Zhaohui Hou
Navi-plus: Managing Ambiguous GUI Navigation Tasks with Follow-up
Mar 31, 2025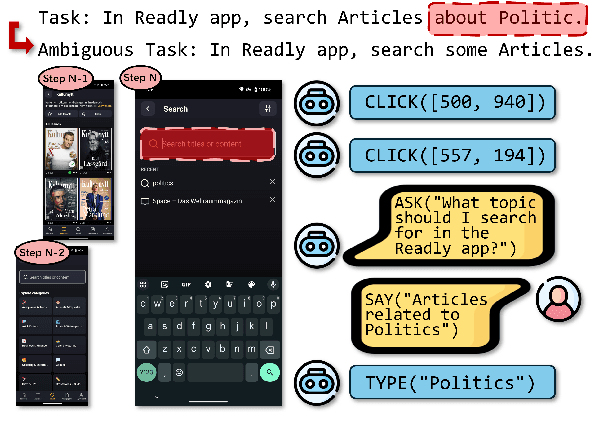
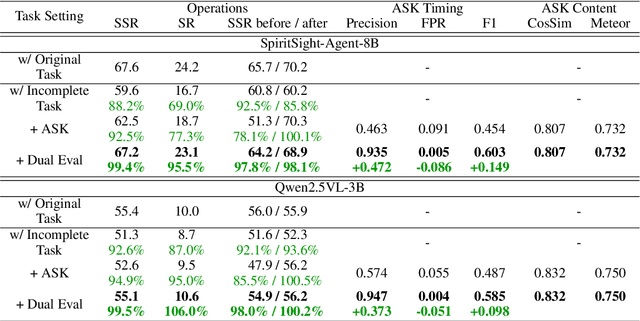
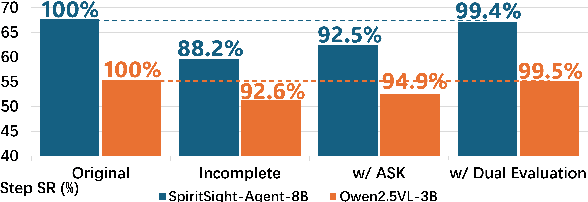
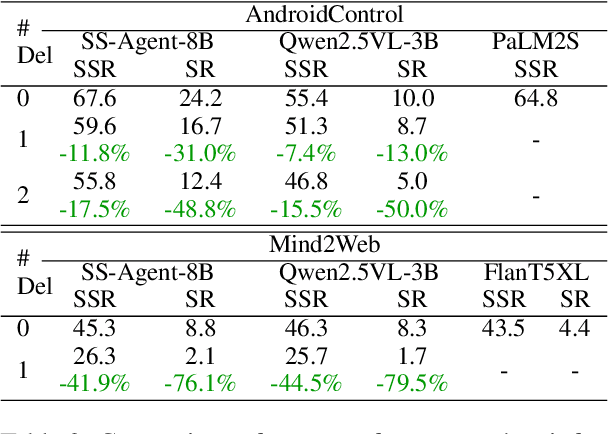
Abstract:Graphical user interfaces (GUI) automation agents are emerging as powerful tools, enabling humans to accomplish increasingly complex tasks on smart devices. However, users often inadvertently omit key information when conveying tasks, which hinders agent performance in the current agent paradigm that does not support immediate user intervention. To address this issue, we introduce a $\textbf{Self-Correction GUI Navigation}$ task that incorporates interactive information completion capabilities within GUI agents. We developed the $\textbf{Navi-plus}$ dataset with GUI follow-up question-answer pairs, alongside a $\textbf{Dual-Stream Trajectory Evaluation}$ method to benchmark this new capability. Our results show that agents equipped with the ability to ask GUI follow-up questions can fully recover their performance when faced with ambiguous user tasks.
SpiritSight Agent: Advanced GUI Agent with One Look
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents show amazing abilities in assisting human-computer interaction, automating human user's navigation on digital devices. An ideal GUI agent is expected to achieve high accuracy, low latency, and compatibility for different GUI platforms. Recent vision-based approaches have shown promise by leveraging advanced Vision Language Models (VLMs). While they generally meet the requirements of compatibility and low latency, these vision-based GUI agents tend to have low accuracy due to their limitations in element grounding. To address this issue, we propose $\textbf{SpiritSight}$, a vision-based, end-to-end GUI agent that excels in GUI navigation tasks across various GUI platforms. First, we create a multi-level, large-scale, high-quality GUI dataset called $\textbf{GUI-Lasagne}$ using scalable methods, empowering SpiritSight with robust GUI understanding and grounding capabilities. Second, we introduce the $\textbf{Universal Block Parsing (UBP)}$ method to resolve the ambiguity problem in dynamic high-resolution of visual inputs, further enhancing SpiritSight's ability to ground GUI objects. Through these efforts, SpiritSight agent outperforms other advanced methods on diverse GUI benchmarks, demonstrating its superior capability and compatibility in GUI navigation tasks. Models are available at $\href{https://huggingface.co/SenseLLM/SpiritSight-Agent-8B}{this\ URL}$.
UFO: Enhancing Diffusion-Based Video Generation with a Uniform Frame Organizer
Dec 12, 2024
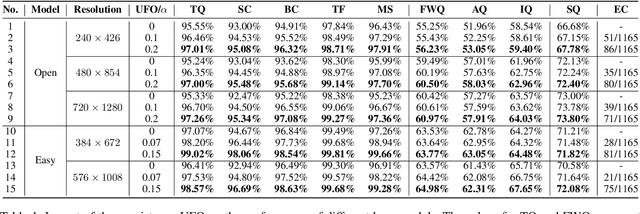
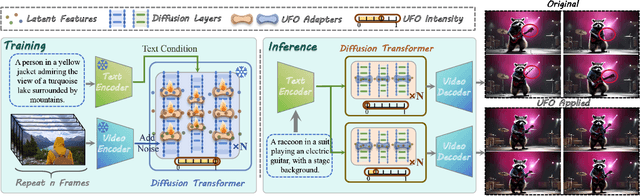
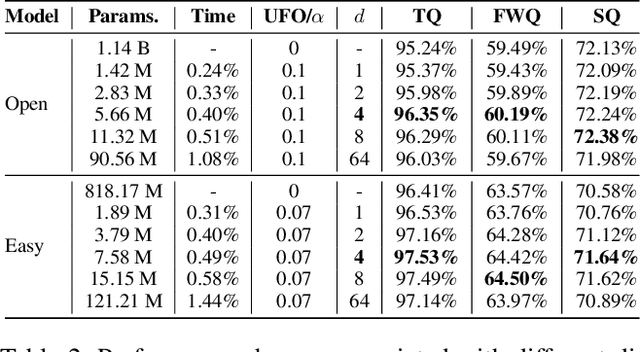
Abstract:Recently, diffusion-based video generation models have achieved significant success. However, existing models often suffer from issues like weak consistency and declining image quality over time. To overcome these challenges, inspired by aesthetic principles, we propose a non-invasive plug-in called Uniform Frame Organizer (UFO), which is compatible with any diffusion-based video generation model. The UFO comprises a series of adaptive adapters with adjustable intensities, which can significantly enhance the consistency between the foreground and background of videos and improve image quality without altering the original model parameters when integrated. The training for UFO is simple, efficient, requires minimal resources, and supports stylized training. Its modular design allows for the combination of multiple UFOs, enabling the customization of personalized video generation models. Furthermore, the UFO also supports direct transferability across different models of the same specification without the need for specific retraining. The experimental results indicate that UFO effectively enhances video generation quality and demonstrates its superiority in public video generation benchmarks. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/Delong-liu-bupt/UFO.
TeacherLM: Teaching to Fish Rather Than Giving the Fish, Language Modeling Likewise
Oct 31, 2023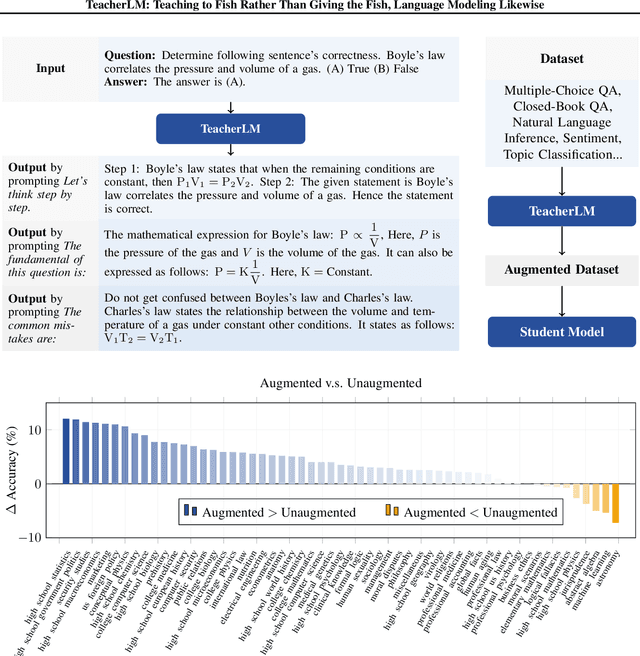
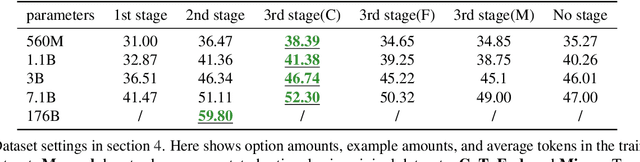
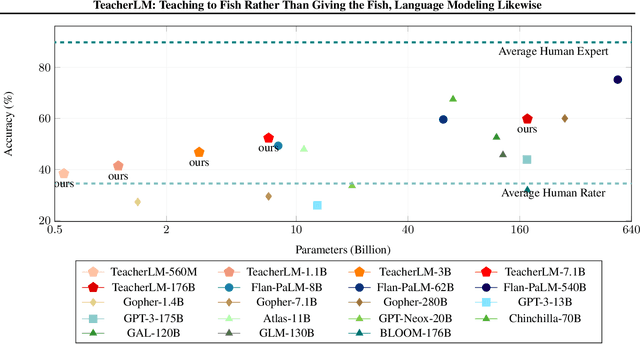
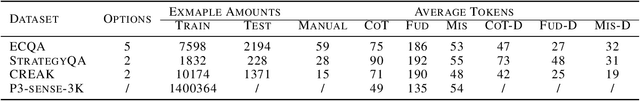
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit impressive reasoning and data augmentation capabilities in various NLP tasks. However, what about small models? In this work, we propose TeacherLM-7.1B, capable of annotating relevant fundamentals, chain of thought, and common mistakes for most NLP samples, which makes annotation more than just an answer, thus allowing other models to learn "why" instead of just "what". The TeacherLM-7.1B model achieved a zero-shot score of 52.3 on MMLU, surpassing most models with over 100B parameters. Even more remarkable is its data augmentation ability. Based on TeacherLM-7.1B, we augmented 58 NLP datasets and taught various student models with different parameters from OPT and BLOOM series in a multi-task setting. The experimental results indicate that the data augmentation provided by TeacherLM has brought significant benefits. We will release the TeacherLM series of models and augmented datasets as open-source.
VCSUM: A Versatile Chinese Meeting Summarization Dataset
May 15, 2023
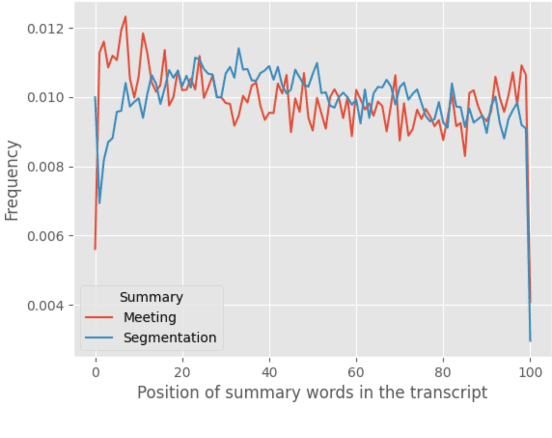
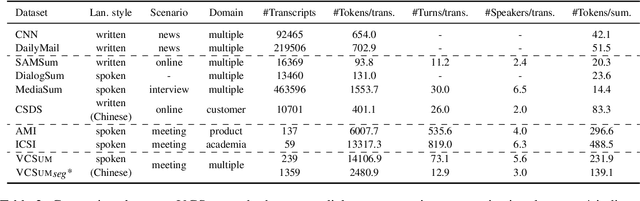
Abstract:Compared to news and chat summarization, the development of meeting summarization is hugely decelerated by the limited data. To this end, we introduce a versatile Chinese meeting summarization dataset, dubbed VCSum, consisting of 239 real-life meetings, with a total duration of over 230 hours. We claim our dataset is versatile because we provide the annotations of topic segmentation, headlines, segmentation summaries, overall meeting summaries, and salient sentences for each meeting transcript. As such, the dataset can adapt to various summarization tasks or methods, including segmentation-based summarization, multi-granularity summarization and retrieval-then-generate summarization. Our analysis confirms the effectiveness and robustness of VCSum. We also provide a set of benchmark models regarding different downstream summarization tasks on VCSum to facilitate further research. The dataset and code will be released at https://github.com/hahahawu/VCSum.
Self-Supervised Sentence Compression for Meeting Summarization
May 13, 2023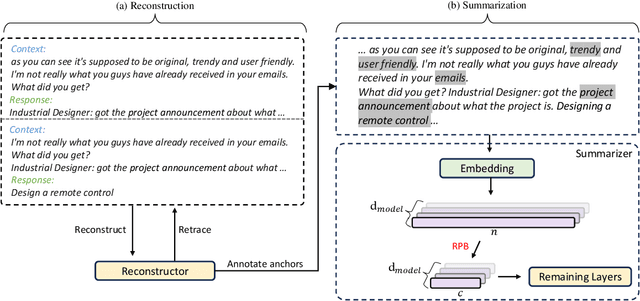
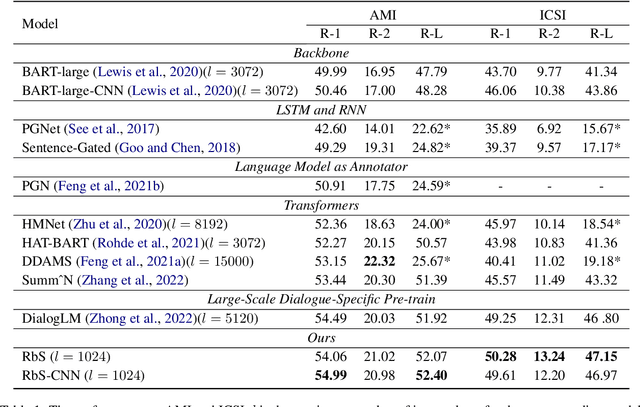
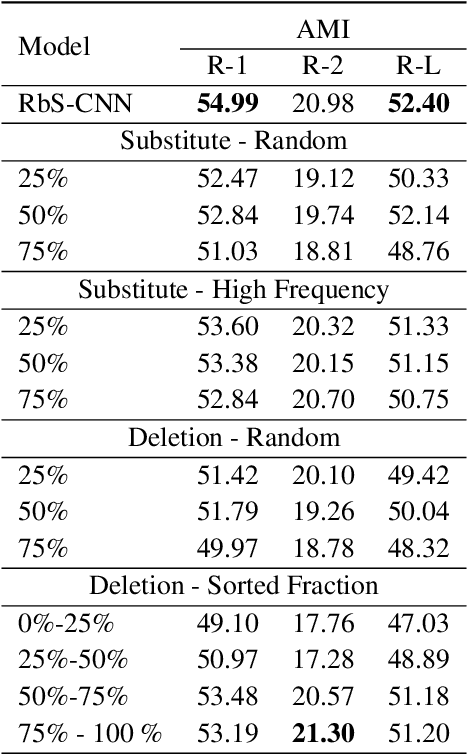
Abstract:The conventional summarization model often fails to capture critical information in meeting transcripts, as meeting corpus usually involves multiple parties with lengthy conversations and is stuffed with redundant and trivial content. To tackle this problem, we present SVB, an effective and efficient framework for meeting summarization that `compress' the redundancy while preserving important content via three processes: sliding-window dialogue restoration and \textbf{S}coring, channel-wise importance score \textbf{V}oting, and relative positional \textbf{B}ucketing. Specifically, under the self-supervised paradigm, the sliding-window scoring aims to rate the importance of each token from multiple views. Then these ratings are aggregated by channel-wise voting. Tokens with high ratings will be regarded as salient information and labeled as \textit{anchors}. Finally, to tailor the lengthy input to an acceptable length for the language model, the relative positional bucketing algorithm is performed to retain the anchors while compressing other irrelevant contents in different granularities. Without large-scale pre-training or expert-grade annotating tools, our proposed method outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches. A vast amount of evaluations and analyses are conducted to prove the effectiveness of our method.
GroupLink: An End-to-end Multitask Method for Word Grouping and Relation Extraction in Form Understanding
May 10, 2021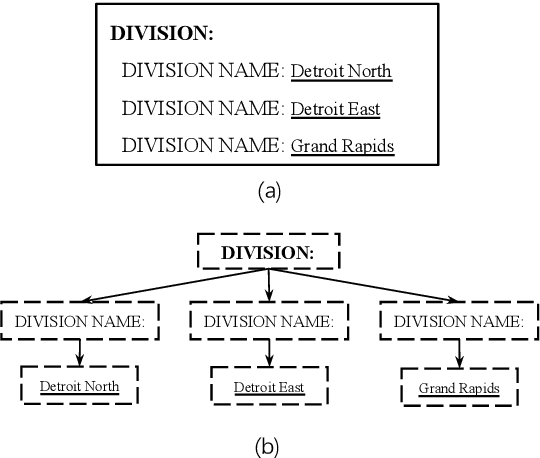
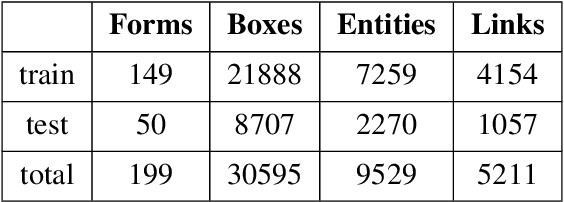
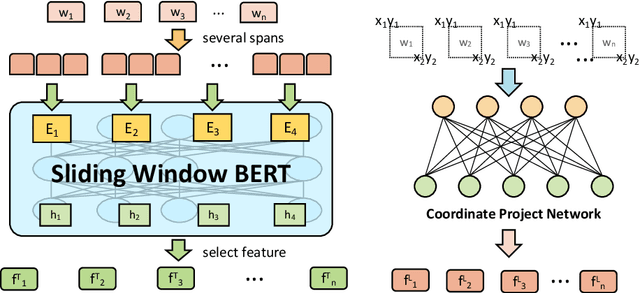
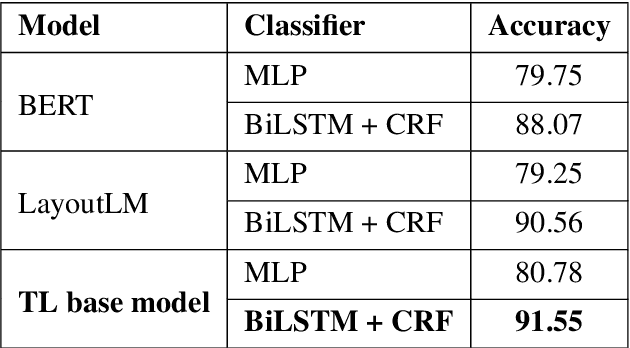
Abstract:Forms are a common type of document in real life and carry rich information through textual contents and the organizational structure. To realize automatic processing of forms, word grouping and relation extraction are two fundamental and crucial steps after preliminary processing of optical character reader (OCR). Word grouping is to aggregate words that belong to the same semantic entity, and relation extraction is to predict the links between semantic entities. Existing works treat them as two individual tasks, but these two tasks are correlated and can reinforce each other. The grouping process will refine the integrated representation of the corresponding entity, and the linking process will give feedback to the grouping performance. For this purpose, we acquire multimodal features from both textual data and layout information and build an end-to-end model through multitask training to combine word grouping and relation extraction to enhance performance on each task. We validate our proposed method on a real-world, fully-annotated, noisy-scanned benchmark, FUNSD, and extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge