Zijie Wang
AdapTools: Adaptive Tool-based Indirect Prompt Injection Attacks on Agentic LLMs
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:The integration of external data services (e.g., Model Context Protocol, MCP) has made large language model-based agents increasingly powerful for complex task execution. However, this advancement introduces critical security vulnerabilities, particularly indirect prompt injection (IPI) attacks. Existing attack methods are limited by their reliance on static patterns and evaluation on simple language models, failing to address the fast-evolving nature of modern AI agents. We introduce AdapTools, a novel adaptive IPI attack framework that selects stealthier attack tools and generates adaptive attack prompts to create a rigorous security evaluation environment. Our approach comprises two key components: (1) Adaptive Attack Strategy Construction, which develops transferable adversarial strategies for prompt optimization, and (2) Attack Enhancement, which identifies stealthy tools capable of circumventing task-relevance defenses. Comprehensive experimental evaluation shows that AdapTools achieves a 2.13 times improvement in attack success rate while degrading system utility by a factor of 1.78. Notably, the framework maintains its effectiveness even against state-of-the-art defense mechanisms. Our method advances the understanding of IPI attacks and provides a useful reference for future research.
MIRNet: Integrating Constrained Graph-Based Reasoning with Pre-training for Diagnostic Medical Imaging
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Automated interpretation of medical images demands robust modeling of complex visual-semantic relationships while addressing annotation scarcity, label imbalance, and clinical plausibility constraints. We introduce MIRNet (Medical Image Reasoner Network), a novel framework that integrates self-supervised pre-training with constrained graph-based reasoning. Tongue image diagnosis is a particularly challenging domain that requires fine-grained visual and semantic understanding. Our approach leverages self-supervised masked autoencoder (MAE) to learn transferable visual representations from unlabeled data; employs graph attention networks (GAT) to model label correlations through expert-defined structured graphs; enforces clinical priors via constraint-aware optimization using KL divergence and regularization losses; and mitigates imbalance using asymmetric loss (ASL) and boosting ensembles. To address annotation scarcity, we also introduce TongueAtlas-4K, a comprehensive expert-curated benchmark comprising 4,000 images annotated with 22 diagnostic labels--representing the largest public dataset in tongue analysis. Validation shows our method achieves state-of-the-art performance. While optimized for tongue diagnosis, the framework readily generalizes to broader diagnostic medical imaging tasks.
LaneDiffusion: Improving Centerline Graph Learning via Prior Injected BEV Feature Generation
Nov 09, 2025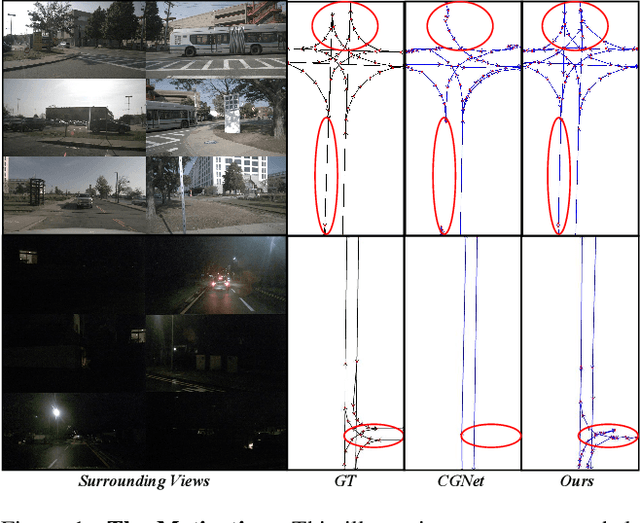
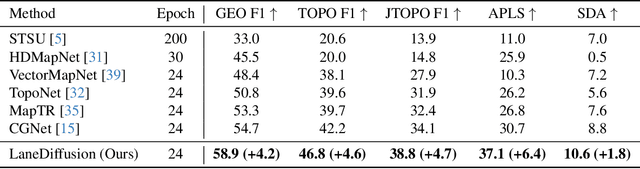
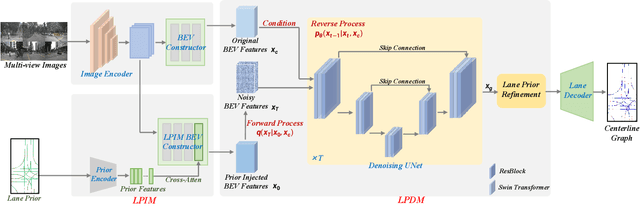
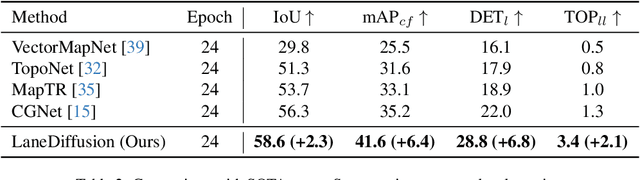
Abstract:Centerline graphs, crucial for path planning in autonomous driving, are traditionally learned using deterministic methods. However, these methods often lack spatial reasoning and struggle with occluded or invisible centerlines. Generative approaches, despite their potential, remain underexplored in this domain. We introduce LaneDiffusion, a novel generative paradigm for centerline graph learning. LaneDiffusion innovatively employs diffusion models to generate lane centerline priors at the Bird's Eye View (BEV) feature level, instead of directly predicting vectorized centerlines. Our method integrates a Lane Prior Injection Module (LPIM) and a Lane Prior Diffusion Module (LPDM) to effectively construct diffusion targets and manage the diffusion process. Furthermore, vectorized centerlines and topologies are then decoded from these prior-injected BEV features. Extensive evaluations on the nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets demonstrate that LaneDiffusion significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving improvements of 4.2%, 4.6%, 4.7%, 6.4% and 1.8% on fine-grained point-level metrics (GEO F1, TOPO F1, JTOPO F1, APLS and SDA) and 2.3%, 6.4%, 6.8% and 2.1% on segment-level metrics (IoU, mAP_cf, DET_l and TOP_ll). These results establish state-of-the-art performance in centerline graph learning, offering new insights into generative models for this task.
Identifying and Answering Questions with False Assumptions: An Interpretable Approach
Aug 21, 2025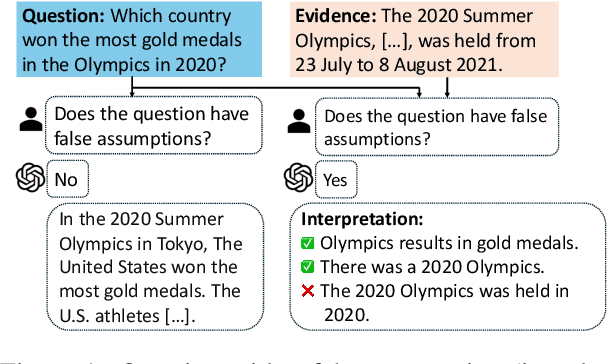
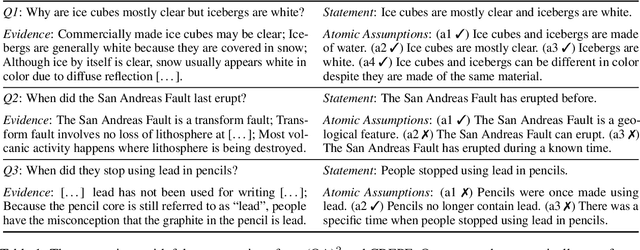
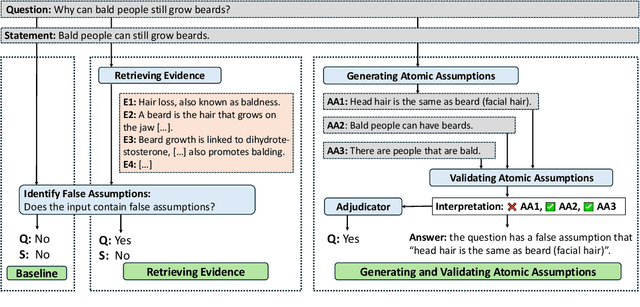
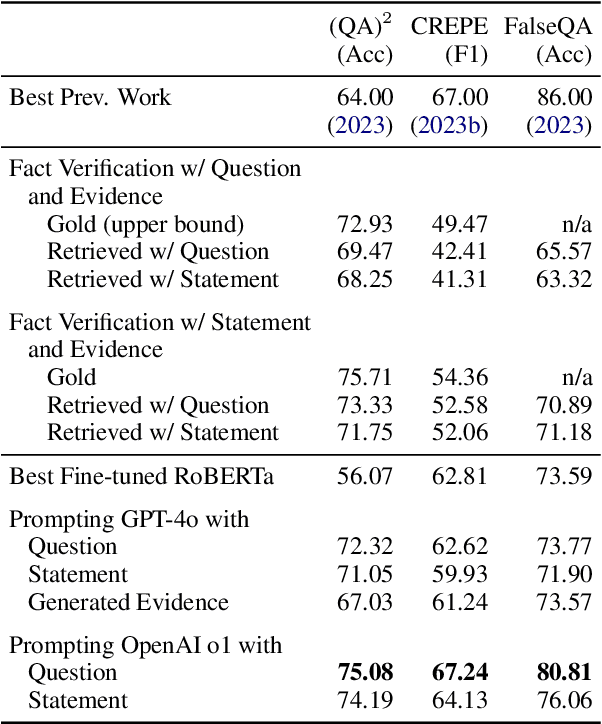
Abstract:People often ask questions with false assumptions, a type of question that does not have regular answers. Answering such questions require first identifying the false assumptions. Large Language Models (LLMs) often generate misleading answers because of hallucinations. In this paper, we focus on identifying and answering questions with false assumptions in several domains. We first investigate to reduce the problem to fact verification. Then, we present an approach leveraging external evidence to mitigate hallucinations. Experiments with five LLMs demonstrate that (1) incorporating retrieved evidence is beneficial and (2) generating and validating atomic assumptions yields more improvements and provides an interpretable answer by specifying the false assumptions.
Construction of an Organ Shape Atlas Using a Hierarchical Mesh Variational Autoencoder
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:An organ shape atlas, which represents the shape and position of the organs and skeleton of a living body using a small number of parameters, is expected to have a wide range of clinical applications, including intraoperative guidance and radiotherapy. Because the shape and position of soft organs vary greatly among patients, it is difficult for linear models to reconstruct shapes that have large local variations. Because it is difficult for conventional nonlinear models to control and interpret the organ shapes obtained, deep learning has been attracting attention in three-dimensional shape representation. In this study, we propose an organ shape atlas based on a mesh variational autoencoder (MeshVAE) with hierarchical latent variables. To represent the complex shapes of biological organs and nonlinear shape differences between individuals, the proposed method maintains the performance of organ shape reconstruction by hierarchizing latent variables and enables shape representation using lower-dimensional latent variables. Additionally, templates that define vertex correspondence between different resolutions enable hierarchical representation in mesh data and control the global and local features of the organ shape. We trained the model using liver and stomach organ meshes obtained from 124 cases and confirmed that the model reconstructed the position and shape with an average distance between vertices of 1.5 mm and mean distance of 0.7 mm for the liver shape, and an average distance between vertices of 1.4 mm and mean distance of 0.8 mm for the stomach shape on test data from 19 of cases. The proposed method continuously represented interpolated shapes, and by changing latent variables at different hierarchical levels, the proposed method hierarchically separated shape features compared with PCA.
Fundamental MMSE-Rate Performance Limits of Integrated Sensing and Communication Systems
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) demonstrates promise for 6G networks; yet its performance limits, which require addressing functional Pareto stochastic optimizations, remain underexplored. Existing works either overlook the randomness of ISAC signals or approximate ISAC limits from sensing and communication (SAC) optimum-achieving strategies, leading to loose bounds. In this paper, ISAC limits are investigated by considering a random ISAC signal designated to simultaneously estimate the sensing channel and convey information over the communication channel, adopting the modified minimum-mean-square-error (MMSE), a metric defined in accordance with the randomness of ISAC signals, and the Shannon rate as respective SAC metrics. First, conditions for optimal channel input and output distributions on the MMSE-Rate limit are derived employing variational approaches, leading to high-dimensional convolutional equations. Second, leveraging variational conditions, a Blahut-Arimoto-type algorithm is proposed to numerically determine optimal distributions and SAC performance, with its convergence to the limit proven. Third, closed-form SAC-optimal waveforms are derived, characterized by power allocation according to channel statistics/realization and waveform selection; existing methods to establish looser ISAC bounds are rectified. Finally, a compound signaling strategy is introduced for coincided SAC channels, which employs sequential SAC-optimal waveforms for channel estimation and data transmission, showcasing significant rate improvements over non-coherent "capacity". This study systematically investigates ISAC performance limits from joint estimation- and information-theoretic perspectives, highlighting key SAC tradeoffs and potential ISAC design benefits. The methodology readily extends to various metrics, such as estimation rate and the Cramer-Rao Bound.
Interpreting Indirect Answers to Yes-No Questions in Multiple Languages
Oct 20, 2023
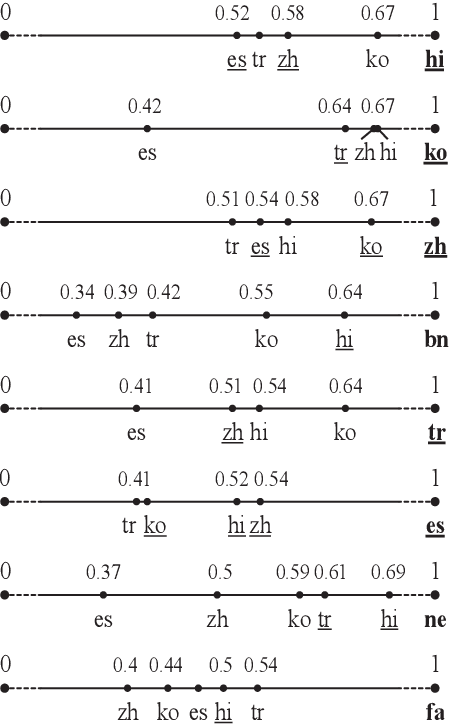
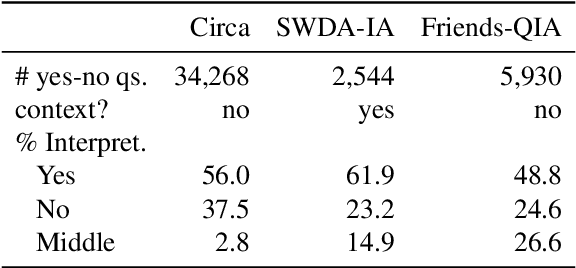

Abstract:Yes-no questions expect a yes or no for an answer, but people often skip polar keywords. Instead, they answer with long explanations that must be interpreted. In this paper, we focus on this challenging problem and release new benchmarks in eight languages. We present a distant supervision approach to collect training data. We also demonstrate that direct answers (i.e., with polar keywords) are useful to train models to interpret indirect answers (i.e., without polar keywords). Experimental results demonstrate that monolingual fine-tuning is beneficial if training data can be obtained via distant supervision for the language of interest (5 languages). Additionally, we show that cross-lingual fine-tuning is always beneficial (8 languages).
ByteCover3: Accurate Cover Song Identification on Short Queries
Mar 21, 2023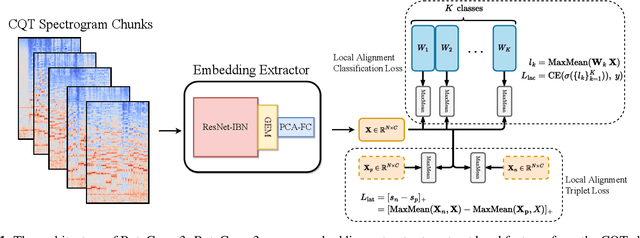
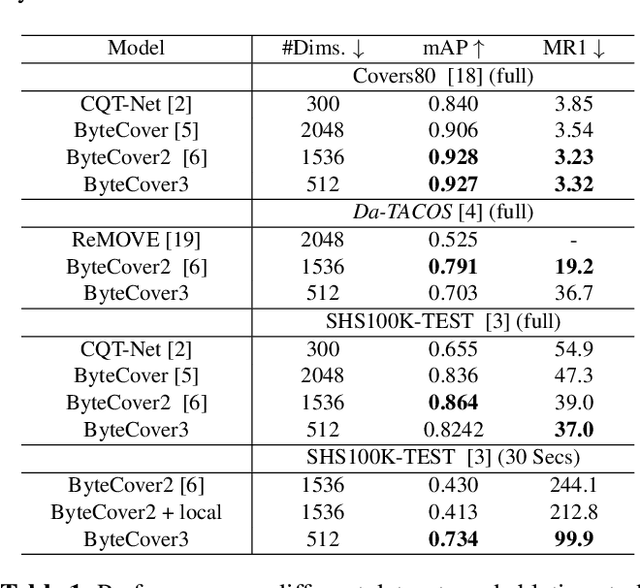
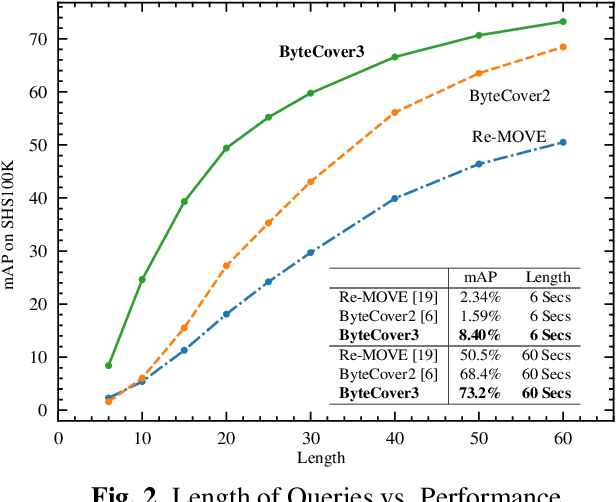
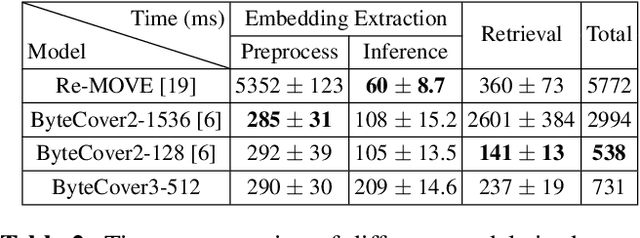
Abstract:Deep learning based methods have become a paradigm for cover song identification (CSI) in recent years, where the ByteCover systems have achieved state-of-the-art results on all the mainstream datasets of CSI. However, with the burgeon of short videos, many real-world applications require matching short music excerpts to full-length music tracks in the database, which is still under-explored and waiting for an industrial-level solution. In this paper, we upgrade the previous ByteCover systems to ByteCover3 that utilizes local features to further improve the identification performance of short music queries. ByteCover3 is designed with a local alignment loss (LAL) module and a two-stage feature retrieval pipeline, allowing the system to perform CSI in a more precise and efficient way. We evaluated ByteCover3 on multiple datasets with different benchmark settings, where ByteCover3 beat all the compared methods including its previous versions.
Look Before You Leap: Improving Text-based Person Retrieval by Learning A Consistent Cross-modal Common Manifold
Sep 13, 2022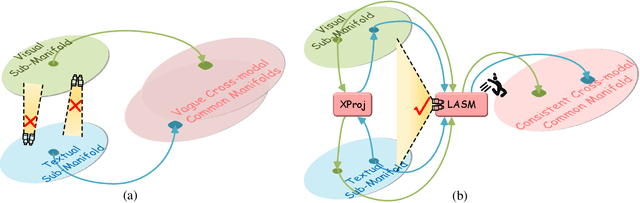
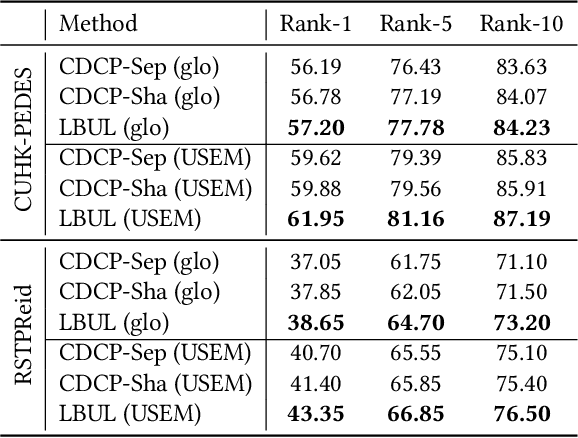
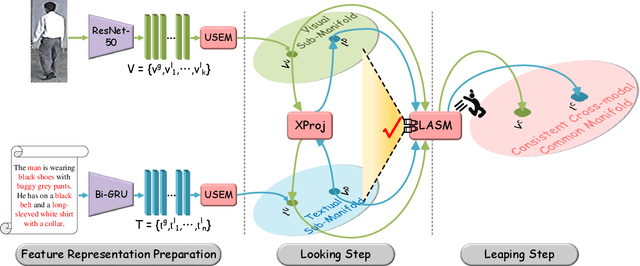
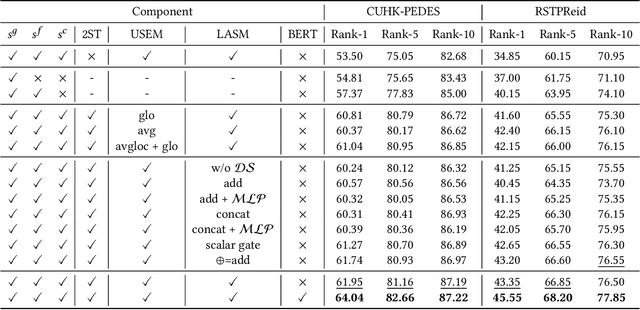
Abstract:The core problem of text-based person retrieval is how to bridge the heterogeneous gap between multi-modal data. Many previous approaches contrive to learning a latent common manifold mapping paradigm following a \textbf{cross-modal distribution consensus prediction (CDCP)} manner. When mapping features from distribution of one certain modality into the common manifold, feature distribution of the opposite modality is completely invisible. That is to say, how to achieve a cross-modal distribution consensus so as to embed and align the multi-modal features in a constructed cross-modal common manifold all depends on the experience of the model itself, instead of the actual situation. With such methods, it is inevitable that the multi-modal data can not be well aligned in the common manifold, which finally leads to a sub-optimal retrieval performance. To overcome this \textbf{CDCP dilemma}, we propose a novel algorithm termed LBUL to learn a Consistent Cross-modal Common Manifold (C$^{3}$M) for text-based person retrieval. The core idea of our method, just as a Chinese saying goes, is to `\textit{san si er hou xing}', namely, to \textbf{Look Before yoU Leap (LBUL)}. The common manifold mapping mechanism of LBUL contains a looking step and a leaping step. Compared to CDCP-based methods, LBUL considers distribution characteristics of both the visual and textual modalities before embedding data from one certain modality into C$^{3}$M to achieve a more solid cross-modal distribution consensus, and hence achieve a superior retrieval accuracy. We evaluate our proposed method on two text-based person retrieval datasets CUHK-PEDES and RSTPReid. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed LBUL outperforms previous methods and achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
CAIBC: Capturing All-round Information Beyond Color for Text-based Person Retrieval
Sep 13, 2022
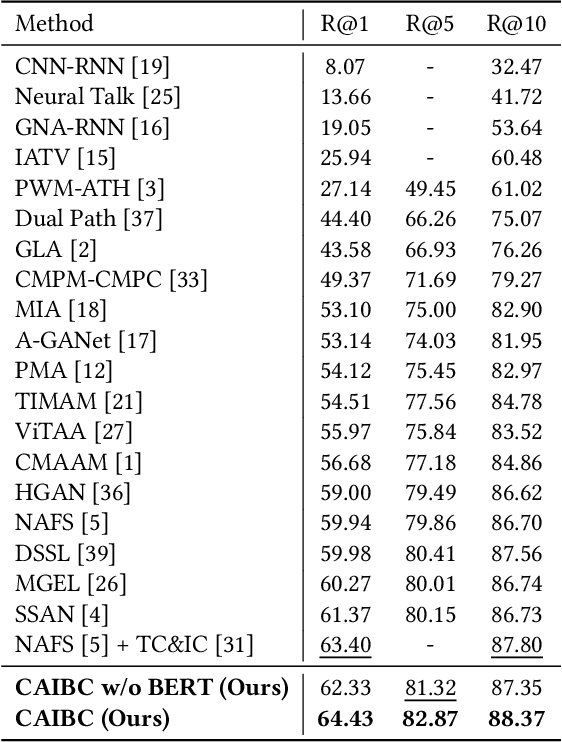
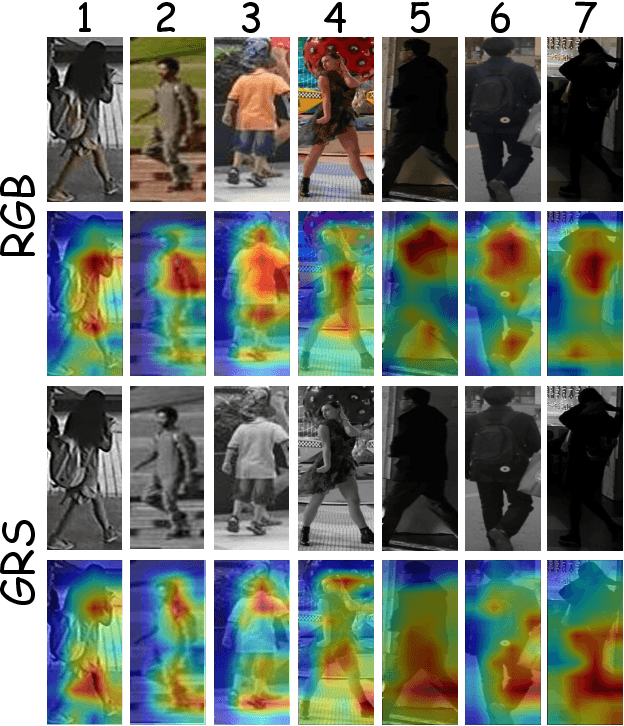
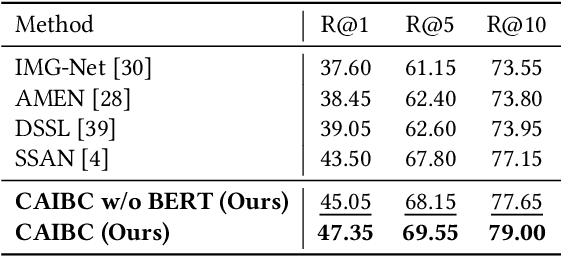
Abstract:Given a natural language description, text-based person retrieval aims to identify images of a target person from a large-scale person image database. Existing methods generally face a \textbf{color over-reliance problem}, which means that the models rely heavily on color information when matching cross-modal data. Indeed, color information is an important decision-making accordance for retrieval, but the over-reliance on color would distract the model from other key clues (e.g. texture information, structural information, etc.), and thereby lead to a sub-optimal retrieval performance. To solve this problem, in this paper, we propose to \textbf{C}apture \textbf{A}ll-round \textbf{I}nformation \textbf{B}eyond \textbf{C}olor (\textbf{CAIBC}) via a jointly optimized multi-branch architecture for text-based person retrieval. CAIBC contains three branches including an RGB branch, a grayscale (GRS) branch and a color (CLR) branch. Besides, with the aim of making full use of all-round information in a balanced and effective way, a mutual learning mechanism is employed to enable the three branches which attend to varied aspects of information to communicate with and learn from each other. Extensive experimental analysis is carried out to evaluate our proposed CAIBC method on the CUHK-PEDES and RSTPReid datasets in both \textbf{supervised} and \textbf{weakly supervised} text-based person retrieval settings, which demonstrates that CAIBC significantly outperforms existing methods and achieves the state-of-the-art performance on all the three tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge