Ziran Zhang
EGVD: Event-Guided Video Diffusion Model for Physically Realistic Large-Motion Frame Interpolation
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Video frame interpolation (VFI) in scenarios with large motion remains challenging due to motion ambiguity between frames. While event cameras can capture high temporal resolution motion information, existing event-based VFI methods struggle with limited training data and complex motion patterns. In this paper, we introduce Event-Guided Video Diffusion Model (EGVD), a novel framework that leverages the powerful priors of pre-trained stable video diffusion models alongside the precise temporal information from event cameras. Our approach features a Multi-modal Motion Condition Generator (MMCG) that effectively integrates RGB frames and event signals to guide the diffusion process, producing physically realistic intermediate frames. We employ a selective fine-tuning strategy that preserves spatial modeling capabilities while efficiently incorporating event-guided temporal information. We incorporate input-output normalization techniques inspired by recent advances in diffusion modeling to enhance training stability across varying noise levels. To improve generalization, we construct a comprehensive dataset combining both real and simulated event data across diverse scenarios. Extensive experiments on both real and simulated datasets demonstrate that EGVD significantly outperforms existing methods in handling large motion and challenging lighting conditions, achieving substantial improvements in perceptual quality metrics (27.4% better LPIPS on Prophesee and 24.1% on BSRGB) while maintaining competitive fidelity measures. Code and datasets available at: https://github.com/OpenImagingLab/EGVD.
Event-assisted 12-stop HDR Imaging of Dynamic Scene
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:High dynamic range (HDR) imaging is a crucial task in computational photography, which captures details across diverse lighting conditions. Traditional HDR fusion methods face limitations in dynamic scenes with extreme exposure differences, as aligning low dynamic range (LDR) frames becomes challenging due to motion and brightness variation. In this work, we propose a novel 12-stop HDR imaging approach for dynamic scenes, leveraging a dual-camera system with an event camera and an RGB camera. The event camera provides temporally dense, high dynamic range signals that improve alignment between LDR frames with large exposure differences, reducing ghosting artifacts caused by motion. Also, a real-world finetuning strategy is proposed to increase the generalization of alignment module on real-world events. Additionally, we introduce a diffusion-based fusion module that incorporates image priors from pre-trained diffusion models to address artifacts in high-contrast regions and minimize errors from the alignment process. To support this work, we developed the ESHDR dataset, the first dataset for 12-stop HDR imaging with synchronized event signals, and validated our approach on both simulated and real-world data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, successfully extending HDR imaging to 12 stops in dynamic scenes.
Physical prior guided cooperative learning framework for joint turbulence degradation estimation and infrared video restoration
Aug 08, 2024Abstract:Infrared imaging and turbulence strength measurements are in widespread demand in many fields. This paper introduces a Physical Prior Guided Cooperative Learning (P2GCL) framework to jointly enhance atmospheric turbulence strength estimation and infrared image restoration. P2GCL involves a cyclic collaboration between two models, i.e., a TMNet measures turbulence strength and outputs the refractive index structure constant (Cn2) as a physical prior, a TRNet conducts infrared image sequence restoration based on Cn2 and feeds the restored images back to the TMNet to boost the measurement accuracy. A novel Cn2-guided frequency loss function and a physical constraint loss are introduced to align the training process with physical theories. Experiments demonstrate P2GCL achieves the best performance for both turbulence strength estimation (improving Cn2 MAE by 0.0156, enhancing R2 by 0.1065) and image restoration (enhancing PSNR by 0.2775 dB), validating the significant impact of physical prior guided cooperative learning.
From Sim-to-Real: Toward General Event-based Low-light Frame Interpolation with Per-scene Optimization
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) is important for video enhancement, frame rate up-conversion, and slow-motion generation. The introduction of event cameras, which capture per-pixel brightness changes asynchronously, has significantly enhanced VFI capabilities, particularly for high-speed, nonlinear motions. However, these event-based methods encounter challenges in low-light conditions, notably trailing artifacts and signal latency, which hinder their direct applicability and generalization. Addressing these issues, we propose a novel per-scene optimization strategy tailored for low-light conditions. This approach utilizes the internal statistics of a sequence to handle degraded event data under low-light conditions, improving the generalizability to different lighting and camera settings. To evaluate its robustness in low-light condition, we further introduce EVFI-LL, a unique RGB+Event dataset captured under low-light conditions. Our results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in low-light environments. Both the dataset and the source code will be made publicly available upon publication. Project page: https://naturezhanghn.github.io/sim2real.
Deep Linear Array Pushbroom Image Restoration: A Degradation Pipeline and Jitter-Aware Restoration Network
Jan 16, 2024



Abstract:Linear Array Pushbroom (LAP) imaging technology is widely used in the realm of remote sensing. However, images acquired through LAP always suffer from distortion and blur because of camera jitter. Traditional methods for restoring LAP images, such as algorithms estimating the point spread function (PSF), exhibit limited performance. To tackle this issue, we propose a Jitter-Aware Restoration Network (JARNet), to remove the distortion and blur in two stages. In the first stage, we formulate an Optical Flow Correction (OFC) block to refine the optical flow of the degraded LAP images, resulting in pre-corrected images where most of the distortions are alleviated. In the second stage, for further enhancement of the pre-corrected images, we integrate two jitter-aware techniques within the Spatial and Frequency Residual (SFRes) block: 1) introducing Coordinate Attention (CoA) to the SFRes block in order to capture the jitter state in orthogonal direction; 2) manipulating image features in both spatial and frequency domains to leverage local and global priors. Additionally, we develop a data synthesis pipeline, which applies Continue Dynamic Shooting Model (CDSM) to simulate realistic degradation in LAP images. Both the proposed JARNet and LAP image synthesis pipeline establish a foundation for addressing this intricate challenge. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed two-stage method outperforms state-of-the-art image restoration models. Code is available at https://github.com/JHW2000/JARNet.
Real-world Deep Local Motion Deblurring
Apr 18, 2022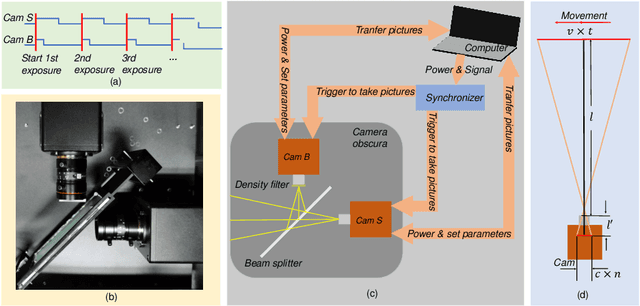
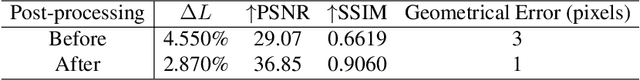

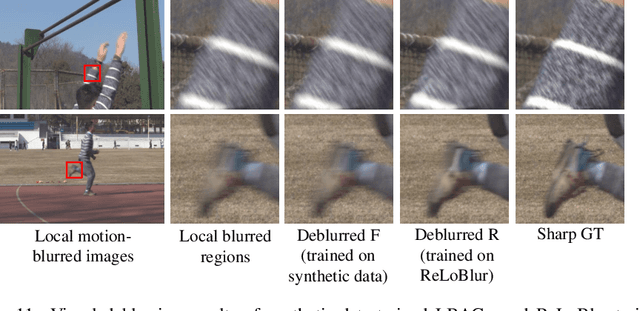
Abstract:Most existing deblurring methods focus on removing global blur caused by camera shake, while they cannot well handle local blur caused by object movements. To fill the vacancy of local deblurring in real scenes, we establish the first real local motion blur dataset (ReLoBlur), which is captured by a synchronized beam-splitting photographing system and corrected by a post-progressing pipeline. Based on ReLoBlur, we propose a Local Blur-Aware Gated network (LBAG) and several local blur-aware techniques to bridge the gap between global and local deblurring: 1) a blur detection approach based on background subtraction to localize blurred regions; 2) a gate mechanism to guide our network to focus on blurred regions; and 3) a blur-aware patch cropping strategy to address data imbalance problem. Extensive experiments prove the reliability of ReLoBlur dataset, and demonstrate that LBAG achieves better performance than state-of-the-art global deblurring methods without our proposed local blur-aware techniques.
Design and Control of A Hybrid Sailboat for Enhanced Tacking Maneuver
Nov 29, 2018
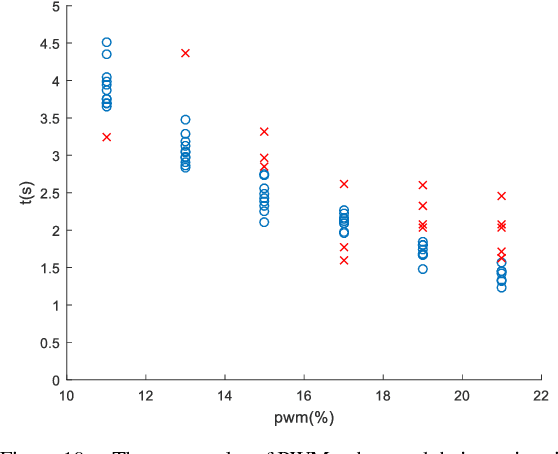
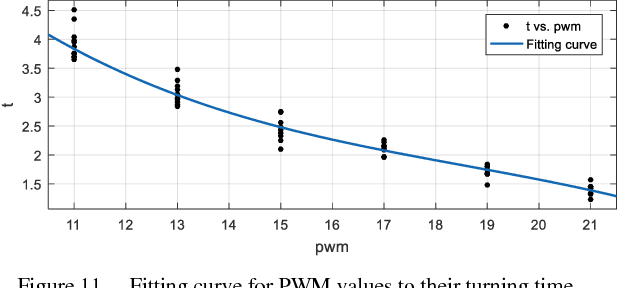
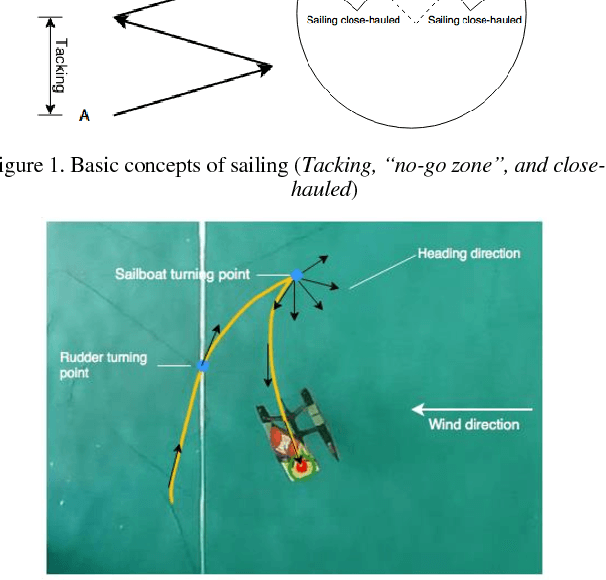
Abstract:Sailing robots provide a low-cost solution to conduct the ocean missions such as marine exploration, pollution detection, and border surveillance, etc. However, compared with other propeller-driven surface vessels, sailboat suffers in complex marine wind field due to its low mobility. Especially in tacking, sailboats are required to head upwind, and need to make a zig-zag path. In this trajectory, a series of turnings, which will cross the challenging no-go zone, place significant challenge as it will reduce speed greatly and consequently result in unsuccessful turning. This paper presents a hybrid sailboat design to solve this issue. Electric propellers and control system are added to a model sailboat. We have further designed the control strategy and tuned the parameters (PWM-time) experimentally. Finally, the system and control can complete the tacking maneuver with average speed approximately 10% higher and enhanced success rate, though the sailboat weight is much heavier.
Energy Optimization of Automatic Hybrid Sailboat
Nov 28, 2018
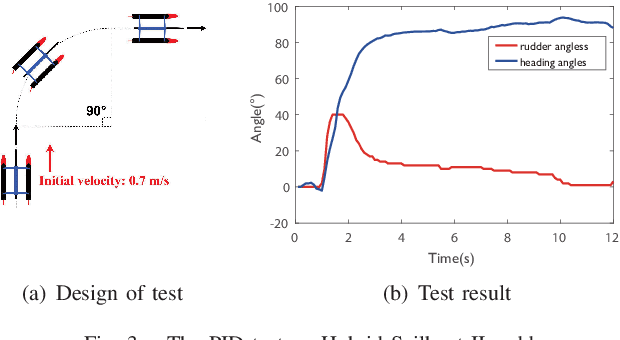


Abstract:Autonomous Surface Vehicles (ASVs) provide an effective way to actualize applications such as environment monitoring, search and rescue, and scientific researches. However, the conventional ASVs depends overly on the stored energy. Hybrid Sailboat, mainly powered by the wind, can solve this problem by using an auxiliary propulsion system. The electric energy cost of Hybrid Sailboat needs to be optimized to achieve the ocean automatic cruise mission. Based on adjusted setting on sails and rudders, this paper seeks the optimal trajectory for autonomic cruising to reduce the energy cost by changing the heading angle of sailing upwind. The experiment results validate the heading angle accounts for energy cost and the trajectory with the best heading angle saves up to 23.7% than other conditions. Furthermore, the energy-time line can be used to predict the energy cost for long-time sailing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge