Zijin Gu
SpeakStream: Streaming Text-to-Speech with Interleaved Data
May 25, 2025Abstract:The latency bottleneck of traditional text-to-speech (TTS) systems fundamentally hinders the potential of streaming large language models (LLMs) in conversational AI. These TTS systems, typically trained and inferenced on complete utterances, introduce unacceptable delays, even with optimized inference speeds, when coupled with streaming LLM outputs. This is particularly problematic for creating responsive conversational agents where low first-token latency is critical. In this paper, we present SpeakStream, a streaming TTS system that generates audio incrementally from streaming text using a decoder-only architecture. SpeakStream is trained using a next-step prediction loss on interleaved text-speech data. During inference, it generates speech incrementally while absorbing streaming input text, making it particularly suitable for cascaded conversational AI agents where an LLM streams text to a TTS system. Our experiments demonstrate that SpeakStream achieves state-of-the-art latency results in terms of first-token latency while maintaining the quality of non-streaming TTS systems.
Reversal Blessing: Thinking Backward May Outpace Thinking Forward in Multi-choice Questions
Feb 25, 2025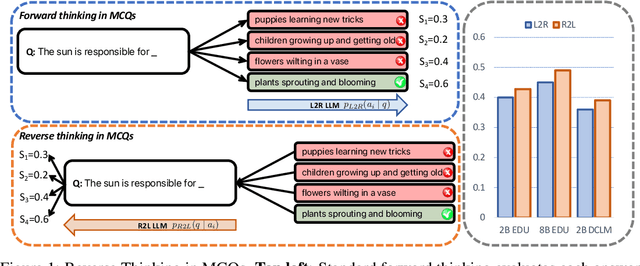
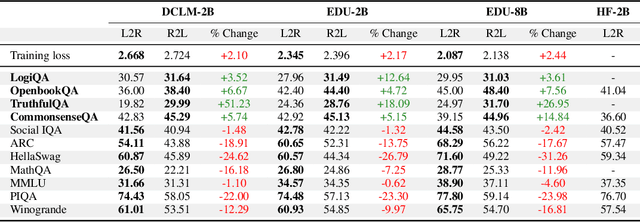
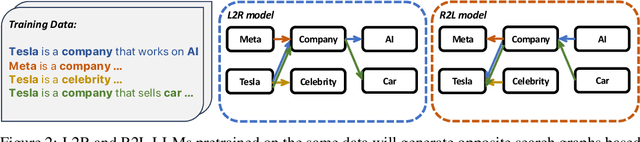
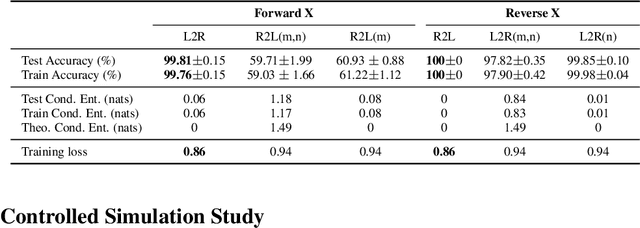
Abstract:Language models usually use left-to-right (L2R) autoregressive factorization. However, L2R factorization may not always be the best inductive bias. Therefore, we investigate whether alternative factorizations of the text distribution could be beneficial in some tasks. We investigate right-to-left (R2L) training as a compelling alternative, focusing on multiple-choice questions (MCQs) as a test bed for knowledge extraction and reasoning. Through extensive experiments across various model sizes (2B-8B parameters) and training datasets, we find that R2L models can significantly outperform L2R models on several MCQ benchmarks, including logical reasoning, commonsense understanding, and truthfulness assessment tasks. Our analysis reveals that this performance difference may be fundamentally linked to multiple factors including calibration, computability and directional conditional entropy. We ablate the impact of these factors through controlled simulation studies using arithmetic tasks, where the impacting factors can be better disentangled. Our work demonstrates that exploring alternative factorizations of the text distribution can lead to improvements in LLM capabilities and provides theoretical insights into optimal factorization towards approximating human language distribution, and when each reasoning order might be more advantageous.
Theory, Analysis, and Best Practices for Sigmoid Self-Attention
Sep 06, 2024



Abstract:Attention is a key part of the transformer architecture. It is a sequence-to-sequence mapping that transforms each sequence element into a weighted sum of values. The weights are typically obtained as the softmax of dot products between keys and queries. Recent work has explored alternatives to softmax attention in transformers, such as ReLU and sigmoid activations. In this work, we revisit sigmoid attention and conduct an in-depth theoretical and empirical analysis. Theoretically, we prove that transformers with sigmoid attention are universal function approximators and benefit from improved regularity compared to softmax attention. Through detailed empirical analysis, we identify stabilization of large initial attention norms during the early stages of training as a crucial factor for the successful training of models with sigmoid attention, outperforming prior attempts. We also introduce FLASHSIGMOID, a hardware-aware and memory-efficient implementation of sigmoid attention yielding a 17% inference kernel speed-up over FLASHATTENTION2 on H100 GPUs. Experiments across language, vision, and speech show that properly normalized sigmoid attention matches the strong performance of softmax attention on a wide range of domains and scales, which previous attempts at sigmoid attention were unable to fully achieve. Our work unifies prior art and establishes best practices for sigmoid attention as a drop-in softmax replacement in transformers.
dMel: Speech Tokenization made Simple
Jul 22, 2024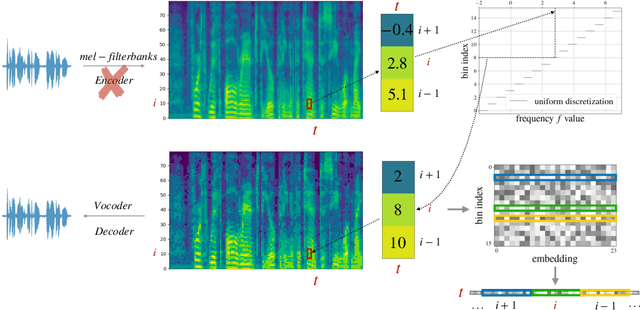
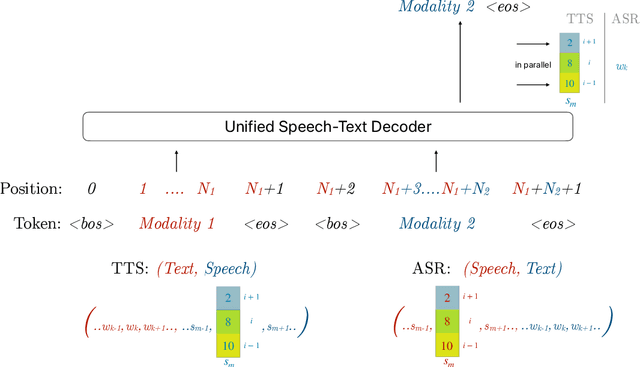
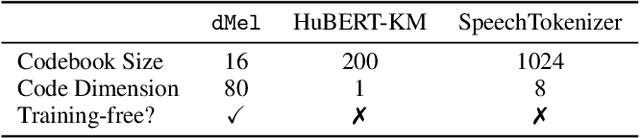
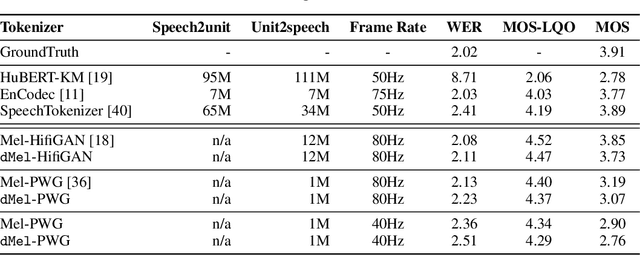
Abstract:Large language models have revolutionized natural language processing by leveraging self-supervised pretraining on vast textual data. Inspired by this success, researchers have investigated complicated speech tokenization methods to discretize continuous speech signals so that language modeling techniques can be applied to speech data. However, existing approaches either model semantic tokens, potentially losing acoustic information, or model acoustic tokens, risking the loss of semantic information. Having multiple token types also complicates the architecture and requires additional pretraining. Here we show that discretizing mel-filterbank channels into discrete intensity bins produces a simple representation (dMel), that performs better than other existing speech tokenization methods. Using a transformer decoder-only architecture for speech-text modeling, we comprehensively evaluate different speech tokenization methods on speech recognition (ASR), speech synthesis (TTS). Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of dMel in achieving high performance on both tasks within a unified framework, paving the way for efficient and effective joint modeling of speech and text.
Denoising LM: Pushing the Limits of Error Correction Models for Speech Recognition
May 24, 2024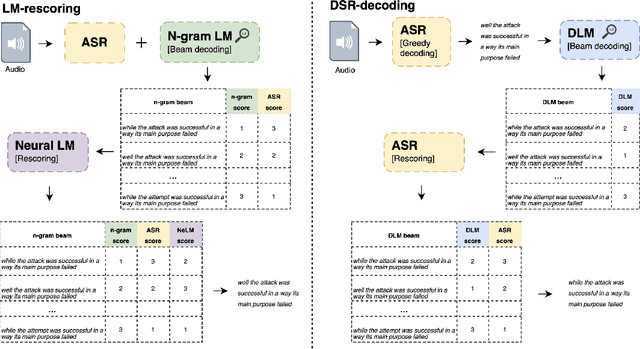
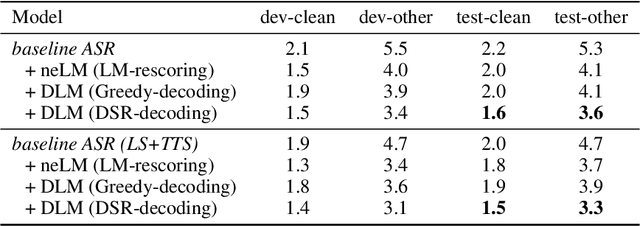

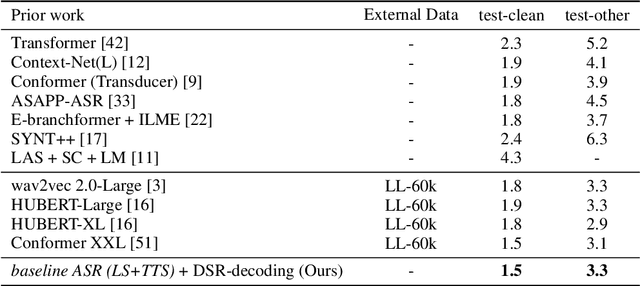
Abstract:Language models (LMs) have long been used to improve results of automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, but they are unaware of the errors that ASR systems make. Error correction models are designed to fix ASR errors, however, they showed little improvement over traditional LMs mainly due to the lack of supervised training data. In this paper, we present Denoising LM (DLM), which is a $\textit{scaled}$ error correction model trained with vast amounts of synthetic data, significantly exceeding prior attempts meanwhile achieving new state-of-the-art ASR performance. We use text-to-speech (TTS) systems to synthesize audio, which is fed into an ASR system to produce noisy hypotheses, which are then paired with the original texts to train the DLM. DLM has several $\textit{key ingredients}$: (i) up-scaled model and data; (ii) usage of multi-speaker TTS systems; (iii) combination of multiple noise augmentation strategies; and (iv) new decoding techniques. With a Transformer-CTC ASR, DLM achieves 1.5% word error rate (WER) on $\textit{test-clean}$ and 3.3% WER on $\textit{test-other}$ on Librispeech, which to our knowledge are the best reported numbers in the setting where no external audio data are used and even match self-supervised methods which use external audio data. Furthermore, a single DLM is applicable to different ASRs, and greatly surpassing the performance of conventional LM based beam-search rescoring. These results indicate that properly investigated error correction models have the potential to replace conventional LMs, holding the key to a new level of accuracy in ASR systems.
Decoding natural image stimuli from fMRI data with a surface-based convolutional network
Dec 05, 2022Abstract:Due to the low signal-to-noise ratio and limited resolution of functional MRI data, and the high complexity of natural images, reconstructing a visual stimulus from human brain fMRI measurements is a challenging task. In this work, we propose a novel approach for this task, which we call Cortex2Image, to decode visual stimuli with high semantic fidelity and rich fine-grained detail. In particular, we train a surface-based convolutional network model that maps from brain response to semantic image features first (Cortex2Semantic). We then combine this model with a high-quality image generator (Instance-Conditioned GAN) to train another mapping from brain response to fine-grained image features using a variational approach (Cortex2Detail). Image reconstructions obtained by our proposed method achieve state-of-the-art semantic fidelity, while yielding good fine-grained similarity with the ground-truth stimulus. Our code is available at: https://github.com/zijin-gu/meshconv-decoding.git.
Personalized visual encoding model construction with small data
Feb 04, 2022
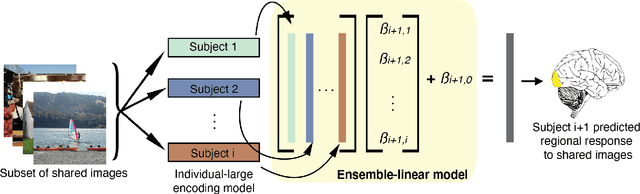
Abstract:Encoding models that predict brain response patterns to stimuli are one way to capture this relationship between variability in bottom-up neural systems and individual's behavior or pathological state. However, they generally need a large amount of training data to achieve optimal accuracy. Here, we propose and test an alternative personalized ensemble encoding model approach to utilize existing encoding models, to create encoding models for novel individuals with relatively little stimuli-response data. We show that these personalized ensemble encoding models trained with small amounts of data for a specific individual, i.e. ~400 image-response pairs, achieve accuracy not different from models trained on ~24,000 image-response pairs for the same individual. Importantly, the personalized ensemble encoding models preserve patterns of inter-individual variability in the image-response relationship. Additionally, we use our personalized ensemble encoding model within the recently developed NeuroGen framework to generate optimal stimuli designed to maximize specific regions' activations for a specific individual. We show that the inter-individual differences in face area responses to images of dog vs human faces observed previously is replicated using NeuroGen with the ensemble encoding model. Finally, and most importantly, we show the proposed approach is robust against domain shift by validating on a prospectively collected set of image-response data in novel individuals with a different scanner and experimental setup. Our approach shows the potential to use previously collected, deeply sampled data to efficiently create accurate, personalized encoding models and, subsequently, personalized optimal synthetic images for new individuals scanned under different experimental conditions.
NeuroGen: activation optimized image synthesis for discovery neuroscience
May 15, 2021



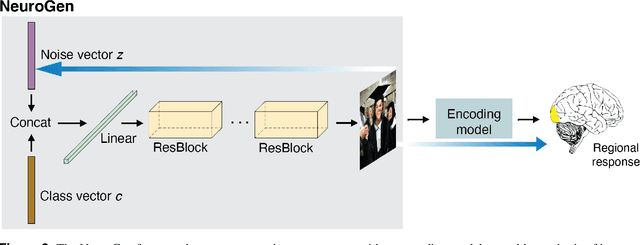
Abstract:Functional MRI (fMRI) is a powerful technique that has allowed us to characterize visual cortex responses to stimuli, yet such experiments are by nature constructed based on a priori hypotheses, limited to the set of images presented to the individual while they are in the scanner, are subject to noise in the observed brain responses, and may vary widely across individuals. In this work, we propose a novel computational strategy, which we call NeuroGen, to overcome these limitations and develop a powerful tool for human vision neuroscience discovery. NeuroGen combines an fMRI-trained neural encoding model of human vision with a deep generative network to synthesize images predicted to achieve a target pattern of macro-scale brain activation. We demonstrate that the reduction of noise that the encoding model provides, coupled with the generative network's ability to produce images of high fidelity, results in a robust discovery architecture for visual neuroscience. By using only a small number of synthetic images created by NeuroGen, we demonstrate that we can detect and amplify differences in regional and individual human brain response patterns to visual stimuli. We then verify that these discoveries are reflected in the several thousand observed image responses measured with fMRI. We further demonstrate that NeuroGen can create synthetic images predicted to achieve regional response patterns not achievable by the best-matching natural images. The NeuroGen framework extends the utility of brain encoding models and opens up a new avenue for exploring, and possibly precisely controlling, the human visual system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge