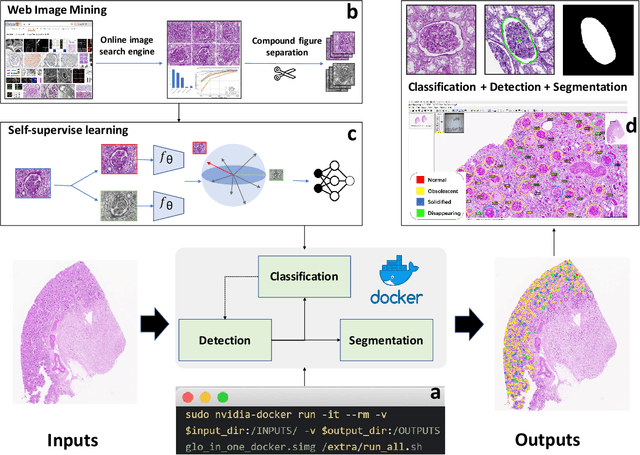
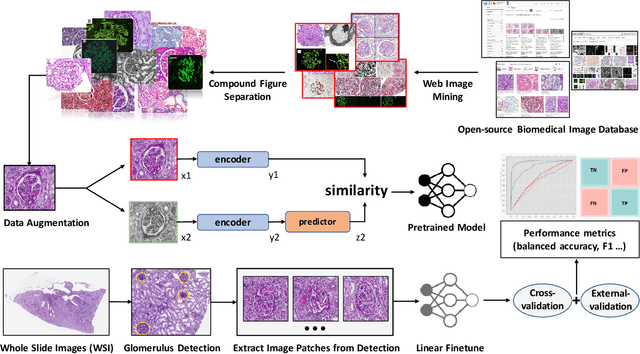
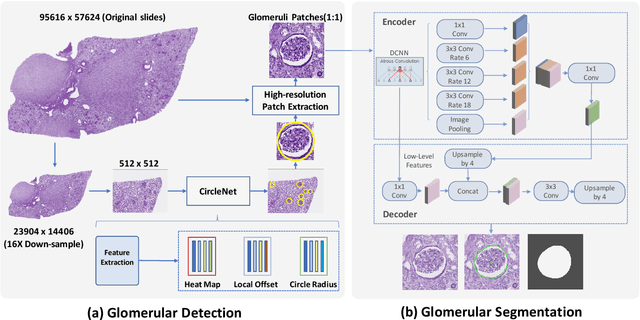
Abstract:The quantitative detection, segmentation, and characterization of glomeruli from high-resolution whole slide imaging (WSI) play essential roles in the computer-assisted diagnosis and scientific research in digital renal pathology. Historically, such comprehensive quantification requires extensive programming skills in order to be able to handle heterogeneous and customized computational tools. To bridge the gap of performing glomerular quantification for non-technical users, we develop the Glo-In-One toolkit to achieve holistic glomerular detection, segmentation, and characterization via a single line of command. Additionally, we release a large-scale collection of 30,000 unlabeled glomerular images to further facilitate the algorithmic development of self-supervised deep learning. The inputs of the Glo-In-One toolkit are WSIs, while the outputs are (1) WSI-level multi-class circle glomerular detection results (which can be directly manipulated with ImageScope), (2) glomerular image patches with segmentation masks, and (3) different lesion types. To leverage the performance of the Glo-In-One toolkit, we introduce self-supervised deep learning to glomerular quantification via large-scale web image mining. The GGS fine-grained classification model achieved a decent performance compared with baseline supervised methods while only using 10% of the annotated data. The glomerular detection achieved an average precision of 0.627 with circle representations, while the glomerular segmentation achieved a 0.955 patch-wise Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC).
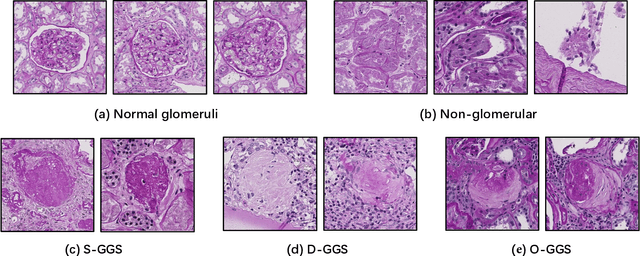
Holistic Fine-grained GGS Characterization: From Detection to Unbalanced Classification
Jan 31, 2022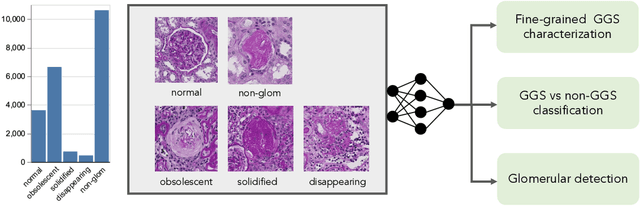



Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated the diagnostic and prognostic values of global glomerulosclerosis (GGS) in IgA nephropathy, aging, and end-stage renal disease. However, the fine-grained quantitative analysis of multiple GGS subtypes (e.g., obsolescent, solidified, and disappearing glomerulosclerosis) is typically a resource extensive manual process. Very few automatic methods, if any, have been developed to bridge this gap for such analytics. In this paper, we present a holistic pipeline to quantify GGS (with both detection and classification) from a whole slide image in a fully automatic manner. In addition, we conduct the fine-grained classification for the sub-types of GGS. Our study releases the open-source quantitative analytical tool for fine-grained GGS characterization while tackling the technical challenges in unbalanced classification and integrating detection and classification.
Circle Representation for Medical Object Detection
Oct 22, 2021
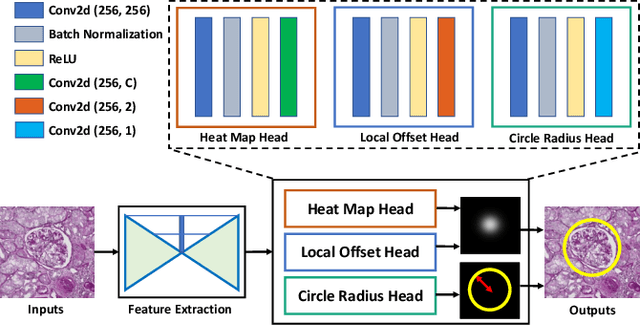

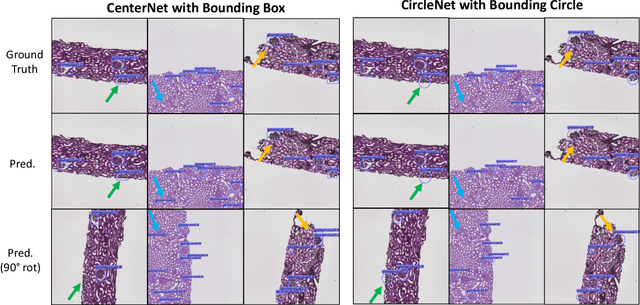
Abstract:Box representation has been extensively used for object detection in computer vision. Such representation is efficacious but not necessarily optimized for biomedical objects (e.g., glomeruli), which play an essential role in renal pathology. In this paper, we propose a simple circle representation for medical object detection and introduce CircleNet, an anchor-free detection framework. Compared with the conventional bounding box representation, the proposed bounding circle representation innovates in three-fold: (1) it is optimized for ball-shaped biomedical objects; (2) The circle representation reduced the degree of freedom compared with box representation; (3) It is naturally more rotation invariant. When detecting glomeruli and nuclei on pathological images, the proposed circle representation achieved superior detection performance and be more rotation-invariant, compared with the bounding box. The code has been made publicly available: https://github.com/hrlblab/CircleNet
Compound Figure Separation of Biomedical Images with Side Loss
Jul 19, 2021



Abstract:Unsupervised learning algorithms (e.g., self-supervised learning, auto-encoder, contrastive learning) allow deep learning models to learn effective image representations from large-scale unlabeled data. In medical image analysis, even unannotated data can be difficult to obtain for individual labs. Fortunately, national-level efforts have been made to provide efficient access to obtain biomedical image data from previous scientific publications. For instance, NIH has launched the Open-i search engine that provides a large-scale image database with free access. However, the images in scientific publications consist of a considerable amount of compound figures with subplots. To extract and curate individual subplots, many different compound figure separation approaches have been developed, especially with the recent advances in deep learning. However, previous approaches typically required resource extensive bounding box annotation to train detection models. In this paper, we propose a simple compound figure separation (SimCFS) framework that uses weak classification annotations from individual images. Our technical contribution is three-fold: (1) we introduce a new side loss that is designed for compound figure separation; (2) we introduce an intra-class image augmentation method to simulate hard cases; (3) the proposed framework enables an efficient deployment to new classes of images, without requiring resource extensive bounding box annotations. From the results, the SimCFS achieved a new state-of-the-art performance on the ImageCLEF 2016 Compound Figure Separation Database. The source code of SimCFS is made publicly available at https://github.com/hrlblab/ImageSeperation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge