Zhenbo Luo
Video-OPD: Efficient Post-Training of Multimodal Large Language Models for Temporal Video Grounding via On-Policy Distillation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning has emerged as a principled post-training paradigm for Temporal Video Grounding (TVG) due to its on-policy optimization, yet existing GRPO-based methods remain fundamentally constrained by sparse reward signals and substantial computational overhead. We propose Video-OPD, an efficient post-training framework for TVG inspired by recent advances in on-policy distillation. Video-OPD optimizes trajectories sampled directly from the current policy, thereby preserving alignment between training and inference distributions, while a frontier teacher supplies dense, token-level supervision via a reverse KL divergence objective. This formulation preserves the on-policy property critical for mitigating distributional shift, while converting sparse, episode-level feedback into fine-grained, step-wise learning signals. Building on Video-OPD, we introduce Teacher-Validated Disagreement Focusing (TVDF), a lightweight training curriculum that iteratively prioritizes trajectories that are both teacher-reliable and maximally informative for the student, thereby improving training efficiency. Empirical results demonstrate that Video-OPD consistently outperforms GRPO while achieving substantially faster convergence and lower computational cost, establishing on-policy distillation as an effective alternative to conventional reinforcement learning for TVG.
Restoring Exploration after Post-Training: Latent Exploration Decoding for Large Reasoning Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have recently achieved strong mathematical and code reasoning performance through Reinforcement Learning (RL) post-training. However, we show that modern reasoning post-training induces an unintended exploration collapse: temperature-based sampling no longer increases pass@$n$ accuracy. Empirically, the final-layer posterior of post-trained LRMs exhibit sharply reduced entropy, while the entropy of intermediate layers remains relatively high. Motivated by this entropy asymmetry, we propose Latent Exploration Decoding (LED), a depth-conditioned decoding strategy. LED aggregates intermediate posteriors via cumulative sum and selects depth configurations with maximal entropy as exploration candidates. Without additional training or parameters, LED consistently improves pass@1 and pass@16 accuracy by 0.61 and 1.03 percentage points across multiple reasoning benchmarks and models. Project page: https://GitHub.com/Xiaomi-Research/LED.
GAIA: A Data Flywheel System for Training GUI Test-Time Scaling Critic Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:While Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly advanced GUI agents' capabilities in parsing textual instructions, interpreting screen content, and executing tasks, a critical challenge persists: the irreversibility of agent operations, where a single erroneous action can trigger catastrophic deviations. To address this, we propose the GUI Action Critic's Data Flywheel System (GAIA), a training framework that enables the models to have iterative critic capabilities, which are used to improve the Test-Time Scaling (TTS) of basic GUI agents' performance. Specifically, we train an Intuitive Critic Model (ICM) using positive and negative action examples from a base agent first. This critic evaluates the immediate correctness of the agent's intended actions, thereby selecting operations with higher success probability. Then, the initial critic guides agent actions to collect refined positive/negative samples, initiating the self-improving cycle. The augmented data then trains a second-round critic with enhanced discernment capability. We conduct experiments on various datasets and demonstrate that the proposed ICM can improve the test-time performance of various closed-source and open-source models, and the performance can be gradually improved as the data is recycled. The code and dataset will be publicly released.
Federated Balanced Learning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Federated learning is a paradigm of joint learning in which clients collaborate by sharing model parameters instead of data. However, in the non-iid setting, the global model experiences client drift, which can seriously affect the final performance of the model. Previous methods tend to correct the global model that has already deviated based on the loss function or gradient, overlooking the impact of the client samples. In this paper, we rethink the role of the client side and propose Federated Balanced Learning, i.e., FBL, to prevent this issue from the beginning through sample balance on the client side. Technically, FBL allows unbalanced data on the client side to achieve sample balance through knowledge filling and knowledge sampling using edge-side generation models, under the limitation of a fixed number of data samples on clients. Furthermore, we design a Knowledge Alignment Strategy to bridge the gap between synthetic and real data, and a Knowledge Drop Strategy to regularize our method. Meanwhile, we scale our method to real and complex scenarios, allowing different clients to adopt various methods, and extend our framework to further improve performance. Numerous experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. The code is released upon acceptance.
Federated Joint Learning for Domain and Class Generalization
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Efficient fine-tuning of visual-language models like CLIP has become crucial due to their large-scale parameter size and extensive pretraining requirements. Existing methods typically address either the issue of unseen classes or unseen domains in isolation, without considering a joint framework for both. In this paper, we propose \textbf{Fed}erated Joint Learning for \textbf{D}omain and \textbf{C}lass \textbf{G}eneralization, termed \textbf{FedDCG}, a novel approach that addresses both class and domain generalization in federated learning settings. Our method introduces a domain grouping strategy where class-generalized networks are trained within each group to prevent decision boundary confusion. During inference, we aggregate class-generalized results based on domain similarity, effectively integrating knowledge from both class and domain generalization. Specifically, a learnable network is employed to enhance class generalization capabilities, and a decoupling mechanism separates general and domain-specific knowledge, improving generalization to unseen domains. Extensive experiments across various datasets show that \textbf{FedDCG} outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of accuracy and robustness.
Think-Clip-Sample: Slow-Fast Frame Selection for Video Understanding
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Recent progress in multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) has significantly advanced video understanding. However, their performance on long-form videos remains limited by computational constraints and suboptimal frame selection. We present Think-Clip-Sample (TCS), a training-free framework that enhances long video understanding through two key components: (i) Multi-Query Reasoning, which generates multiple queries to capture complementary aspects of the question and video; and (ii) Clip-level Slow-Fast Sampling, which adaptively balances dense local details and sparse global context. Extensive experiments on MLVU, LongVideoBench, and VideoMME demonstrate that TCS consistently improves performance across different MLLMs, boosting up to 6.9% accuracy, and is capable of achieving comparable accuracy with 50% fewer inference time cost, highlighting both efficiency and efficacy of TCS on long video understanding.
Xiaomi MiMo-VL-Miloco Technical Report
Dec 22, 2025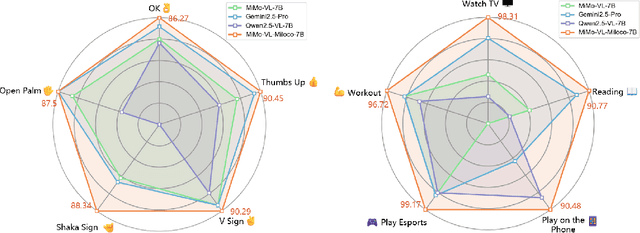
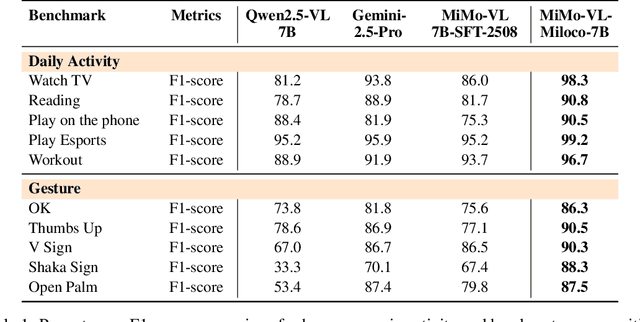
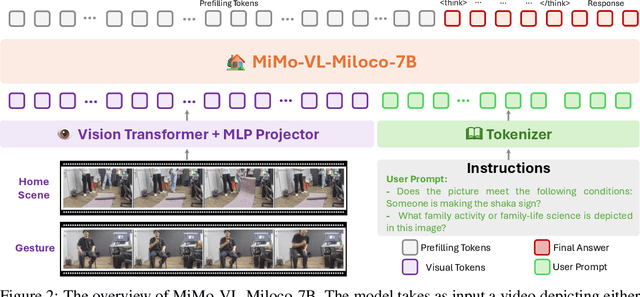
Abstract:We open-source MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B and its quantized variant MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B-GGUF, a pair of home-centric vision-language models that achieve strong performance on both home-scenario understanding and general multimodal reasoning. Built on the MiMo-VL-7B backbone, MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B is specialized for smart-home environments, attaining leading F1 scores on gesture recognition and common home-scenario understanding, while also delivering consistent gains across video benchmarks such as Video-MME, Video-MMMU, and Charades-STA, as well as language understanding benchmarks including MMMU-Pro and MMLU-Pro. In our experiments, MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B outperforms strong closed-source and open-source baselines on home-scenario understanding and several multimodal reasoning benchmarks. To balance specialization and generality, we design a two-stage training pipeline that combines supervised fine-tuning with reinforcement learning based on Group Relative Policy Optimization, leveraging efficient multi-domain data. We further incorporate chain-of-thought supervision and token-budget-aware reasoning, enabling the model to learn knowledge in a data-efficient manner while also performing reasoning efficiently. Our analysis shows that targeted home-scenario training not only enhances activity and gesture understanding, but also improves text-only reasoning with only modest trade-offs on document-centric tasks. Model checkpoints, quantized GGUF weights, and our home-scenario evaluation toolkit are publicly available at https://github.com/XiaoMi/xiaomi-mimo-vl-miloco to support research and deployment in real-world smart-home applications.
REVISOR: Beyond Textual Reflection, Towards Multimodal Introspective Reasoning in Long-Form Video Understanding
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Self-reflection mechanisms that rely on purely text-based rethinking processes perform well in most multimodal tasks. However, when directly applied to long-form video understanding scenarios, they exhibit clear limitations. The fundamental reasons for this lie in two points: (1)long-form video understanding involves richer and more dynamic visual input, meaning rethinking only the text information is insufficient and necessitates a further rethinking process specifically targeting visual information; (2) purely text-based reflection mechanisms lack cross-modal interaction capabilities, preventing them from fully integrating visual information during reflection. Motivated by these insights, we propose REVISOR (REflective VIsual Segment Oriented Reasoning), a novel framework for tool-augmented multimodal reflection. REVISOR enables MLLMs to collaboratively construct introspective reflection processes across textual and visual modalities, significantly enhancing their reasoning capability for long-form video understanding. To ensure that REVISOR can learn to accurately review video segments highly relevant to the question during reinforcement learning, we designed the Dual Attribution Decoupled Reward (DADR) mechanism. Integrated into the GRPO training strategy, this mechanism enforces causal alignment between the model's reasoning and the selected video evidence. Notably, the REVISOR framework significantly enhances long-form video understanding capability of MLLMs without requiring supplementary supervised fine-tuning or external models, achieving impressive results on four benchmarks including VideoMME, LongVideoBench, MLVU, and LVBench.
HyperClick: Advancing Reliable GUI Grounding via Uncertainty Calibration
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Autonomous Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents rely on accurate GUI grounding, which maps language instructions to on-screen coordinates, to execute user commands. However, current models, whether trained via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) or reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT), lack self-awareness of their capability boundaries, leading to overconfidence and unreliable predictions. We first systematically evaluate probabilistic and verbalized confidence in general and GUI-specific models, revealing a misalignment between confidence and actual accuracy, which is particularly critical in dynamic GUI automation tasks, where single errors can cause task failure. To address this, we propose HyperClick, a novel framework that enhances reliable GUI grounding through uncertainty calibration. HyperClick introduces a dual reward mechanism, combining a binary reward for correct actions with a truncated Gaussian-based spatial confidence modeling, calibrated using the Brier score. This approach jointly optimizes grounding accuracy and confidence reliability, fostering introspective self-criticism. Extensive experiments on seven challenge benchmarks show that HyperClick achieves state-of-the-art performance while providing well-calibrated confidence. By enabling explicit confidence calibration and introspective self-criticism, HyperClick reduces overconfidence and supports more reliable GUI automation.
BTL-UI: Blink-Think-Link Reasoning Model for GUI Agent
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:In the field of AI-driven human-GUI interaction automation, while rapid advances in multimodal large language models and reinforcement fine-tuning techniques have yielded remarkable progress, a fundamental challenge persists: their interaction logic significantly deviates from natural human-GUI communication patterns. To fill this gap, we propose "Blink-Think-Link" (BTL), a brain-inspired framework for human-GUI interaction that mimics the human cognitive process between users and graphical interfaces. The system decomposes interactions into three biologically plausible phases: (1) Blink - rapid detection and attention to relevant screen areas, analogous to saccadic eye movements; (2) Think - higher-level reasoning and decision-making, mirroring cognitive planning; and (3) Link - generation of executable commands for precise motor control, emulating human action selection mechanisms. Additionally, we introduce two key technical innovations for the BTL framework: (1) Blink Data Generation - an automated annotation pipeline specifically optimized for blink data, and (2) BTL Reward -- the first rule-based reward mechanism that enables reinforcement learning driven by both process and outcome. Building upon this framework, we develop a GUI agent model named BTL-UI, which demonstrates consistent state-of-the-art performance across both static GUI understanding and dynamic interaction tasks in comprehensive benchmarks. These results provide conclusive empirical validation of the framework's efficacy in developing advanced GUI Agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge