Zhonghua Zheng
Reinforcement Learning (RL) Meets Urban Climate Modeling: Investigating the Efficacy and Impacts of RL-Based HVAC Control
May 11, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL)-based heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) control has emerged as a promising technology for reducing building energy consumption while maintaining indoor thermal comfort. However, the efficacy of such strategies is influenced by the background climate and their implementation may potentially alter both the indoor climate and local urban climate. This study proposes an integrated framework combining RL with an urban climate model that incorporates a building energy model, aiming to evaluate the efficacy of RL-based HVAC control across different background climates, impacts of RL strategies on indoor climate and local urban climate, and the transferability of RL strategies across cities. Our findings reveal that the reward (defined as a weighted combination of energy consumption and thermal comfort) and the impacts of RL strategies on indoor climate and local urban climate exhibit marked variability across cities with different background climates. The sensitivity of reward weights and the transferability of RL strategies are also strongly influenced by the background climate. Cities in hot climates tend to achieve higher rewards across most reward weight configurations that balance energy consumption and thermal comfort, and those cities with more varying atmospheric temperatures demonstrate greater RL strategy transferability. These findings underscore the importance of thoroughly evaluating RL-based HVAC control strategies in diverse climatic contexts. This study also provides a new insight that city-to-city learning will potentially aid the deployment of RL-based HVAC control.
Using large language models to produce literature reviews: Usages and systematic biases of microphysics parametrizations in 2699 publications
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Large language models afford opportunities for using computers for intensive tasks, realizing research opportunities that have not been considered before. One such opportunity could be a systematic interrogation of the scientific literature. Here, we show how a large language model can be used to construct a literature review of 2699 publications associated with microphysics parametrizations in the Weather and Research Forecasting (WRF) model, with the goal of learning how they were used and their systematic biases, when simulating precipitation. The database was constructed of publications identified from Web of Science and Scopus searches. The large language model GPT-4 Turbo was used to extract information about model configurations and performance from the text of 2699 publications. Our results reveal the landscape of how nine of the most popular microphysics parameterizations have been used around the world: Lin, Ferrier, WRF Single-Moment, Goddard Cumulus Ensemble, Morrison, Thompson, and WRF Double-Moment. More studies used one-moment parameterizations before 2020 and two-moment parameterizations after 2020. Seven out of nine parameterizations tended to overestimate precipitation. However, systematic biases of parameterizations differed in various regions. Except simulations using the Lin, Ferrier, and Goddard parameterizations that tended to underestimate precipitation over almost all locations, the remaining six parameterizations tended to overestimate, particularly over China, southeast Asia, western United States, and central Africa. This method could be used by other researchers to help understand how the increasingly massive body of scientific literature can be harnessed through the power of artificial intelligence to solve their research problems.
Integrating remote sensing data assimilation, deep learning and large language model for interactive wheat breeding yield prediction
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Yield is one of the core goals of crop breeding. By predicting the potential yield of different breeding materials, breeders can screen these materials at various growth stages to select the best performing. Based on unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing technology, high-throughput crop phenotyping data in breeding areas is collected to provide data support for the breeding decisions of breeders. However, the accuracy of current yield predictions still requires improvement, and the usability and user-friendliness of yield forecasting tools remain suboptimal. To address these challenges, this study introduces a hybrid method and tool for crop yield prediction, designed to allow breeders to interactively and accurately predict wheat yield by chatting with a large language model (LLM). First, the newly designed data assimilation algorithm is used to assimilate the leaf area index into the WOFOST model. Then, selected outputs from the assimilation process, along with remote sensing inversion results, are used to drive the time-series temporal fusion transformer model for wheat yield prediction. Finally, based on this hybrid method and leveraging an LLM with retrieval augmented generation technology, we developed an interactive yield prediction Web tool that is user-friendly and supports sustainable data updates. This tool integrates multi-source data to assist breeding decision-making. This study aims to accelerate the identification of high-yield materials in the breeding process, enhance breeding efficiency, and enable more scientific and smart breeding decisions.
Towards Human-centered Proactive Conversational Agents
Apr 19, 2024


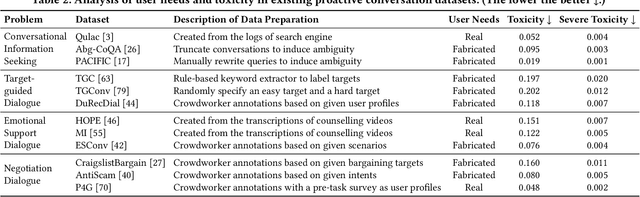
Abstract:Recent research on proactive conversational agents (PCAs) mainly focuses on improving the system's capabilities in anticipating and planning action sequences to accomplish tasks and achieve goals before users articulate their requests. This perspectives paper highlights the importance of moving towards building human-centered PCAs that emphasize human needs and expectations, and that considers ethical and social implications of these agents, rather than solely focusing on technological capabilities. The distinction between a proactive and a reactive system lies in the proactive system's initiative-taking nature. Without thoughtful design, proactive systems risk being perceived as intrusive by human users. We address the issue by establishing a new taxonomy concerning three key dimensions of human-centered PCAs, namely Intelligence, Adaptivity, and Civility. We discuss potential research opportunities and challenges based on this new taxonomy upon the five stages of PCA system construction. This perspectives paper lays a foundation for the emerging area of conversational information retrieval research and paves the way towards advancing human-centered proactive conversational systems.
Building Emotional Support Chatbots in the Era of LLMs
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:The integration of emotional support into various conversational scenarios presents profound societal benefits, such as social interactions, mental health counseling, and customer service. However, there are unsolved challenges that hinder real-world applications in this field, including limited data availability and the absence of well-accepted model training paradigms. This work endeavors to navigate these challenges by harnessing the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). We introduce an innovative methodology that synthesizes human insights with the computational prowess of LLMs to curate an extensive emotional support dialogue dataset. Our approach is initiated with a meticulously designed set of dialogues spanning diverse scenarios as generative seeds. By utilizing the in-context learning potential of ChatGPT, we recursively generate an ExTensible Emotional Support dialogue dataset, named ExTES. Following this, we deploy advanced tuning techniques on the LLaMA model, examining the impact of diverse training strategies, ultimately yielding an LLM meticulously optimized for emotional support interactions. An exhaustive assessment of the resultant model showcases its proficiency in offering emotional support, marking a pivotal step in the realm of emotional support bots and paving the way for subsequent research and implementations.
HyperTime: Hyperparameter Optimization for Combating Temporal Distribution Shifts
May 28, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we propose a hyperparameter optimization method named \emph{HyperTime} to find hyperparameters robust to potential temporal distribution shifts in the unseen test data. Our work is motivated by an important observation that it is, in many cases, possible to achieve temporally robust predictive performance via hyperparameter optimization. Based on this observation, we leverage the `worst-case-oriented' philosophy from the robust optimization literature to help find such robust hyperparameter configurations. HyperTime imposes a lexicographic priority order on average validation loss and worst-case validation loss over chronological validation sets. We perform a theoretical analysis on the upper bound of the expected test loss, which reveals the unique advantages of our approach. We also demonstrate the strong empirical performance of the proposed method on multiple machine learning tasks with temporal distribution shifts.
Unsupervised Regionalization of Particle-resolved Aerosol Mixing State Indices on the Global Scale
Dec 06, 2020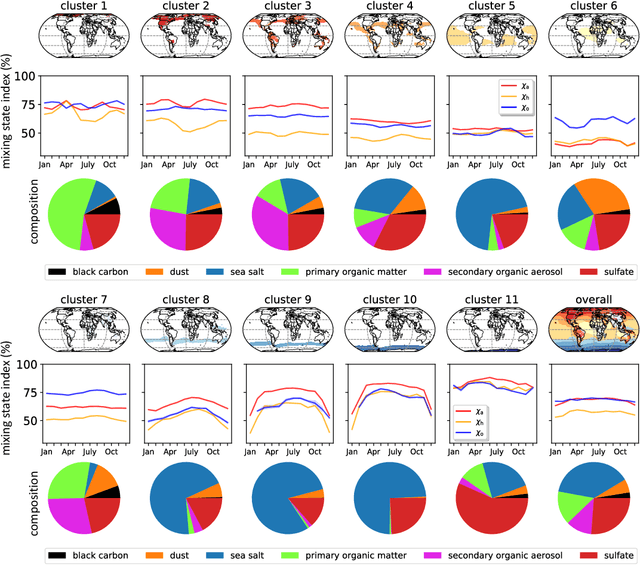
Abstract:The aerosol mixing state significantly affects the climate and health impacts of atmospheric aerosol particles. Simplified aerosol mixing state assumptions, common in Earth System models, can introduce errors in the prediction of these aerosol impacts. The aerosol mixing state index, a metric to quantify aerosol mixing state, is a convenient measure for quantifying these errors. Global estimates of aerosol mixing state indices have recently become available via supervised learning models, but require regionalization to ease spatiotemporal analysis. Here we developed a simple but effective unsupervised learning approach to regionalize predictions of global aerosol mixing state indices. We used the monthly average of aerosol mixing state indices global distribution as the input data. Grid cells were then clustered into regions by the k-means algorithm without explicit spatial information as input. This approach resulted in eleven regions over the globe with specific spatial aggregation patterns. Each region exhibited a unique distribution of mixing state indices and aerosol compositions, showing the effectiveness of the unsupervised regionalization approach. This study defines "aerosol mixing state zones" that could be useful for atmospheric science research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge